* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download userfiles/1208/ecosystems and food chains
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
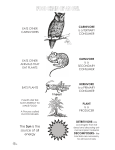
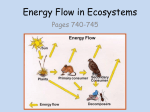
Bringing Together Living and Non-living Things. How Do Living and Nonliving Things Interact? Ecosystem- the living AND nonliving things in an environment and all their interactions. The ecosystem includes rocks, water, plants, and animals. Community- the living part of an ecosystem. The community includes the plants and animals. Population- one type of organism living in an area. The squirrel monkey Habitat- the home of an organism. Trees are the squirrel monkey’s home. Roles Organisms Play Producer- an organism, such as a plant, that makes food. All food chains must begin with a producer. Algae is a protist that produces chlorophyll. It is a producer in many water ecosystem food chains. Plants like grass are producers. Roles Organisms Play Consumer- any organism that eats the food producers make or eats other consumers. There are consumers at different levels of every food chain. This grasshopper consumes leaves and grass. This polar bear consumes penguins and seals to gain energy. Types of Consumers Herbivore- a consumer that eats only plants. Herbivores are always the 1st level consumers in a food chain. Carnivore- a consumer that eats only animals Omnivore- a consumer that eats both plants and animals. This deer only eats plants like grass. It is an herbivore. The lion below is obviously a carnivore. The black bear above eats fruits like berries, but also eats other animals. Both the black bear and the baby below are omnivores. Roles Organisms Play Decomposers- an organism that breaks down the wastes and remains of other organisms. Examples: bacteria, fungi like mushrooms, some types of insects worms mushrooms bacteria decomposing waste Food chain- the set of steps in which organisms get the food they need to survive. Energy comes from the sun. It is transferred to the producer. The 1st consumer eats the producer to gain energy. Energy is passed to the 2nd and 3rd level consumers when they eat the other animals. The top-level consumer dies or gives off waste and energy is transferred to the decomposers. Decomposers take this energy and return the nutrients to the soil. This helps the producers grow and starts food chain again. This is a common forest food chain. Tundra Food Chain The sun provides for the seaweed (producer) to grow. The minnow (herbivore, 1st level consumer) eats the seaweed. The penguin (carnivore, 2nd level consumer) gets energy by eating the minnow. The polar bear (carnivore and top-level consumer) gets energy by eating the penguin. The polar bear dies or gets rid of waste and bacteria (decomposers) and passes the nutrients and energy on to other producers so the food chain can continue. Food Web- the pattern that shows how food chains are related.