* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War 2 - HCC Learning Web
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
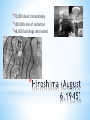
* * Adolph Hitler-Germany * 1933-Chancellor * Benito Mussolini-Italy * Japan * * 1933 - Adolf Hitler is elected Chancellor of Germany. * He abolishes democracy and becomes a dictator. * 1935 - The German military enters the neutral Saar region, Hitler * * * * * * resumes conscription to the German military. 1936 - The German military enters the demilitarized Rhine region. The German-Italian "Axis" is formed. 1938 - Hitler annexes Austria and western Czechoslovakia. Mar 1939 - Czechoslovakia surrenders to imminent German invasion Aug 1939 - Germany and Russia sign non-aggression pact, secretly agreeing to invade Poland and share it. Germany Expansionism— Rhineland (1936) Munich Pact Poland (1939)-Start of WW2 Europe * * Neutrality Laws * Italian invastion of Ethiopia * Spanish Civil War * Atlantic Charter (August 1941) * England-US * They would work to establish freedom from fear and want. * Lend-Lease Act * * 5 When the President proclaimed the existence of a foreign war, certain restrictions would automatically go into effect: Prohibited sales of arms to belligerent nations. Non-military goods must be purchased on a “cash-andcarry” basis pay when goods are picked up. Defined “belligerents” 5 This limited the options of the President in a crisis. * 5 In response to Germany’s invasion of Poland. 5 FDR persuades Congress in special session to allow the US to aid European democracies in a limited way: The US could sell weapons to the European democracies on a “cash-and-carry” basis. 5 Results of the 1939 Neutrality Act: Aggressors could not send ships to buy US munitions. The US economy improved as European demands for war goods helped bring the country out of the 1937-38 recession. 5 America becomes the “Arsenal of Democracy.” * Great Britain.........................$31 billion Soviet Union...........................$11 billion France......................................$ 3 billion China.......................................$1.5 billion Other European.................$500 million South America...................$400 million The amount totaled: $48,601,365,000 * US-Isolationism * Japan-sphere of influence-regional hegemon * Japan and China * Stimson Doctrine * Sino-Japanese War (1937) * * 5 League of Nations condemned the action. 5 Hoover wanted no part in an American military action in the Far East. 5 Stimson Doctrine * December 7, 1941 * 1st attack on American soil since War of 1812 * 2,000 American servicemen killed/187 aircraft and 18 naval vessels(8 battleships) * Declaration of War * 477 in favor and 1 against (Jeannette Rankinpacifist) * * FDR- created federal agencies ( NEW DEAL??) * WPB/War Manpower Commission/Office of Price Administration * Office for Emergency Management and its key suborganization, the National Defense Advisory Commission; the Office of Production Management; and the Supply Priorities Allocation Board * Regulate allocation of labor, fix wages, prices, quotas * # of federal workers increased from 1 mil to 4 mil * * Office of War Information (1942) * Mobilize public opinion * * Women—Traditional—Rosie the Riveter * * African Americans * * * * More than 1 million served in military-segregated units Migration from South Birth of Civil Rights Movement-1942-A.Phillip Randolph-March on Washington-EO 8802banned discrimination in defense jobs-Fair Employment Practices Commission-Lacked enforcement Mexican Americans * * * * 1944-Made up 1/3 of civilian labor force and 350,000 served in auxiliary military units 500,000 served in armed forces Bracero Program Zoot Suit Riots (1943) Japanese Americans * * * Internment-110,000- 200,000 EO 9066---War Relocation Authority Supreme Court Challenges—Korematsu and Hirabayashi-upheld legality of camps * * D-Day—Saving Private Ryan * On June 6, 1944, more than 160,000 Allied troops landed along a 50-mile stretch of heavily-fortified French coastline * More than 5,000 Ships and 13,000 aircraft supported the D-Day invasion * Hitler and Nazis defeated—VE Day (May 8, 1945) * * Island Hopping * 450 B-29 bombers bomb Yokohama Jun 2 - 660 B-29 bombers bomb Japanese cities * * * * Bretton Woods- July 1944-World Bank and IMF-framework for postwar capitalist system 1944-Dumbarton Oaks-United Nations-General Assembly and Security Council Yalta Conference-FDR/Churchill/Stalin (February 1945) Allies * * * * * * * divide Germany into four ‘zones’, which Britain, France, the USA and the USSR would occupy after the war. bring Nazi war-criminals to trial. set up a Polish Provisional Government of National Unity 'pledged to the holding of free and unfettered elections as soon as possible'. help the freed peoples of Europe set up democratic and self-governing countries by helping them to (a) maintain law and order; (b) carry out emergency relief measures; (c) set up governments; and (d) hold elections (this was called the 'Declaration of Liberated Europe'). set up a commission to look into reparations. Russia would join the war in the Pacific, in return for occupation zones in North Korea and Manchuria. Russia also agreed to join the United Nations. * * to set up the four ‘zones of occupation’ in Germany. The Nazi Party, government and laws were to be destroyed, and 'German education shall be so controlled as completely to eliminate Nazi and militarist doctrines and to make possible the successful development of democratic ideas. * to bring Nazi war-criminals to trial. * to recognize the Polish Provisional Government of National Unity and hold 'free and unfettered elections as soon as possible'. * Russia was allowed to take reparations from the Soviet Zone, and also 10% of the industrial equipment of the western zones as reparations. America and Britain could take reparations from their zones if they wished. * * Develops the atomic bomb * * 70,000 dead immediately * 100,000s die of radiation * 48,000 buildings decimated * * 70,000 dead immediately * 60,000 injured * 100,000s die of radiation * * * * * * * * * * 1. Liberals and reformers gave priority to military spending over social and economic reform. 2. Provided an excuse to abolish segments of the New Deal. * E.g. CCC 3. Rise in federal deficit 4. Put the poor "back in their place.“ * 20 million Americans were on the border of subsistence and starvation. 25% of all employed Americans earned less than 64 cents an hour * skilled workers often earned $7 or $8 an hour. 5. Increase in the reach and power of the federal government and the presidency * 1940-1945, the number of civilian employees working for the federal government rose from 1 million to nearly 4 million . * Washington's expenditures grew from $9 billion to $98.4 also accelerated the growth of executive power. * At war's end, the President and his advisors, more than Congress, seemed to drive the nation's domestic and foreign agenda. Furthermore, the Supreme Court refused to hear cases that challenged this increase in executive authority. 6. The "Military-Industrial Complex.“ * A systematic relationship arose between big business and the military's expenditures on defense. During the war, the average daily expenditure on military contracts was $250 million 7. Further solidification of the "Corporate State.“ * helped to solidify the strength of organized labor and to cement the intimate relationship between big business and big government 8. A more urban and technological society. * The federal government expanded its role in research and development in a wide variety of projects, from the manufacture of artificial rubber to the construction of the atomic bomb. * more urbanized, as the six largest cities got two million new inhabitants and 15 million Americans moved from rural areas to the cities.