* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Cardiorespiratory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
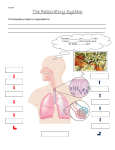
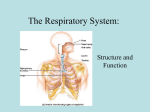
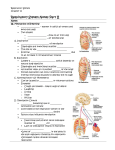
Chapter 3 Cardiorespiratory System *The cardiorespiratory system-System of the body composed of cardiovascular and respiratory system. –Allows kinetic chain to receive O2, nutrients, and removes wastes. *Cardiovascular system-Composed of blood, blood vessels, and heart. *The Heart *Heart-Hollow muscular organ pump that circulates blood throughout the body by needs of rhythmic contractions. *Mediastinum-Space between the lungs that hold all internal organs of the chest except the lungs. -Heart-300g/10oz -Heart made up of cardiac muscle similar to skeletal muscle. Involuntary. -Cardiac muscle fibers are shorter and more tightly connected enabling contraction of one fiber to stimulate others to contract synchronously. -Cardiac muscles built in contraction rhythm- 70-80BPM *AV node-Located in right atrium initiates heart beat (Pace maker) *SV node-Located above the ventricles delays impulses before moving them onto the ventricles. Passes impulse to right and left bundle branches and purkinje fibers. *Structure of heart -4 hollow chambers -Valves prevent backflow -2 pumps -Semilunar valves/AV valves *Atria-Superior collects blood. -Ventricles-Inferior main pumps of heart. *Function of heart *Stroke volume-Amount of blood pumped out with each beat 75-80ml/beat. *Heart rate-Rate at which heart pumps 70-80 BPM *Cardiac output=Stroke volumexHR=blood pumped out per minute. *Blood *Blood-Carries O2 and nutrients to all body parts and also way to rid body of waste products. -Acts as a medium to deliver and collect products. -Thicker than water. -8% body -1.5 gallons/5 liters *3 Functions of blood -Transportation-Blood transports o2, waste products, hormones, heat. -Regulation-Body temp, pH balance, water content in cells. -Protection-Clotting mechanism, immune cells. *Blood vessels *Blood vessels-Network hollow tubes that circulate blood throughout body. -Arteries-carry blood away from heart -Veins- carry blood to the heart *Arteries -Elastic -Arteries>Aterioles>Capillaries *Veins -Waste products -Capillaries>Venules>Veins>Heart *Respiratory system-Respiratory system- A system of organs that collects O2 from external environment and transports it to the blood stream. *Respiratory pump -Thorax *Breathing -2 phases *Inspiration-Actively contracting inspratory muscles to move air into lungs. *Expiration-Actively or passively relaxing inspiratory muscles to move air out of lungs. *Primary respiratory muscles-Diaphragm, external intercostals. *Secondary respiratory muscles-Scalenes, pectoralis minor *Structures of respiratory system -Bones=sternum, ribs, vertebrae -Muscle inspiration-Diaphragm, external intercostals, scalene, sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis minor. -Muscles expiration-Abdominals, internal intercostals *Respiratory passageways -Conduction=Nasal, oral, pharynx, larynx, trachea, right and left bronchi, bronchioles -Respiratory=Alveoli, Alveolar sacs *Cardio respiratory function -Primary element needed for proper body function is=oxygen *O2 consumption -Usage of O2 by body is known as O2 uptake. *VO2=Oxygen consumption at rest 3.5ml/kg 1 MET *VO2 MAX=gauge for cardio respiratory fitness (11-23METS) *Oxygen and energy -Greater than 30 seconds O2 is needed -Aerobic=requires O2 -Anaeorbic=No o2 required *Bioenergetics-Biology of energy transformation and exchanges within body and between it and environment. *Adenosine-Triphosphate-Cellular structure that supplies energy for many biochemical processes by undergoing enzymatic hydrolysis. *3 main bioenergetics pathways -ATP-CP=up to 10 seconds/anaerobic -Glycolysis=30-50 seconds/anaerobic -Oxidative=Greater than 2 minutes/aerobic *Dysfunctional breathing Breathing dysfunction common predecessor to kinetic chain dysfunction -Breathing associated with higher levels of stress -Leads to secondary respiratory muscles predominately used than Diaphragm. -Overuse of secondary muscles scalene, sternocleidomastiod, pectoralis minor, upper traps, levator scapulae. -Leads to tension headaches, light headiness, dizziness -Short shallow breaths altered O2 and CO2 blood content -Increase anxiety -Increases retention of metabolic wastes within muscles=Stiffness. -Inadequate joint motion of spine and rib cage results of improper breathing, causing joints to become restricted and stiff. =Decreased functional capacity. .