* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fringing Reef
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
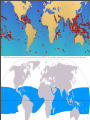
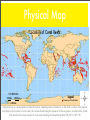
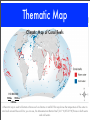
CORAL REEFS Sambavan Jeyakumar Yr 7 What Are They? Coral reefs are structures found underwater, constructed of calcium carbonate secreted by limestone objects known widely as corals. Most coral reefs are composed from stony corals, which consists of tiny animals belonging to the family Cnidaria called polyps. Polyps excrete a hard exoskeleton to protect their bodies. They are one the most diverse ecosystems in the world and the vibrant colours of coral reefs astound people internationally. An oblique photograph of a Blue Linckia Starfish Three Main Types Of all coral reefs in the world, only three types distinguish itself from the others. These include... Barrier Reefs Atolls Fringing Reefs A barrier reef is a coral reef parallel to the shore but is separated by a channel of water. An atoll is a ring-shaped coral reef, consisting of a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. A fringing reef is a reef that forms around a land mass. Other Types Apart from an atoll, fringing reef and a barrier reef, other coral reefs remain within our oceans today including... Patch Reef - a common, isolated reef, similar to an atoll with grass or plants growing around it. Apron Reef - similar to a fringing reef but shorter and steeper, beginning at a point or peninsula. Bank Reef - linear or semicircular shaped-outline larger than a patch reef. Ribbon Reef - long, narrow, similar to a ribbon featuring a lagoon. Table Reef - an isolated reef with all the characteristics of an atoll excluding the lagoon. An oblique photograph of a school of vibrant orange fish in a ribbon reef. Location Coral reefs are estimated to cover 284,300 square kilometres, just under 0.1% of the oceans’ surface area which is about half the size of France but still support over 25% of the world’s marine population. The majority of the location of coral reefs are in the Indo-Pacific region (consisting of the Red Sea, Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean), covering 91.9% of all coral reefs, followed by Australia with 40.8% and Southeast Asia with 32.3%. Although coral reefs exist within both temperate and tropical waters, shallow water reefs form only within 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. Coral reefs are rare along the western African and American coasts. This is primarily due to upwelling, which is the process when the current is pushed back by the wind, and cold currents that reduce the temperature required for reefs to grow. Coral reefs are seldom found in South Asia and South America for similar reasons. Coral reefs are varied around the world and most well-renowned reefs are excellent tourist destinations including... Great Barrier Reef (Australia) The world’s largest reef, comprising 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over 2,600 km. Mesoamerican Barrier Reef (Honduras) The world’s second largest reef stretching for over 1,000 km, connected by various islands. Pulley Ridge (America) The deepest photosynthetic reef, found just off the coast of Florida. ABOVE: This map shows the location of coral reefs around the world. BELOW: This map depicts the areas in which coral reefs grow in shallow water. Formation The majority of the coral reefs found today were formed prior to the last glacial period when melting ice caused the sea level to increase and flood the continental shelves which are the extended perimeters of each continent and associated coastal plain. This proved that modern coral reefs are less than 10,000 years old. As ‘communities’ were established on the shelves, the coral reefs rose against the rising sea level. Coral reefs that were too slow became ‘drowned reefs’ as the water surrounding them provided lack of essential light. Coral reefs are formed in the deep sea away from these shelves, often around oceanic islands or as atolls (ring-shaped coral reef, consisting of a coral rim that encircles a lagoon). The majority of the islands were previously volcanic and others are formed by tectonic origins with the movement of the plates causing the ocean floor to rise above surface. The first man to endeavour to interpret how coral reefs became fringing, barrier and as atolls was Charles Darwin. In 1842, Charles Darwin set out his theory of the formation of coral reefs, in his monograph ‘The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs’. Darwin theorised that it was due to uplift and subsidence of the Earth’s crust underwater that was forming coral reefs. Darwin’s theory is as follows... Darwin’s theory begins with an extinct volcano or island. As the island and ocean floor subside, coral growth forms a fringing reef, including a shallow lagoon between the land and the main reef. As the subsidence continues, the fringing reef becomes a larger barrier reef enlarging the lagoon and creating space between itself and shore. Fringing Reef Barrier Reef Ultimately, when the island is submerged, the barrier reef becomes an atoll enclosing a lagoon. Atoll Formation According to Charles Darwin, the bottom of the lagoon should be bed rock, remnants of the volcano. A team of scientific drillers proved this correct and the rest of Darwin’s theory. Darwin’s theory succeeded his work on coral reefs, proving that the polyps of coral reefs thrive in the clean seas of the tropics, where the water is agitated but not at a substantial depth. He discovered that coral reefs must start of formation in a shallow condition to survive, hence the theory. When the bottom of the sea is rising , fringing reefs grow around the coast but if they leave the water they die and become white limestone. To stay alive, the coral reef rises with the sea level, forming a lagoon within. The encircling of a lagoon can be broken by storms or extremely strong winds. Similar to a rising sea level, a subsiding bottom can also overwhelm the reef, killing the polyps and causing the to drown. Coral reefs that rely on algae, such as zooxanthellae, to survive are vulnerable to drowning. Formation of coral reefs vary between fringing reefs, that uses nutrients to stay with the sea elevation; barrier reefs, that form when a subsiding island is still not submerged, separating the reef and the land mass; and an atoll, which forms when a subsiding island is submerged. Fringing Reef Barrier Reef This line drawing summaries the formation of a fringing reef, barrier reef and atoll. Atoll Zones A coral reef ecosystem has different zones with distinct areas for numerous habitats. There are three predominant zones consisting of a fore reef, reef crest and back reef (frequently referred to as a reef lagoon). These components interconnect both physically and ecologically. Reef life and oceanic processes assist in exchanging of nutrients, seawater, sediments and marine life between themselves. Therefore, the three zones provide an essential role to the nurturing of the coral reef ecosystem and the abundant marine assemblages. Zones Although the fore reef, reef crest and back reef are the major zones, other zones feature in various coral reefs over the world. These consist of... Reef Surface - the shallowest part of a coral reef, making itself exposed to sunlight for photosynthesis and digestion of zooxanthellae and plankton . It is subject to shoal due to the incoming waves (diagram on right). Off-Reef Floor - the shallow sea floor of a coral reef that is often found on a continental shelf. It is a home to plants, sea grass and fish. Reef Drop-Off -similar to a cliff but home to many marine life and plankton. Reef Face -found between the reef floor and reef drop off, this zone is the most diverse, providing hiding places such as crevices and is a dominant ground for algae and small organisms. Reef Flat - a sandy floor, where chunks of coral are found. Possibly bordering a lagoon, it is a preferred place of habitat for fish. Reef Lagoon - an entirely enclosed section, festooned with various coral reefs. This area is not affected by wave action. This diagram signifies the shoaling of water. Water in the reef surface is often agitated and when it encounters shallow water, it shoals,which is when the wave height increases but the movement is slowed. Geographical Processes Geographical processes determine the lives of coral reefs. They are a combination of human and physical forces that form and transform parts of the world.They shape the way coral reefs grow and interact and plays an essential role is investigation of coral reefs. The geographical processes consist of atmospheric, biotic, geomorphic and hydrologic. Atmospheric Processes - physical or chemical processes operating simultaneously in complex and interdependent ways. They cover predominantly on climate, location and conditions of the area. Biotic Processes - any process associated with life and living things including bacteria. Geomorphic Processes - processes corresponding with topography and appearance of the landscape. They focus on erosion, weathering and mass movement. Hydrologic Processes - processes that convene on water and marine life. It is the basis of understanding the life of a landscape. Atmospheric Processes The atmospheric processes involved with coral reefs identifies key questions about a coral reef. Why do coral reefs grow where they are? What conditions do coral reefs require to thrive? The atmospheric processes of coral reefs determine these factors and ultimately the survival of a coral reef. Coral reefs thrive in shallow, warm waters most commonly near land. Predominantly found in the tropics, they require a temperature of 21-30 degrees Celsius. The majority of coral reefs is found in waters up to 50m deep, as they do not rise into tide level to decrease the risk of exiting the water. They are usually found in waters of latitude 30 degrees north and 30 degrees south as these are ideal temperatures for growth. For coral reefs to survive they must also rely on saltwater and zooxanthellae to assist their growth. Consequently, coral reefs become dependent and independent biomes, creating a vast contrast of atmospheric processes, varying for each type. This ground-level image shows the flourishing of coral reefs. Biotic Processes Biotic processes have a significant influence on coral reefs. The vibrant and diverse ecosystem can be distinguished by the large limestone structures known as coral. Coral provides a shelter, a hiding place and as a reliable resource of food for the marine life residing in a coral reef. As a coral reef is a securely interconnected ecosystem, damage to a part of a coral reef will consequently affect the entire ecosystem. Although this biome is only found in 1% of the oceans internationally, coral reefs host 25 % of the marine life population. The vast variety of marine animals and plants is a representation of the biodiversity of coral reefs thriving within our oceans. Symbiotic relationships exist within this ecosystem, an example of a mutually beneficial interaction between objects of coral reefs is the clownfish and the anemone or between different zones of the coral reef. The biodiversity of the ecosystem is depicted using an oblique image. Geomorphic Processes Geomorphic processes determine the physical shape and structure of coral reefs and also the formation of this ecosystem. Formation of coral reefs consist of... Fringing Reef - forms along a coastline, growing on a continental shelf in shallow water (1). Barrier Reef - parallel to the shore, these reefs are separated from land by a channel of water. (2). Atolls - a ring-shaped reef enclosing a partially or entirely closed lagoon (3). 1 2 3 The topography of a coral reef is varies as contemplates Joseph H. Connell, in his book ‘Diversity in Rainforests & Coral Reefs’. ‘"topography of coral reefs is constantly changing. Each reef is made up of irregular patches of algae, sessile invertebrates, and bare rock and sand. The size, shape and relative abundance of these patches changes from year to year in response to the various factors that favour one type of patch over another. Growing coral, for example, produces constant change in the fine structure of reefs. On a larger scale, tropical storms may knock out large sections of reef and cause boulders on sandy areas to move." Hydrologic Processes Hydrologic processes are a prominent feature in coral reefs. Coral reefs are composed of numerous individual creatures known as coral polyps. Coral polyps are the foundation of the structure of coral reefs. The calcium carbonate gives the coral its shape and due to the inaccurate quantity of calcium carbonate, the topography is varied. The coral polyps feed on zooplankton, tiny animals present in the watery presence of the hydrosphere. The range of colour of coral is due to the amount of zooxanthellae, an algae produced in the polyps. Biodiversity Coral reefs have an extremely productive biodiversity, hosting numerous plants and animals in complex and varied habitats that sustain life for a wide variety of creatures. They are a home to an abundant variety of living creatures such as algae, sponges, fish, invertebrates and other animals. Algae - coral reefs are chronically threatened by algae and it’s consequences to the ecosystem. Inhabiting a large percentage of area of surveyed locations, algae consists of turf algae, coralline algae and macro algae. Sponges - sponges are an essential role in the ensuring the ecosystem maintains function. It filters the organic produce secreted by corals and algae that are absorbed by corals in turn. Fish - the reasons for the vast diversity of 4000 species of fish remain controversial. Around 35 tonnes of fish are found every square kilometre of a coral reef unless damaged that will reduce the quantity. Invertebrates - numerous invertebrates, such as sea urchins and sea slugs, play a pivotal part in preventing algae from overrunning reefs. Other - although the main animals found in the prolific biodiversity of a coral reef are eminent, the other animals such as seabirds such as herons, monitor lizards and sea snakes are all another aspect of coral reefs that must be implied. Biodiversity Here are some examples of diverse animals that inhabit coral reefs. Interactions Interactions between human beings and coral reefs have been evident from the discovery of the diverse ecosystem. Organisations such as UNESCO and Greenpeace assist and nurture coral reefs to ensure their growth is sufficient. To prevent numerous hazards, they carefully monitor each coral reef and observe any changes or improvements to the area. Some Aboriginal Dreamtime stories also use the presence of coral reefs to represent exuberance and a vibrant perspective of our world. Although interactions between humans and coral reefs are at substantial levels, humans pose threats that might cease the life of this ecosystem on the face of this planet. Some practices consist of... Cyanide and Dynamite Fishing - coral reefs are in close proximity due to such activities that have depleted the population of coral reefs substantially, overturning the ecosystem and gravely impacting life for marine life. Pollution - human pollutants are causing a lot of harm to coral reefs. Fertilisers, herbicides and pesticides all runoff from farmland on the shore that results in less clarity in the water. This leads to lack of sun exposure that may kill the coral reef. Climate Change - the consequences of human-induced climate change are colossal. The impacts of increased ultraviolet radiation, anomalies in ocean temperature and increased ocean acidification result in tissue damage, exposure to disease, bleaching frequency and change of skeletal formation including the secretion of calcium carbonate that will ultimately destroy coral reefs. Sea Life Depletion - as over 25% of fish species reside in coral reefs, when marine life is caught, this not only affects coral reefs but the entire species of that specific fish. This not only affects coral reefs by gradually decreasing its population but also humans as well, especially those that are dependent on food for sustenance. Diving - when divers touch coral reefs, they damage the delicate structure of the ecosystem. Photographs, residue left from boats such as petroleum and waste material, collisions between humans and the ecosystems shape the entire coral reef. Maximum Overexploitation Minimum - Marine. Range - 15% Rank - 27% Average - 33.33% Physical Map Location of Coral Reefs 1:50 000 000 500km 1500km 1000km Legend Presence of Coral Reefs A physical map is a interpretation of natural location, depicting where a feature is on the Earth’s surface. This physical map displays the location of coral reefs, the red marks indicating the presence of the ecosystem. As observable, SouthEast Asia hosts the most amount of coral reefs including the Great Barrier Reef (18.261°S,147.7°E) Topographic Map Topography Of The Formation Of Coral Reefs A topographic map is a detailed, large-scale map of part of the Earth’s surface, illustrating selected features of the physical environment. As the topography of coral reefs is inconsistent, the hand-drawn map shows the formation of coral reefs. Thematic Map Climatic Map of Coral Reefs 1:50 000 000 500km 1500km 1000km A thematic map is used to illustrate a theme such as climate or rainfall. This map shows the temperature of the water in coral reefs around the world. As you can see, the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef (14.1°N, 87.22°W) thrives in both warm and cold water. Sketch Map Sketch Map Of A Coral Reef Bibliography Bibliography Bibliography