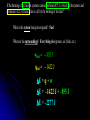* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy, Heat, and Work* Oh My*
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
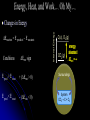
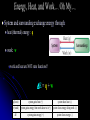
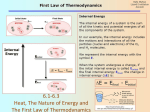
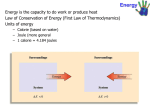
Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Energy – The capacity to do work Kinetic Energy – Energy of Motion Thermal A Energy – Associated with Temperature type of kinetic energy – motion of atoms and molecules Potential Energy – Stored Energy Chemical A Energy – Position of electrons and nuclei type of potential energy – changes in position change stored energy Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… joule (J) is the amount of energy needed to move a 1-kg mass a distance of 1 meter 1 J = 1 N∙m = 1 kg∙m2/s2 calorie (cal) is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water 1°C kcal = energy needed to raise 1000 g of water 1°C food Calories = kcals Energy Conversion Factors 1 calorie (cal) = 4.184 joules (J) 1 Calorie (Cal) = 1000 cal = 1 kcal = 4184 J 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) = 3.60 x 106 J Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… nanojoule (nJ) 160 nJ is about the kinetic energy of a mosquito megajoule (MJ) Kinetic energy of a 1 ton car moving at 100 mi/hr 3.6 MJ = 1 kilowatt-hour gigajoule (GJ) 6 GJ = chemical energy in 1 barrel of oil when burned exajoule (EJ = 1x1018 J) 1.41 EJ = 2011 earthquake in Japan 52 EJ = Energy release per day of the average hurricane 94 EJ = annual energy consumption in the US Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Heat – The transfer of thermal energy as a result of a temperature difference Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Heat – The transfer of thermal energy as a result of a temperature difference Work – Force acting through a distance Lifting a book Pushing a desk Inflating a balloon Breathing Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Law of Conservation of Energy “Energy can be neither created nor destroyed” Etotal @ start = Etotal @ end Energy CAN be transformed from one type to another Energy CAN be transferred between system Transfer can take place through WORK or HEAT Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Energy can be transferred between systems System Stuff – The “stuff” in which changes in energy are being studied = material or process Surroundings – Everything with which the system can exchange energy System + Surroundings = UNIVERSE! (energy of the universe must remain constant) Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Energy can be transferred between systems System – The “stuff” in which changes in energy are being studied Surroundings – Everything with which the system can exchange energy system UNIVERSE surroundings Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Law of Conservation of Energy “Energy can be neither created nor destroyed” Etotal @ start = Etotal @ end Energy can be transferred between systems a system and its surroundings If energy is lost by the system, what must happen? Its surrounding must gain the same amount of energy! If energy is gained by the system, what must happen? Its surrounding must lose the same amount of energy! Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… When energy flows out of a system, it must all flow into the surroundings When energy flows out of a system, DEsystem is ─ When energy flows into the surroundings, DEsurroundings is + Therefore: ─ DEsystem= DEsurroundings Surroundings DE + System DE ─ Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… When energy flows into a system, it must all come from the surroundings When energy flows into a system, DEsystem is + When energy flows out of the surroundings, DEsurroundings is ─ Therefore: DEsystem= ─ DEsurroundings Surroundings DE ─ System DE + Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… A student drops some magnesium turnings into a styrofoam coffee cup containing HCl(aq) and uses a thermometer to monitor the reaction. Assume that the cup is a perfect insulator. 1) What is the system? the reaction (Mg(s) + 2 H+ Mg2+ + H2(g)) gives off energy 2) What are the surroundings? water thermometer air in the cup absorbs energy Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Energy is a “State Function” Path independent – does not matter HOW it got there Matters only on the state of the system Change in elevation is Elv final – Elv initial OR D Elv = Elv final – Elv initial Change in ENERGY is E final – E initial OR D E = E final – E initial Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Changes in Energy Change in ENERGY is E final – E initial OR DE = E final – E initial OR DEreaction = E products – E reactants Conditions DErxn sign E prod > E react + (DErxn > 0) E prod < E react – (DErxn < 0) Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… Changes in Energy DEreaction = E products – E reactants Internal Energy C(s), O2(g) CO2(g) energy energy released absorbed DE DErxn + rxn==─ Conditions DErxn sign E prod > E react + (DErxn > 0) Surroundings E prod < E react – (DErxn < 0) System CO O22 C + 2O→C 2 →+CO Energy, Heat, and Work… Oh My… System and surrounding exchange energy through: heat (thermal) energy: q work: w work and heat are NOT state functions!! DE = q + w q (heat) system gains heat (+) w (work) system gains energy from work done to it (+) DE system gains energy (+) system loses heat (–) system loses energy doing work (–) system loses energy (–) If the burning of the fuel in a potato cannon performs 855 J of work on the potato and produces 1422 J of heat, what is DE for the burning of the fuel? What is the system being investigated? Fuel What are the surroundings? Everything else (potato, air, birds, etc.) wfuel = – 855 J qfuel = – 1422 J DE = q + w DE = –1422 J + –855 J DE = –2277 J If the burning of the fuel in a potato cannon performs 855 J of work on the potato and produces 1422 J of heat, what is DE for the burning of the fuel? What is the system being investigated? Fuel What are the surroundings? Everything else (potato, air, birds, etc.) wpotato = + 855 J wpotato = - wfuel wfuel = – 855 J Reacting 50 mL of H2(g) with 50 mL of C2H4(g) produces 50 mL of C2H6(g) at 1.5 atm. If the reaction produces 3.1 x 102 J of heat and the decrease in volume requires 7.6 J of work, what is the change in internal energy of the gases? What is the system being investigated? Reaction What are the surroundings? Everything outside the container qrxn = – 310 J wsur = – 7.6 J wsur = – wrxn wrxn = + 7.6 J DE = q + w DE = –310 J + (+7.6 J) DE = –3.0x102 J