* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HUMAN REPRODUCTION BIOLOGY 269
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
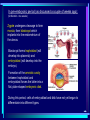
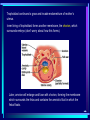
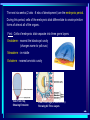
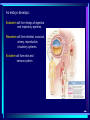
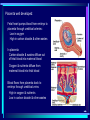
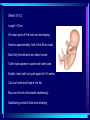
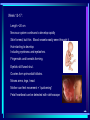
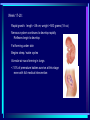
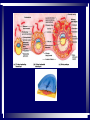
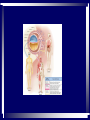
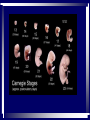
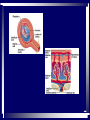
In pre-embryonic period (as discussed a couple of weeks ago): (fertilization - two weeks) Zygote undergoes cleavage to form morula, then blastocyst which implants into the endometrium of the uterus. Blastocyst forms trophoblast (will develop into placenta) and embryoblast (will develop into the embryo). Formation of the amniotic cavity between trophoblast and embryoblast forces the latter into a flat, plate-shaped embryonic disk. During this period, cells of embryoblast and disk have not yet begun to differentiate into different types. Trophoblast continues to grow and invade endometrium of mother’s uterus. Inner lining of trophoblast forms another membrane, the chorion, which surrounds embryo (don’t worry about how this forms). Later, amnion will enlarge and fuse with chorion, forming the membrane which surrounds the fetus and contains the amniotic fluid in which the fetus floats. The next six weeks (2 wks - 8 wks of development) are the embryonic period. During this period, cells of the embryonic disk differentiate to create primitive forms of almost all of the organs. First: Cells of embryonic disk separate into three germ layers: Endoderm - nearest the blastocyst cavity (changes name to yolk sac) Mesoderm - in middle Ectoderm - nearest amniotic cavity View From Top, Showing Ectoderm View From Edge (Cross-section) Showing All Three Layers As embryo develops: Endoderm will form linings of digestive and respiratory systems. Mesoderm will form skeletal, muscular, urinary, reproductive, circulatory systems. Ectoderm will form skin and nervous system The first system to begin developing is the nervous system. This appears as a groove along the ectoderm, which closes over to form a neural tube. The neural tube enlarges at one end to form brain; remains cylindrical at the other end to form spinal cord ~ Day 22 – 23, sides of flat embryonic disk begin to fold toward yolk sac. By day 28: Embryo has “normal” body shape, amniotic cavity pulled around to surround it. Placenta continues to develop from trophoblast; many blood vessels develop within it and form villi which project into pools of the mother’s blood in her endometrium. Embryo floating in amniotic fluid, stays attached to placenta by umbilical cord. Umbilical vessels carry blood between placenta and embryo. ~ Day 28: Arm buds and leg buds begin developing. Bones, muscles, and blood vessels develop from mesoderm as limbs get bigger, nerves grow out from spinal cord. Vertebrae forming Other organs continue developing internally. Length ~ 4mm (width of pencil) Late embryonic period (4 – 8 weeks): Nervous system continues to develop; brain rapidly enlarges and folds Electrical activity begins Eyes and ears begin to develop Limbs continue developing, fingers and toes separate Digestive system forms esophagus, stomach, intestine, liver, pancreas Lungs bud off from digestive system and grow Heart folds, divides into two chambers and then four, begins contractions Kidneys, bladder, gonads develop Face develops as two halves on side of head; move to front and fuse End of embryonic period (8 weeks): Beginning of fetal period Body has human shape Almost all organs have begun developing Head growth still most pronounced Cartilage tissue in bones being replaced by bone tissue Limbs complete Some movement of limbs and head Length ~ 3 centimeters Mass ~ 1 – 2 grams Mass of quarter: 5.7 grams Placenta well developed: Fetal heart pumps blood from embryo to placenta through umbilical arteries: Low in oxygen High in carbon dioxide & other wastes In placenta: Carbon dioxide & wastes diffuse out of fetal blood into maternal blood Oxygen & nutrients diffuse from maternal blood into fetal blood Blood flows from placenta back to embryo through umbilical veins: High in oxygen & nutrients Low in carbon dioxide & other wastes Ninth week: (Organs and systems continue development) Fetus = 5 cm long, 4 - 5 grams Facial features well formed External genitalia develop, but male and female still very similar: penis / clitoris scrotum / labia Tenth week: (Organs and systems continue development) Fetus = 7 cm long, 8 - 10 grams External genitalia easily determined to be male or female, but not yet large enough to visualize by ultrasound After tenth week: Fetus increases rapidly in size Organs and systems continue to develop, begin functioning Week 10-12: Length ~15cm All major parts of the brain are developing Head is approximately half of the fetus' mass Ears fully formed and can detect sound Tooth buds appear in upper and lower jaws Eyelids close (will not open again for 16 weeks Can curl hand and fingers into fist May suck thumb (stimulates swallowing) Swallowing amniotic fluid and urinating Week 13-17: Length ~20 cm Nervous system continues to develop rapidly Skin formed, but thin. Blood vessels easily seen through it Hair starting to develop Including eyebrows and eyelashes. Fingernails and toenails forming. Eyelids still fused shut. Ovaries form primordial follicles. Moves arms, legs, head Mother can feel movement = “quickening” Fetal heartbeat can be detected with stethoscope Week 17-20: Rapid growth: length ~28 cm; weight ~500 grams (18 oz) Nervous system continues to develop rapidly Reflexes begin to develop Fat forming under skin Begins sleep / wake cycles Alveolar air sacs forming in lungs < 10% of premature babies survive at this stage even with full medical intervention Week 21-26 (six months): Length ~38 cm; Weight ~ 1200 grams (2 lb 11 oz) Nervous system continues to develop rapidly Starting to control body functions Hair present over entire body. Will become longer on scalp Eyelids ready to open Lungs producing some surfactant Testes begin descent through inguinal canal Swallowing amniotic fluid Movement of hands, feet, face More than half of premature babies survive at this stage with medical intervention, often with no permanent problems Week 26-28: Length ~42 cm; Weight ~1500 grams (3 lbs) Rhythmic breathing motions Eyelids open and close Most bones fully formed, but pliable and capable of rapid growth Body fat rapidly increasing 90% of premature babies survive at this stage with medical intervention, usually with no permanent problems Week 29-32: Length 40-48 cm; Weight 2.5 – 3 kg (5.5 – 6.5 lbs) Body fat significantly increasing Longer hair on head Eyes open, respond to light Fingernails and toenails have reached ends of fingers and toes >90% of premature babies survive at this stage with medical intervention, usually with no permanent problems Week 33-37 (9 months): Can gain as much as half a pound per week Lungs continue to develop; Strong respiratory motions Skin pink, smooth Testes have reached scrotum Fingers can intentionally grasp objects, fine movement of face and eyes Immune system now competent – can build antibodies Nine months: Ready for birth During development, a couple of openings had to form in the heart and large blood vessels to allow blood to bypass being sent to the lungs. We will talk about what happens to those in a couple of weeks. X X Following slides for review X X