* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prevention and treatment of diabetes through dietary
Survey
Document related concepts
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Thrifty gene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
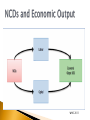
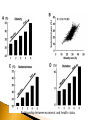
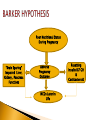
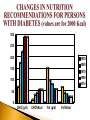
Ex-Dean and Visiting Professor Department of Human Nutrition Agricultural University Peshawar WHO 2011 Relationship between economic and health status RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN NUTRITION & HEALTH NUTRITION HEALTH SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT & PERFORMANCE FOOD SUPPORTIVE ENVIRONMENT NUTRITION CENTRAL TO HEALTH & ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT HEALTH NUTRITION •IMMUNE FUNCTIONS •MENTAL DEVELOPMENT •BEHAVIORAL •SCHOLASTIC •PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE •SOCIAL & ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT IMBALANCE BETWEEN NUTRIENTS INTAKE AND REQUIREMENTS UNDERNUTRITION & OVERNUTRITION MALNUTRITION TRENDS IN PAKISTAN Source: NNS (2011) Hattersley (1999) Lancet 353:1789 Poor Nutritional Status During Pregnancy “Brain Sparing” Impaired Liver, Kidney , Pancreas Functions Adverse Pregnancy Outcome NCDs Later in Life Hormonal Resetting Insulin IGF GH & Corticosteroid ids Dietary Management is essential for: Maintaining healthy weight and to prevent overweight and obesity Maintaining blood glucose levels in the normal range Maintaining lipid and lipoprotein profile in the normal range Preventing or reducing the risk of diabetes Managing existing diabetes Preventing and reducing risk of micro and macro vascular complications such as retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, amputation of lower limbs and premature deaths Meta-analysis of 70 randomized controlled trials shows correlation between fall in LDL-C and amount of weight loss Weight loss reduces triglycerides, increases HDL-C, and lowers LDL-C Weight loss reduces insulin resistance and improves glycemic control and reduces the risk of cardiovascular abnormalities 7% weight loss in pre-diabetic patients resulted in a 58% reduction in the risk of diabetes Combined programs of weight loss and exercise are associated with greater increases in HDL-C and more significant loss of weight and fat. Macronutrients Micronutrients All Macro and Micronutrients are required but need modifications during illness Carbohydrates---Plants & Dairy --Simple & Complex -- Low and High Glycemic Index--- Source of Energy --cals---Essential role in Weight and Diabetes Management Protein—Plants and Animals— Body Building, Enzymes, Hormones, Immune System Fat---Plants and Animals-Rich Source of Energy— saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids, omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids, cis and trans fatty acids Vitamins ----Plants and Animals–- physiological and metabolic functions Minerals-----Plants and Animals—physiological and metabolic functions The total amount of carbohydrates consumed is the primary predictor of glycemic response and has a direct effect on postprandial glucose levels The primary macronutrient of concern in glycemic management Quantity and type of carbohydrates in a food influence blood glucose level Carbohydrates a potential source of energy Monitoring carbohydrate portions is a useful tool for improving postprandial glucose control History dates back to 18th and 19th centuries-Era of dietary restriction and fasting by clinicians J. Rollo (1797) emphasized increased consumption of fat and protein for diabetic treatment Bouchardat (1871): Noticed disappearance of glycosuria during food rationing and suggested individualized diets to treat diabetes Joslin (1916): 20% reduction in case fatality rate by fasting and physical activity Allen (1919): suggested strict dietary restriction or “starvation treatment” for hyperglycemia 300 250 200 1930 1955 1970 1990 2014 150 100 50 0 CHO (g/d) CHO%Kcal Fat (g/d) Fat%Kcal Mediterranean, vegetarian, low CHO, high protein and high fat diets have been tried on diabetic individuals over a period of time Conflicting results on postprandial glucose levels, lipid profile and weight loss Insufficient evidence to recommend any specific diet or amount of CHO, protein and fat for all diabetic people Weight loss has been associated with reduction in insulin resistance, improved glycemic control and lipid profile Dietary management in combination with physical activity has proven to be most effective in improving glycemic control and reducing the risk of cardiovascular abnormalities Irregular Meals Small Frequency Energy Dense Small CHO Refined/Processed Animal Protein Animal Fat Saturated Fat Regular Meals Large Frequency Nutrient Dense Complex CHO Whole Grain Meat Protein Meat Fat Unsaturated Fat Eat in moderation or minimum 2-3 Servings 2-3 Servings 3-5 Servings 2-4 Servings 5-9 Servings FOOD PYRAMID FOR PAKISTANI POPULATION Appropriate meal planning is critical for the prevention and treatment of diabetes Nutrition education, counseling and meal planning is a prerequisite for effective management of diabetes There is NO standard meal plan or eating pattern that works universally for all people with diabetes There are NO standard recommended dietary allowances as well as the recommended amount or percentage of each macro and micro nutrient for diabetics Individualized dietary approaches are needed in the light of nutritional status, cultural, economic, religious, dietary preferences and metabolic goals Consultation of Dietitian is must for developing an individualized meal plan that focuses on weight, glycemic and metabolic controls Comprehensive diabetes management and awareness programmes that includes nutrition education, counseling, seminars, workshops at the community levels shall be started Diploma Courses in Nutrition/Dietetics focusing on NCDs shall be started to produce technically skilled human resource who may work at community level for screening, prevention and treatment of NCDS Periodic monitoring of metabolic parameters (e.g., glucose, lipids, blood pressure, body weight, renal function) is recommended to ensure successful health outcomes