* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 power point
Jamestown, Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
Colony of Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
History of Jamestown, Virginia (1607–99) wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Colonial South and the Chesapeake wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
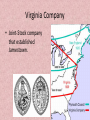
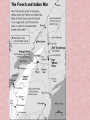
U.S. History GHSGT Preparation SSUSH 1 Virginia Company • Joint-Stock company that established Jamestown. Jamestown, VA • 1st Permanent English settlement Tobacco • An agricultural crop that yielded great cash for Virginia. • Called a Cash Crop. • Helped Jamestown and Virginia survive. Powhatan • Native American tribe near Jamestown. • Initially good relations. • Relations became hostile and they warred with Jamestown settlers. Bacon’s Rebellion • Uprising of Virginia frontiersmen. • Led by Nathaniel Bacon. • Against the VA government due to Indian attacks on the frontier. • 1st example of class struggle in America. House of Burgesses • Established in Virginia in 1619 • Elected representatives helped govern the colony. • Example of a representative democracy in the Colonies. Town Hall Meetings • Example of Direct Democracy • A promising step toward genuine selfgovernment. Religious Tensions – Rhode Island • Roger Williams was banished from Massachusetts. • Founded Rhode Island based on freedom of religious and political beliefs. • Separation of Church and State. Religious Tensions – Half Way Covenant • A compromise made by the Puritans that allowed the younger generation of children to become members of the Church. • To expand church membership. Religious Tensions – Salem Witchcraft Trials • Unsettled social & religious conditions in a rapidly evolving Massachusetts. • Example of how religion and government was mixed with disastrous results. French Settlement of Quebec • Settled to establish a fur trade with the Native Americans. Navigation Acts • A series of laws enacted by parliament, beginning in 1651, to tighten England’s control of trade in its American Colonies. The Mayflower Compact • Established a colonial government deriving power from consent of the governed. • Example of a direct democracy in the colonies. • Present day town meetings are and example of direct democracy. SSUSH 2 Mercantilism • Trade with the colonies was regulated by Great Britain. • The British sold expensive manufactured goods to colonists • While the colonist sold cheaper raw materials, such as tobacco and cotton, to the British. Triangular Trade • The transatlantic system of trade • in which goods and people, including slaves, were exchanged • between Africa, England, Europe, The west Indies, and the colonies in North America. Middle Passage • The voyage that brought enslaved Africans to the West Indies and later to North America. Benjamin Franklin • An example of Social Mobility in that he was born in poverty and through his efforts become a successful businessman. • As ambassador to France was instrumental in acquiring French foreign assistance during the Revolutionary war. Great Awakening • A period of dramatic religious revival in Colonial history 1730’s • Influenced politics by driving colonist to question authority of government. • A spiritual belief in democratic concepts such as freedom, equality, etc. SSUSH 3 French and Indian War • 1754-1763 • War between Britain and France • British eventually defeated the French and gained control of Canada • The large debt caused by the war made the British collect taxes from the colonist. • The collection of taxes angered the Colonist. Proclamation Line of 1763 • Line created by Parliament and King George III that outlawed colonist from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains. Stamp Act • 1765 Law in which Parliament established the first direct taxation of goods and services within the colonies. • Required a tax on newspapers and Legal documents. • Colonist Protested by Boycott Townshend Act • A series of laws enacted by parliament in 1767, establishing indirect taxes on goods imported from Britain by the British Colonies in North America. • Levied tax on everyday items including tea, glass, and paint. Tea Act • Gave the British East India Company a monopoly on tea. • Sparked the Boston Tea Party, which was conducted by the Sons of Liberty Sons of Liberty • Protest group formed after the passing of the Stamp Act. Led by Samuel Adams. Intolerable “Coercive” Acts • A series of laws enacted by Parliament in 1774, to punish Massachusetts colonist for the Boston Tea party. • These laws took away colonists right to trial by jury • soldiers could search and seize any property at any time • Colonist were required to house soldiers at any time. Thomas Paine • Wrote the pamplet, Common Sense • Promoted American Independence!