* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vascular Plants vs. Nonvascular Plants
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
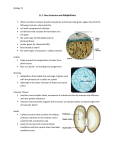
Vascular Plants vs. Nonvascular Plants Plants are broken down into two main groups. They are either vascular or nonvascular. Nonvascular Plants include the mosses, liverworts and hornworts. These are also called bryophytes. They are small, short plants found in wet places. Their gametophyte generation dominates. The sporophyte generation grows from it and depends on it for food. Vascular plants make up about 80% of all plants. They have special tissues in their stems to move water and nutrients up and down the plant. This allows the plant to grow to a much larger size. They are also characterized by their reproductive phase. In vascular plants the sporophyte generation is dominant. Vascular plants are broken down into three groups: 1. Seedless vascular plants – the ferns, horsetails and clubmosses. 2. Naked seed vascular plants - the conifers. 3. Protected seed vascular plants – the flowering plants, grasses and deciduous trees. Use the following poster to illustrate the differences. Then try the Plant Terminology Quiz. Match the Description to the Plant Structure ____ 1. photosynthetic sunlight collection structure ____ 2. structure that houses reproductive A organs for pollination ____ 3. embryonic plant ready for B dispersal ____ 4. hydration collection structure ____ 5. nonvascular, non-seed-bearing, C green plant ____ 6. vascular, non-seed-bearing, green plant ____ 7. vascular, seed-bearing, herbaceous D plant ____ 8.vascular, seed-bearing, woody F plant ____ 9. cultivated leaves used to carpet G J H I E large areas ____ 10. structure that houses xylem transport system ©Sheri Amsel www.exploringnature.org Match and Name the Plant Structure to the Description __________________ 1. photosynthetic sunlight collection structure __________________ 2. structure that A houses reproductive organs for pollination __________________ 3. embryonic plant B ready for dispersal __________________ 4. hydration collection structure C __________________ 5. nonvascular, nonseed-bearing, green plant __________________ 6. vascular, nonseed-bearing, green plant D __________________ 7. vascular, seedbearing, herbaceous plant F __________________ 8.vascular, seedbearing, woody plant G J H I E __________________ 9. cultivated leaves used to carpet large areas __________________ 10. structure that houses xylem transport system ©Sheri Amsel www.exploringnature.org Match the Name to the Plant Structure ______ 1.leaf ______ 2. flower A ______ 3. seed B ______ 4. roots ______ 5. moss C ______ 6. fern ______ 7. plant ______ 8. tree D ______ 9. grass F ______ 10. trunk of tree G J H I E ©Sheri Amsel www.exploringnature.org