* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coagulation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
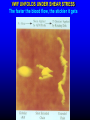
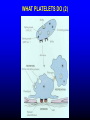
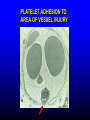
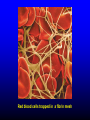
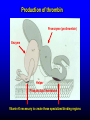
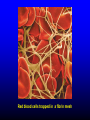
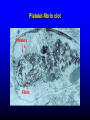
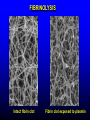
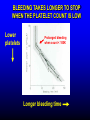
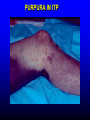
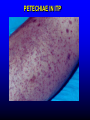
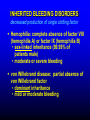
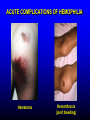
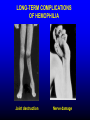
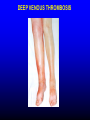
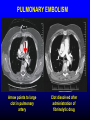
FUNCTIONS OF THE COAGULATION SYSTEM ACTION DESIRED RESULT Rapid formation of mechanically sound clot Stop bleeding quickly Prevent clot formation at non-injured sites Prevent thrombosis Gradual replacement of clot with viable tissue Wound healing BLOOD COAGULATION Platelet plug Fibrin clot PLATELETS WHAT PLATELETS DO Stick to damaged blood vessels • requires von Willebrand factor Spread out to cover damaged area Activate and release contents • partly blocked by aspirin Aggregate Cause blood vessel constriction Cause retraction of clot to draw wound edges together VWF IS A VERY LARGE PROTEIN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC IMAGES OF SINGLE MOLECULES VWF UNFOLDS UNDER SHEAR STRESS The faster the blood flow, the stickier it gets WHAT PLATELETS DO (2) PLATELET ADHESION TO AREA OF VESSEL INJURY PLATELET SPREADING Patel et al, Blood 2003;101:929-36 PLATELET AGGREGATION FIBRIN CLOT FORMATION Tissue damage exposes blood to tissue factor Coagulation cascade: series of enzymatic reactions leading to thrombin formation • takes place mainly on membrane surface, eg platelet membrane Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin Fibrin polymerizes and becomes crosslinked Red blood cells trapped in a fibrin mesh TISSUE FACTOR INITIATES FIBRIN CLOT FORMATION Ubiquitous lipoprotein (part of cell membrane) Initiates physiologic clotting process Highest concentration in brain, mucous membranes, skin, and immediately outside blood vessels Forms "hemostatic envelope" Not normally found on endothelial cells lining blood vessels, or on circulating blood cells TISSUE FACTOR: THE HEMOSTATIC ENVELOPE Am J Pathol 1989; 134:1087-97 LARGE VESSEL SMALL VESSEL VITAMIN K IS NEEDED FOR PRODUCTION OF SEVERAL CLOTTING PROTEINS Fat-soluble vitamin present in many foods Some made by bacteria in gut Necessary for synthesis of several components of coagulation cascade Deficiency may lead to low levels of clotting factors, causing a bleeding tendency Warfarin (Coumadin™): a drug that interferes with vitamin K action • used as an anticoagulant (prevent thrombosis) Production of thrombin Proenzyme (prothrombin) Enzyme Helper Phospholipid membrane Vitamin K necessary to create these specialized binding regions THROMBIN CONVERTS FIBRINOGEN TO FIBRIN Fibrinogen Thrombin Fibrin FIBRIN FORMS LARGE POLYMERS Red blood cells trapped in a fibrin mesh Platelet-fibrin clot Platelets Fibrin FIBRINOLYSIS Degradation of fibrin clot by enzyme called plasmin Necessary to remove clot so wound healing can proceed Plasminogen activators from blood vessels and other cells convert plasminogen to plasmin to begin the process FIBRINOLYSIS Intact fibrin clot Fibrin clot exposed to plasmin REGULATION OF COAGULATION CONFINES CLOT TO INJURED AREA HELPS PREVENT THROMBOSIS Antithrombin: inhibits thrombin and other enzymes Protein C: degrades activated factors V and VIII Protein S: cofactor for protein C Deficiency of any of these proteins can increase risk of thrombosis DISEASES OF PLATELETS Thrombocytopenia = low platelet count (may cause bleeding) • decreased production: bone marrow failure, leukemia • increased consumption • autoimmune (ITP) • disseminated intravascular coagulation • microangiopathy • enlarged spleen - sequesters (soaks up) platelets from the bloodstream Thrombocytosis = high platelet count • myeloproliferative disorders (may cause thrombosis) • inflammation, iron deficiency Platelet dysfunction • drugs (eg, aspirin) BLEEDING TAKES LONGER TO STOP WHEN THE PLATELET COUNT IS LOW Lower platelets Prolonged bleeding when count < 100K Longer bleeding time ACUTE IMMUNE THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA (ITP) Mainly in children Often associated with viral infection 1. Antigen (virus?) sticks to platelet 2. Antibody in blood sticks to antigen on platelet surface 3. Macrophages (immune cells in spleen, elsewhere) consume antibody-coated platelets 4. Platelet number in blood drops 5. Platelet count usually returns to normal when infection resolves CHRONIC IMMUNE THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA (ITP) Mainly in adults 1. Immune system makes antibody against molecule on platelet surface (auto-antibody) 2. Antibody sticks to platelet 3. Macrophages (immune cells in spleen, elsewhere) ingest antibody-coated platelets 4. Platelet number in blood drops 5. Often chronic, treated with immune suppression or splenectomy Childhood (acute) ITP Usually goes away when virus eliminated Adult (chronic) ITP Does not go away on its own; usually requires immune suppressive medication or splenectomy PURPURA IN ITP PETECHIAE IN ITP INHERITED BLEEDING DISORDERS decreased production of single clotting factor Hemophilia: complete absence of factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (hemophilia B) • sex-linked inheritance (99.99% of patients male) • moderate or severe bleeding von Willebrand disease: partial absence of von Willebrand factor • dominant inheritance • mild or moderate bleeding ACUTE COMPLICATIONS OF HEMOPHILIA Hematoma Hemarthrosis (joint bleeding) LONG-TERM COMPLICATIONS OF HEMOPHILIA Joint destruction Nerve damage ACQUIRED BLEEDING DISORDERS partial absence of several clotting factors Liver disease Vitamin K deficiency Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation & fibrinolysis (DIC) Anticoagulant drugs: warfarin or heparin Thrombolytic drugs (plasminogen activators) VITAMIN K DEFICIENCY Newborn/premature infants Poor intake Defective absorption • generalized malabsorption • biliary disease Diminished production by bacteria in gut (antibiotic treatment) Vitamin K antagonists • warfarin (Coumadin) • certain antibiotics DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION Associated with many serious/lifethreatening diseases Circulating blood exposed to excessive amount of tissue factor or other procoagulant Breakdown of normal regulatory processes Formation of circulating (soluble) fibrin Consumption of clotting proteins and platelets Accelerated fibrinolysis – clots break down too quickly Bleeding and/or intravascular clotting in severe cases DIC Soluble fibrin in the blood MONKEY (E. COLI INJECTION) HUMAN (ACUTE LEUKEMIA) TISSUE INJURY IN DIC ASSOCIATED WITH SEPSIS NEJM 2001;344:1593 THROMBOSIS Venous thrombosis • Blockage of blood return and associated inflammation causes swelling, pain • May become chronic • If clot is dislodged from vein can travel to right ventricle and then lungs (pulmonary embolism) Arterial thrombosis • Clot prevents inflow of blood, causing ischemic tissue damage or death (infarction) • Examples: myocardial infarction, stroke DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS PULMONARY EMBOLISM Arrow points to large clot in pulmonary artery Clot dissolved after administration of fibrinolytic drug CAUSES OF THROMBOSIS Abnormal or damaged blood vessels Stasis of blood Inherited lack of protein which regulates coagulation • antithrombin, protein C, protein S Resistance to effect of regulatory protein • Factor V "Leiden" = mutation causing resistance to protein C; found in approx 5% of US population Too many red cells or platelets (thick blood) • polycythemia, thrombocythemia Thrombosis most likely when several factors present at once