* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download parts of speech - smithhalecommarts
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
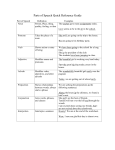
PARTS OF SPEECH NOUNS, VERBS, PRONOUNS, ADVERBS, ADJECTIVES, INTERJECTIONS, PREPOSITIONS AND CONJUNCTIONS NOUN A noun is a . . . 1. Person 2. Place 3. Thing Ask yourself: What is the subject of the sentence? What is the sentence about? Example: The boy waited in line for his lunch. What is the subject of the sentence? (Boy) What are the nouns in the sentence? (Boy, line, lunch) Practice: Determine whether each underlined word is or is not a noun. One of the most well-known fairy tales is “Little Red Riding Hood.” There are (1) yes/no hundreds of versions of this story throughout the world. In the most popular (2) yes/no (3) yes/no version in America, Little Red Riding Hood is saved by a woodsman, who cuts her (5) yes/no (6) yes/no out of a wolf ’s belly. In other versions, Little Red Riding Hood tricks the wolf into (7) yes/no (8) yes/no letting her out. I find these versions more satisfying, because Little Red saves (9) yes/no (4) yes/no herself through her own ingenuity rather than being rescued. (10) yes/no (11) yes/no (10) yes/no N O U N PRONOUN A pronoun is a word that takes the place of, or refers to, a noun. A pronoun is still a noun – a person, place or thing. Pronouns are easy to spot because they are vague. That means they are not specific. Pronouns are not the names of people, places or things. They are general. For example: she is a pronoun. She does tell me anything specific. There are 6 different types of pronouns. PRONOUN PRONOUN Practice: Find and underline the nine words acting as pronouns in the paragraph below. One of the most well-known fairy tales is “Little Red Riding Hood.” There are hundreds of versions of this story throughout the world. In the most popular version in America, Little Red Riding Hood is saved by a woodsman, who cuts her out of a wolf ’s belly. In other versions, Little Red Riding Hood tricks the wolf into letting her out. I find these versions more satisfying, because Little Red saves herself through her own ingenuity rather than being rescued. VERBS Verbs are words that show action or state of being (the way something exists). Verbs change form based on who is doing the action and when the action took place. Base verbs are the main verb or verbs in the sentence. Helping verbs tell use more about when the action took place or will take place. Below are a few examples, with the base verb underlined once and helping verbs bolded. I am exhausted! You should have been more careful. I am having a great time. We did not know you were coming. The evidence does not support your accusations. VERBS Practice: Underline the base verbs in the sentences below, circle the helping verbs. Look before you leap. Don’t count your chicken before they hatch. Those who live in glass houses should not throw stones. The early bird catches the worm. You reap what you sow. Good things come to those who wait. Do unto others as you would have done to you. Sticks and stones will break my bones, but words will never hurt me. A watched pot never boils. Rome was not built in a day. ADJECTIVES Adjectives describe or modify nouns. They tell us which one, how many, or what kind. For example… Talk is cheap. Cheap describes the noun talk. What an outrageous statement! Outrageous describes the noun statement. There are several problems with this paper. Several describes the noun problems. You are so patient with children. Patient describes the pronoun you. ADJECTIVES Practice: In each sentence, circle the word that is an adjective. What does it modify? Meet me at the farmer’s marker. _ Modifies: _________________________ Elena is very smart. _ Modifies: _________________________ Gala apples are in season. _ Modifies: _________________________ She’s also a very likeable person. _ Modifies: _________________________ I’ll buy two dozen of them. _ Modifies: _________________________ Pigs are very docile animals. _ Modifies: _________________________ Who is that woman? _ Modifies: _________________________ ADVERBS Adverbs describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They tell us when, where, how and why, under what conditions and to what degree. Adjectives and adverbs can sometimes be confused. Look at the sentences below for the difference. Adjective: I am very patient. Patient describes the pronoun I. Adverb: I am waiting very patiently. Patiently tells us how I am waiting. Once you have found the main verb in the sentence simply ask if any words tell you how the verb is being done. Is it happening quickly, rapidly, carefully, gracefully. Adverbs can be formed by added –ly to adjectives, but not all adverbs have –ly. ADVERBS Practice: In each sentence, circle the word that is the verb. What is the adverb that describes the verb? Speak softly and carry a big stick. Adverb: ______________________________ May you prosper greatly and grow merry quickly. Adverb: ______________________________ History often repeats itself. Adverb: ______________________________ Love your children unconditionally. Adverb: ______________________________ He waited carefully. Your spot has already been taken. Adverb: ______________________________ Adverb: ______________________________ We are desperately trying to get an answer. Adverb: ______________________________ PREPOSITIONS Prepositions show a relationship between two things in a sentence. Prepositions always come in prepositional phrases. These begin with the preposition and end with a noun or pronoun. Prepositional phrases usually modify the first noun or verb in the relationship. Examples: Please put the book on the table. On is the preposition, on the table is the prepositional phrase that shows the relationship between the verb put and the noun table. It answers the question of where. During the show, I fell asleep in my chair. This sentence contains two prepositional phrases. During the show and in my chair. These phrases tell us when and where falling asleep happened. PREPOSITIONS Here is a list of prepositions you might run into: PREPOSITIONS Practice: Circle the ten prepositional phrases in the paragraph below. In the bottom of the ninth inning, Moses Jones hit a line drive into left field. Ollie Wilkins raced to third and Javier Mercado scored, sliding into home just before the tag. Behind his glove, pitcher Dennis Delaney spit on the ball. It spun wildly over home plate, but Willie Thomas sent the ball sailing out of the park. CONJUNCTIONS Coordinating Conjunctions connect independent clauses. There are 7 coordinating conjunctions that link sentences. FOR AND NOR BUT OR YET FANBOYS SO CONJUNCTIONS Example 1: I went to the store and I bought some milk. Example 2: Last night I watched TV, but not my favorite show. Example 3: Sarah will go to the mall or she will go to the movies. Example 4: Annie had no parents, nor did Simba have a mother and father. Example 5: I show you tomorrow, for you are my best friend. Example 6: Tom had trouble with his homework, yet he finished it before it was due. Example 7: The class wanted to get their requirements so they could go to Disneyland. INTERJECTIONS Interjections are sudden, usually emotional words or phrases that can stand alone as a sentence. Examples: Hey! Look out! Holy cow! Yeah! Wow! Write three of you own sentences using at least 1 interjection.