* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Symbiotic Relationships
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ticks of domestic animals wikipedia , lookup
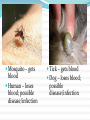
Symbiotic Relationships A close ecological relationship between two or more different species Habitat Places plants and animals normally live Forests, grasslands, deserts, marshes, beaches Niche The organism’s “JOB” or role in an ecosystem Predator, scavenger, producer, decomposer, parasite Commensalism One species benefits The other species is unaffected Example: a bird builds a nest in a tree Bird – gets shelter Tree - unaffected Barnacles – have a home Whale - unaffected Epiphyte – get access to more sunlight Tree - unaffected Mutualism Both species benefit Example: honeybee and dandelion Honeybee – gets to eat the pollen Dandelion – gets bee to spread pollen to another flower Ramora – gets leftover Tickbird – eats flies, food from shark Shark – cleaning service ticks off rhino Rhino – cleaning service Parasitism One species benefits The other species is harmed Example: Deer tick and white tailed deer Deer tick – gets blood from the deer White tailed deer – loses blood; risks possible infection Mosquito – gets blood Human – loses blood; possible disease/infection Tick – gets blood Dog – loses blood; possible disease/infection