* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD WAR II
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
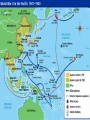
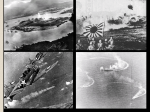
WORLD WAR II Aim: Explain the dictators that came to power in Europe in the 1930s. Do Now: Why do you think a dictator might be able to gain power during a depression? What were the results of the Treaty of Versailles? RISE OF DICTATORS ● Dictator – absolute ruler ● Economic and political problems ● Great Depression ● Result from Treaty of Versailles RISE OF DICTATORS ● Germany – Adolf Hitler ● Soviet Union – Josef Stalin ● Italy – Benito Mussolini ● Japan – Hideki Tojo ● Spain – Francisco Franco FASCISM ● Preached an extreme form of patriotism and nationalism that is often linked to racism ● Persecute those who disagree ● Mussolini of Italy – Il Duce (Boss/Leader) ● Hitler of Germany – Fuhrer ● NAZI – National Socialist Worker’s Party WORLD WAR II Aim: How did Germany/Hitler cause World War II? Do Now: How was Hitler able to take control over Germany? Take out Dictators worksheet ADOLF HITLER ● Failed artist – couldn’t get into art school ● German soldier in WWI ● Devastated with German loss ● Blamed politicians (Jews) and Marxists (Communists) ● Leads NAZI Party ● Swastika as symbol ● Superiority of “Aryan” (white) race ADOLF HITLER ● 1923 – Beer Hall Putsch ● Hitler leads a “coup” – revolt – against government ● Fails and he is imprisoned ● Writes book – “Mein Kampf” – My Struggle ● Becomes famous ● Spoke to mass audiences about making Germany a great nation again - propaganda ● Hitler becomes Chancellor (head of gov’t) in 1933 ADOLF HITLER ● “Reichstag fire” gives Hitler total power ● all parties were outlawed except the Nazi party ● Announces himself dictator AN EVIL CONVERSATION ● Write a script for a possible conversation between one of these groups ● Hitler and Mussolini (left) Hitler and Stalin (right) WORLD WAR II Aim: How did Hitler plan to go about conquering Europe? Do Now: Take out homework. What happened at the Munich Agreement? GERMANY ● Betrays Treaty of Versailles ● Hitler builds up army ● Moves troops into Rhineland ● Rome-Berlin Axis – pact between Italy and Germany ● Takes over ● Austria France MUNICH AGREEMENT ● Germany wants Sudetenland ● Europe on brink of war ● Britain Prime Minister – Neville Chamberlain ● Agreement between Hitler and Chamberlain ● Germany gains Sudetenland ● Hitler promises to stop seeking more territory ● Appeasement – give in to enemy to avoid conflict WORLD WAR II Aim: How was the U.S. gradually brought into World War II? Do Now: How did Hitler plan to conquer Europe? WAR ● Soviet Union and Germany sign Non-aggression Pact ● Agree to not attack one another ● Hitler invades Poland – Sept. 1, 1939 ● GB and France declare war ● Allied Powers vs. Axis Powers ● Axis – Germany, Italy, Japan ● Allies – France, Great Britain, China, Mexico, Canada, Belgium, India, Poland WAR ● Blitzkrieg – lightning war of attacking quickly ● Germany conquers Poland, Belgium, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Denmark, Norway ● Lebensraum – “living space” for German/Aryan race ● Natural right as superior race ● France – conquered in June 1940 WAR ● British – no surrender ● Battle of Britain ● Luftwaffe (German Air Force) vs. Royal Air Force (GB) ● Hitler bombs London and GB ● RAF holds off Luftwaffe ● http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HJhIptKXs1M WAR – OPERATION BARBAROSSA ● Hitler invades Soviet Union in 1941 ● Breaks pact between Stalin and Hitler ● Attack Leningrad, Stalingrad, and Moscow ● Do not conquer these cities ● Hitler’s miscalculations ● Doesn’t concentrate troops on Moscow ● Attacks through winter ● ● Millions starve and freeze Scorched earth policy ● Turning point – Germans advance halted in the East WORLD WAR II Aim: How was the U.S. gradually brought into World War II and how was life on the home front? Do Now: What was the Lend Lease Act? Take out homework USA ● Isolation and neutrality ● FDR vows to stay neutral ● Knows that could be pulled into war ● Prepares US ● Builds up navy ● Neutrality Act of 1939 – “cash and carry act” – warring nations can buy US goods if they buy with cash and car the goods in their own ships ● Selective Service and Training Act – peacetime draft of men ● 21 to 35 years old U.S.A. ● FDR ● Breaks Washington’s precedent of two terms - wins third term in 1940 ● Prepare Americans mindset for possible war ● “arsenal for democracy” – help fight fascism ● Garden hose for neighbor if house on fire ● Lend Lease Act – lend/lease supplies to Allied nations ● US economy getting back on track ● Making more products ● More people working JAPAN ● Seizing land in Asia ● Northern China ● Moving into Philippines (US territory) ● Need oil and rubber ● US response ● Applied economic pressure – froze Japanese funds and stopped trading ● Japanese angered PEARL HARBOR ● Pearl Harbor Hawaii – Dec. 7, 1941 – “a date that will live in infamy” ● Japanese planes attack ● Kill 2400 Americans ● US declares war ● Turning point – US help will turn the tide of the war PEARL HARBOR WORK ● Open up Pearl Harbor website on eChalk ● Answer questions ● What was important about when the Japanese attacked? ● How did the US react to the attack? ● Click on Lt. Phillip Rasmussen and His P-36A ● Why did Rasmussen use an outdated airplane? ● What did his actions show about this man? ● How could have the Americans been better prepared for the attack? HOME FRONT ● Pearl Harbor unites the nation ● Mobilization – military and civilian preparation for war ● Automakers now make trucks, jeeps, and tanks ● Goods being produced for war effort WOMEN ● First time large number of women in army ● WACs – Women’s Army Corps ● Worked as nurses and secretaries ● Important roles for war effort ● Work in jobs previously held by men ● No longer just work in home ● “Rosie the Riveter” MAKING SACRIFICES ● Men drafted into war ● Fear of receiving news of killed family member ● Rations – consumers buy limited amount of a good ● Gasoline, meat, tires AFRICAN AMERICANS ● Army is segregated ● 1 million African Americans in army ● Tuskegee Airmen – Fighter Group in Air Force ● Shot down 200 enemy planes ● Move to the northern cities ● Still experiencing discrimination/racism WORLD WAR II Aim: How did Japanese-Americans face discrimination during World War II? Do Now: How did women take on an important role during the war? JAPANESE AMERICANS ● Feared and hated by many Americans after Pearl Harbor ● Nisei – American citizens born in US ● Internment camps – 100,000 Japanese Americans relocated into detention centers ● Conditions were harsh JAPANESE INTERNMENT CAMPS ● Let’s go back in time to January 1942. How do we feel about Japanese people living in America after the attack on Pearl Harbor? EQUALITY ALL AMERICANS VS HATRED FOR THE PEOPLES WHO ATTACKED THE USA FOR JAPANESE INTERNMENT CAMPS ● Let’s go back in time to January 1942. How do we, as many Americans did, feel about Japanese people living in America? EQUALITY HATRED -ALL AMERICANS DESERVE FREEDOMS - THESE PEOPLE ATTACKED GUARANTEED BY CONSTITUTION AND KILLED THOUSANDS -MOST OF THE JAPANESE HAVE BEEN -ALL JAPANESE HATE USA LIVING HERE FOR GENERATIONS -THEY ARE ON THE SIDE OF -THEY DID NOT ATTACK US, THE JAPAN, NOT THE USA JAPANESE COUNTRY DID DEBATE GIRLS VS BOYS POSITIVES VS NEGATIVES OF A WOMAN PRESIDENT YES – WOMAN PRESIDENT NO – WOMAN PRESIDENT ● EQUALITY ● SEEN AS A MAN’S JOB ● NO DIFFERENCE ● OTHER COUNTRIES WILL ● DOESN’T MATTER WHETHER MALE OR FEMALE ● DESERVE A POSITION OF POWER ● WOULD BE BETTER LEADER VIEW US AS WEAK ● EMOTIONS? WORLD WAR II Aim: How did the Allies plan to defeat the Axis Powers? Do Now: Define: Allies and Axis Powers. WORLD WAR II Aim: How did the Allies defeat Germany in World War II? Do Now: World War II Map worksheet WAR IN AFRICA ● Allies plan – defeat Hitler then Japan ● Start attack in North Africa ● Give American troops experience ● German General Erwin Rommel – “Desert Fox” ● 1942 – British defeat German at Battle of El Alamein ● Prevent Germans from capturing Suez Canal ● Late 1942 – American forces land in N. Africa ● Led by Gen. Dwight Eisenhower ● Drive Germans out by May 1943 MAP WAR IN ITALY ● Attack from N. Africa ● Take over Sicily ● Gen Patton (US) and Gen Montgomery (GB) ● Allies advance ● Mussolini overthrown then surrender (1944) ● Air war on Germany – day and night bombings OPERATION OVERLORD ● Allied invasion of France – June 6, 1944 – D-Day ● Allied commander – Gen. Eisenhower ● Amphibious landing across English Channel ● Invade beaches of Normandy, France ● Soldiers invade by ship and paratroopers ● Invasion successful ● Late August – France taken by Allies http://www.army.mil/d-day/ ● http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QzgKMDydr5Y D-DAY ● 5,000 ships carry 130,000 soldiers ● British, American, Canadian ● More than 10,000 killed WORLD WAR II Aim: How did the Allies defeat Germany in World War II? Do Now: What was the significance of D-Day? YALTA CONFERENCE ● Early 1945 – Germany retreating ● Stalin, FDR, Churchill have meeting in Yalta ● Discuss and plan what Europe will look like after the war ● Stalin promises Soviet help against Japan ● International peacekeeping organization – UNITED NATIONS VICTORY ● US/GB/Fr. Invade from west – Soviets invade from east ● Battle of the Bulge ● Dec. 1944 – hard fought Allied victory ● 1945 – Allies right outside Berlin ● Hitler commits suicide ● V-E Day – May 7, 1945 – Victory in Europe HOLOCAUST ● We must learn so it never happens again ● Do NOT be a spectator ● Speak up and take action against evil JEWS UNDER HITLER ● 1933 – Jewish rights restricted ● Couldn’t vote, marry non-Jews, hold office, own businesses, practice law/medicine ● Yellow stars – star of David – worn by Jews in public ● Krisallnacht – “night of broken glass” ● Jewish temples and shops destroyed ● 1938 JEWS UNDER HITLER ● Concentration camps – prison camps to hold people for political reasons ● Auschwitz and Dachau ● Families hidden for protection (Anne Frank) ● Belongings taken ● Referred to as numbers (dehumanizing) – tattoos ● Fed a little bread and watery soup THE FINAL SOLUTION ● Death camps – purpose to kill of all Jews ● Healthy – work as slaves ● Sick, old, disabled, mothers, children – murdered ● Poison gas chambers and furnaces HOLOCAUST ● The killing of 6 million Jews by the Nazis ● Scapegoats – blame someone else for bad times ● Nazis – belief in Aryan race. Wipe out “inferior” races ● Genocide – wiping out an entire group of people ● How could something like this happen? ● Must learn about it to ensure it never happens again ● Must stand up to evil ● Don’t be a spectator NUREMBURG TRIALS ● Nazi leaders put on trial for war crimes ● Crimes against humanity ● 12 are executed ● People are responsible for their actions, even in war time WORLD WAR II Aim: How was the war fought and won in the Pacific? Do Now: How is the war in the Pacific going to be different from the war in Europe? Take out D-Day homework WAR IN THE PACIFIC WAR IN PACIFIC ● Japan expanding in Southeast Asia ● Attack American Philippines (1942) ● US and Filipino troops unite ● Led by General Douglas MacArthur ● Forced to retreat to Bataan Peninsula ● Macarthur: “I shall return” ● Allies surrender in Philippines ● Bataan Death March ● 20,000 Allies die on 60 mile march WAR IN PACIFIC ● Bombing of Tokyo – James Doolittle ● Lifts Allies spirits ● Island hopping – attacking and capturing key islands ● Battles take place in the air ● Aircraft carriers carry fighter planes ● US victory ● Battle of Midway ● Battle of Guadalcanal WAR IN PACIFIC ● Battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa ● Japanese soldiers – rarely surrender ● Fight to the death ● Kamikazes – suicide pilots ● By 1945 most of Jap. Navy and air force destroyed ● Still must conquer Japan ● No surrender ATOMIC BOMB ● Einstein (flees Germany) – warns FDR of Nazis trying to split atoms to create bomb ● Manhattan Project – top-secret program to develop atomic bomb ● Scientists – Oppenheimer and Fermi ● 1942 – first nuclear reactor – splitting of atoms ● 1945 – first atomic bomb testing in New Mexico successful ATOMIC BOMB ● Invasion of Japan would cost between 400,000 and 1 million soldiers ● President Truman decides to drop the bomb ● Atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima – Aug. 6, 1945 ● No surrender after 3 days ● Second bomb dropped on Nagasaki – Aug. 9, 1945 ● Japan surrenders ● Over 100,000 people killed instantly ● Over 50,000 die later from effects of the bomb ● Radiation sickness/cancer THE ATOMIC BOMB Aim: Was it wrong for the US to drop the Atomic Bomb on Japan? Do Now: Think about the Aim. Think about how you could understand both sides of the argument. Make a decision on your stance. ATOMIC BOMB - DECISION ● Situation – You are the president of the United States. You are about to invade Japan’s main islands. From experience at Okinawa and Iwo Jima, you believe the Japanese will fight to the death and will be willing to fight for years. An estimate of at least 400,000 Americans will die in an invasion. Now America has in its hands a weapon equal to 20,000 tons of TNT. It worked in a test, but it may not work when dropped out of a plane. Possibly you can have a demonstration of the bomb’s power but if it doesn’t work, the Japanese resistance will harden. You also wouldn’t mind portraying this weapon to Stalin and the Soviets to make sure they stay in line. However, the bomb could kill hundreds of thousands of innocent, Japanese civilians. In the back of your mind, you remember what happened at Pearl Harbor. ● What do you do? ● Use the bomb or attack another way? YES - Drop the Bomb ● Save American soldier lives ● At least 400,000 NO - Don’t Drop the Bomb ● Killing civilians is not acceptable ● Innocent Women and children/infants ● #1 job as president is to protect ● How would you feel as a Japanese ● Death is a part of war ● This kind of death is morally wrong – American lives ● Take extreme measures ● Conquer quickly ● Invasion could take years ● Bomb takes few days for surrender ● Revenge? ● Remember Pearl Harbor and Bataan Death March ● Warning to Soviet Union (Russia) ● Make sure they stay in line person – 100% wrong if done to USA vaporize ● US lives are no more important than Jap. ● Death in war should be as limited as possible to soldiers ● Work out another way to win the war ● Revenge is wrong – two wrongs don’t make a right ● Hypocritical LEGACY OF WWII ● Women gain independence in USA ● Political/Economic/Physical destruction of Europe ● Cities in ruins ● Only country to benefit – U.S.A. ● Marshall Plan – US gives $13 billion to help nations of Europe get back on their feet ● Extreme loss of life ● Over 60 million deaths (civilian and military) ● United Nations – US joins along with 50 nations LEGACY OF WWII ● World enters the atomic age ● Soviet Union (Russia) conquers Eastern Europe in 1945 ● Lands under Stalin’s control ● He makes these Communist countries under U.S.S.R. ● Cold War – conflict between Soviet Union and U.S.A. ● Never confronted on battlefield ● Threat of war lasts for decades