* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio-Chem Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
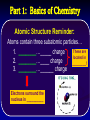
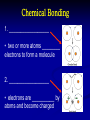
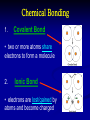
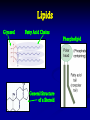
Teacher Instructions • To print handouts for students… • Go to File → print, change “Print what:” to handouts, change # per page if desired to enlarge slides on page • Change “Print range” to slides and type in slide numbers of only those slides you which to print for students Unit 3: Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life Part 1: Basics of Chemistry Atomic Structure Reminder: Atoms contain three subatomic particles… These are 1. ________…_____ charge located in 2. ________…____ charge _________! 3. ________…______ charge Electrons surround the nucleus in __________ Part 1: Basics of Chemistry Atomic Structure Reminder: Atoms contain three subatomic particles… These are 1. Protons…positive charge located in 2. Neutrons…no charge NUCLEUS! 3. Electrons…negative charge Electrons surround the nucleus in orbitals - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 1. _______________ - a ______ substance made up of one type of atom. - organized on ______________ - each element has a unique number of ______…its _____________ - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 1. Element - a pure substance made up of one type of atom. - organized on periodic table - each element has a unique number of protons…its atomic number Examples: Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Carbon (C), and Sodium (Na) The rows are called PERIODS The columns are called GROUPS The elements in each group have the same number of valence electrons…so they react in the same way. These groups are MOST reactive This group is LEAST reactive EachThe element atomic is number described is with theitsnumber name and of PROTONS symbol The atomic mass is the number of PROTONS plus the number of NEUTRONS So an atom of silicon has how many neutrons? 28 – 14 = 14 neutrons - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 2. ________________ - made up of more than one type of substance - __________ combined - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 2. Mixture - made up of more than one type of substance - physically combined Examples: mixture of sugar and salt, salad dressing, solutions, and your blood! - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 3. ________________ - made up of more than one type of substance - ______________ combined - always combined in same _______… that’s the chemical formula! - Elements, Mixtures, and Compounds - 3. Compound - made up of more than one type of substance - chemically combined - always combined in same RATIO… that’s the chemical formula! Examples: water (H2O), glucose (C6H12O6), and salt (NaCl) Chemical Bonding 1. __________________ • two or more atoms ________ electrons to form a molecule 2. __________________ • electrons are __________ by atoms and become charged Chemical Bonding 1. Covalent Bond • two or more atoms share electrons to form a molecule 2. Ionic Bond • electrons are lost/gained by atoms and become charged Part 2: Properties of Water and pH • Draw structure of five water molecules • O and H atoms do not share electrons equally • Oxygen is slightly negative • Hydrogen atoms are slightly positive Part 2: Properties of Water and pH • Draw structure of five water molecules • O and H atoms do not share electrons equally polar covalent bond • Oxygen is slightly negative • Hydrogen atoms are slightly positive hydrogen bond Properties of Water • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ • ___________________ All properties due to the fact that water molecules are _________ Properties of Water • Storage of Heat • Cohesion • Adhesion • Universal Solvent All properties due to the fact that water molecules are POLAR Ions • Remember that atoms that either _______ or _______ electrons become _____, which are ____________ particles • If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a ___________ ion called a ____________ • If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a __________ ion called a __________ Ions • Remember that atoms that either gain or lose electrons become ions, which are charged particles • If an atom loses an electron, it becomes a positive ion called a cation • If an atom gains an electron, it becomes a negative ion called an anion pH Scale • In solutions, water molecules can split into __________ ions and __________ ions • _________ are substances that produce ___________ ions in solution • _________ are substances that produce ___________ ions in solution • The __________ measures how ________ or ________ a solution is, which is based on ratio of __________ and __________ ions pH Scale • In solutions, water molecules can split into hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions • Acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions in solution • Bases are substances that produce hydroxide ions in solution • The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a solution is, which is based on ratio of hydrogen and hydroxide ions pH Scale Acidic solutions have a greater number of ____________ ions than _____________ ions Basic solutions have a greater number of ____________ ions than _____________ ions pH Scale Acidic solutions have a greater number of hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions Basic solutions have a greater number of hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions Part 3: Macromolecules • Four categories of organic molecules 1. __________________ What does the term “organic” mean? 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ • In general, called ________________ • First three categories are also _________ Macromolecules • Four categories of organic molecules 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids Lipids What does the term “organic” mean? • In general, called macromolecules • First three categories are also polymers Polymer Principles • Polymer – • Monomer – Polymer Principles • Polymer – a long molecule consisting of similar or identical building blocks covalently linked together • Monomer – the individual building blocks that make up the polymers Ex. If a sentence is a polymer, words are monomers Polymer Principles Carbohydrates • Commonly called _____________ • Only contain the elements __________, ___________, and __________ in a specific ratio of ____________ Example: __________________________ • Main Function: _____________________ • Found in: _________________________ Carbohydrates • Commonly called sugars • Only contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio of 1:2:1 Example: formula for glucose is C6H12O6 • Main Function: short-term energy source • Found in: foods like fruits, vegetables, grain Carbohydrates • Monomers are called _________________ • Ex. __________________________ • Link two together to form a _____________ • Ex. __________________________ • Many linked together to form a ___________ • Ex. _________________ • Ex. _________________ Carbohydrates • Monomers are called monosaccharides • Ex. simple sugars like glucose and fructose • Link two together to form a disaccharide • Ex. sucrose – common table sugar • Many linked together to form a polysaccharide • Ex. glycogen in animals • Ex. starch and cellulose in plants Proteins • Also called _____________ • Contain elements _________, _________, ________, ________, and _____________ • Monomers are called _________________ • _____ different types of building blocks • _______________ properties vary based on structure of _________________________ • _________ are assembled by __________ Proteins • Also called polypeptides • Contain elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur • Monomers are called amino acids • 20 different types of building blocks • Chemical properties vary based on structure of the amino acids • Proteins are assembled by RIBOSOMES Proteins Proteins Polypeptide Amino Acid Peptide Bond After amino acids are linked together, the chain folds into a specific shape! Shape determines protein’s functions! Proteins • Many Functions! • • • • ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ A Note about Enzymes A _____________ is a molecule that an enzyme reacts with. Enzymes and substrates fit together like a ________________ Proteins • Many Functions! • • • • structural proteins like collagen in skin antibodies in your immune system contractile proteins in your muscles ENZYMES – help speed up chemical reactions by reducing activation energy A Note about Enzymes A substrate is a molecule that an enzyme reacts with. Enzymes and substrates fit together like a lock and key. Proteins Remember the function of all proteins is based on the shape of the protein! If the shape of a protein changes, the protein can no longer do its job! Nucleic Acids • Two types: ___________________ • Contain elements _________, _________, ________, ________, and ___________ • Monomers are called _________________ • made up of three subunits 1. _______________________ 2. _______________________ 3. _______________________ Nucleic Acids • Two types: DNA and RNA • Contain elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus • Monomers are called nucleotides • made up of three subunits 1. 5-carbon sugar 2. nitrogen base 3. phosphate group Nucleic Acids 3. 1. 2. Nucleic Acids 3. 1. Nucleotide 2. 1. Phosphate Group 2. 5-Carbon Sugar (Dexoyribose or Ribose) 3. Nitrogen Base Nucleic Acids • There are 4 different nitrogen bases in DNA: ___________________________________ 1. 3. 2. • RNA uses the nitrogen base ________ instead of ___________ • DNA carries genetic information, while RNA is used in the making of proteins Nucleic Acids • There are 4 different nitrogen bases in DNA: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine 1. 3. 2. • RNA uses the nitrogen base Uracil instead of Thymine • DNA carries genetic information, while RNA is used in the making of proteins Lipids • Technically not a ______________ • Include: _____, ____________, • • ________, and _________. Composed of a backbone __________ and __________________ chains Functions: 1. ____________________________ 2. ____________________________ 3. ____________________________ Lipids • • • • Technically not a polymer Include: fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. Composed of a backbone glycerol and fatty acid chains Functions: 1. Fats serves as long-term energy storage. 2. Cell membranes are made of phospholipids. 3. Many hormones are steroids. Lipids Glycerol Fatty Acid Chains Phospholipid General Structure of a Steroid