* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5-PDH_and_TCA_cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
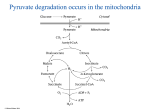
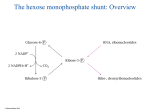
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and the citric acid cycle © Michael Palmer 2016 1 Pyruvate degradation occurs in the mitochondria © Michael Palmer 2016 2 The PDH reaction occurs in three successive steps that are catalyzed by three different subunits © Michael Palmer 2016 3 The structural organization of the PDH complex © Michael Palmer 2016 4 A lipoamide tether guides the substrate from one active site to the next © Michael Palmer 2016 5 The pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction involves multiple coenzymes Coenzyme © Michael Palmer 2016 Subunit Role in catalysis thiamine pyrophosphate E1 provides a carbanion for nucleophilic attack on the substrate lipoamide E2 transfers substrate to coenzyme A, retains hydrogen flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) E3 transfers H2 from lipoamide to NAD+ 6 Thiamine pyrophosphate forms a carbanion © Michael Palmer 2016 7 Decarboxylation of pyruvate by E1 © Michael Palmer 2016 8 Release of acetyl-CoA and disposal of hydrogen © Michael Palmer 2016 9 Alternate metabolic destinations of pyruvate 1. conversion to acetyl-CoA by PDH for complete degradation or for synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol 2. carboxylation to oxaloacetate, for use in gluconeogenesis or in the citric acid cycle 3. synthesis of amino acids, e.g., transamination to alanine 4. reduction to lactate © Michael Palmer 2016 10 Regulation of PDH by allosteric effectors and by phosphorylation © Michael Palmer 2016 11 The overall reaction of the TCA cycle: does it add up? © Michael Palmer 2016 12 The citrate synthase reaction © Michael Palmer 2016 13 Reactions in the TCA cycle: from citrate to succinyl-CoA © Michael Palmer 2016 14 Reactions in the TCA: from succinyl-CoA to oxaloacetate © Michael Palmer 2016 15 α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase resembles PDH © Michael Palmer 2016 16 Regulation of the citric acid cycle • ATP and NADH inhibit isocitrate dehydrogenase • NADH inhibits α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase • High levels of NADH will lower the oxaloacetate concentration, which limits citrate synthase activity © Michael Palmer 2016 17