* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tissues- A group of similar cells that perform a common function.
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
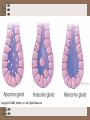
Tissues- A group of similar cells that perform a common function. Ch. 5 Types of Tissues • Epithelial- covers & protects the body surface, lines body cavities, moves substances in & out of blood, and forms many glands. • Connective Tissue- Supports body, holds body parts together, transports substances through the body & protects it from foreign invaders. Embryonic Development of Tissues • After fertilization, the cell divides and becomes a hollow ball of cells called a blastocyst. These cells regroup and form the three primary layers (gastrulation): – – – Endoderm Mesoderm Ectoderm These layers then differentiate into tissues (histogenesis) Functions of Epithelial Tissue • Protection- from injury & foreign particles • Sensory- found in skin, nose, eye & ear • Secretion- include hormone, mucus, digestive juices & sweat. • Absorption- of nutrients & gases in lungs • Excretion- kidney & urine Classification Based on Cell Shape • Four cell shapes: – – – – squamous: flat & platelike cuboidal: cube-shaped columnar: narrow & cylindrical pseudostratified columnar: oddly shaped with some nuclei near the top & some near the bottom of the cell (Figure 5-2) Classification Based on Layers of Cells • Simple- cells arranged in a single layer • Stratified- cells layered one on another • Transitional- differing cell shapes in a stratified or layered sheet (Figure 5-2) Simple Squamous Epithelium • One layer of flat, scalelike cells. • Substances can readily diffuse or filter through. • Examples include the microscopic air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs & lining of blood vessels) (Figure 5-5) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium • One layer of cuboidal cells • Found in many types of glands & ducts. • Also found in organs, such as the kidney. Simple Columnar Epithelium • Lines the stomach, intestine, uterus, uterine tubes, and parts of the respiratory tract. • Because these cells are larger they offer more protection while still allowing secretion/absorption to take place. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium • Found lining the air passages of the respiratory system & certain segments of the male reproductive system such as the urethra. • Cells are of differing heights Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Multiple layers of flat cells • Some are composed of keratin (helps protect & waterproof) & are found in the skin • Others are nonkeratinized and are found in the vagina, mouth & esophagus Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium • Generally serves as protection • Located in sweat gland ducts, in the pharynx & over parts of the epiglottis Stratified Columnar Epithelium • Not common in the body • Found only in parts of the male urethra & in the mucous layer near the anus Stratified Transitional Epithelium • Has the ability to stretch & flatten out • Found in the walls of the bladder • Protects the bladder wall from tearing when stretched Exocrine Glands- discharge their secretions into ducts Endocrine Glands- discharge their secretions directly into the blood Types of Exocrine Glands • Apocrine glands- Milk producing Ex. mammary glands • Holocrine glands- produce oil to lubricate the skin • Merocrine glands- Salivary glands Connective Tissue • Connective tissue connects, supports, transports and defends. • Connects tissue to tissue, muscle to muscle, bone to muscle and bones to bones. • Blood is a connective tissue that transports substances between parts of the body • Other connective tissue cells defend us against microorganisms & invaders Loose Connective Tissue • Stretchable & widely distributed around the body • Not as specialized as other connective tissue Adipose Tissue • Forms a protective barrier around the kidneys & other various structures • Storage for excess food • Insulates the body to conserve heat Reticular Tissue • Forms the framework of the spleen, lymph nodes & bone marrow. • Helps defend the body against foreign substances Dense Fibrous Tissue • Is flexible but very strong • Tendons & ligaments are made of this • Forms the strong inner skin layer called the dermis • Also forms the outer layer of organs like the kidney & the spleen