* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
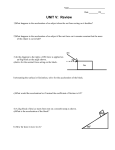
Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Figure 5.17 below shows a block of mass m resting on a 20° slope. The block has coefficients of friction µs = 0.64 and µk = 0.54 with the surface. It is connected via a massless string over a massless, frictionless pulley to a hanging block of mass 2.0 kg. What is the minimum mass m that will cause the two blocks to remain at rest and not move when released? Figure 5.17 A) 3.3 kg B) 2.1 kg C) 3.6 kg D) 1.3 kg E) not enough information given to decide 2) A wheel accelerates from rest to 59 rad/s at a rate of 58 rad/s2. Through what angle (in radians) did the wheel turn while accelerating? A) 24 rad B) 60 rad C) 30 rad D) 38 rad 3) A jumping frog leaves the ground moving at speed v0 at an angle of 45° above the horizontal. What is the speed of the frog when it is at its maximum height? Air resistance can be ignored. A) v0/2 B) between v0 and v0 /2 C) zero D) between v0/2 and zero E) v0 4) You push two boxes from one side of a room to the other. Each box begins and ends at rest. Both boxes are made of the same material, and the contact area between box and floor are the same for both, but one box is heavy while the other is light. There is friction between each box and the floor. Which statement is correct? A) You do more work on the heavy box than on the light box, but the total work done on each box is the same. B) You do the same amount of work on each box, but the total work done on the heavy box is greater than on the light box. C) You do the same amount of work on each box, and the total work done on each box is the same. D) You do more work on the heavy box than on the light box, and the total work done on the heavy box is greater than on the light box. E) You do more work on the heavy box than on the light box, but the total work done on the heavy box is less than on the light box. Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C 5) A force of 16.88 N is applied tangentially to a wheel of radius 0.340 m and gives rise to an angular acceleration of 1.20 rad/s2. Calculate the moment of inertia of the wheel. A) 7.17 kg ∙ m 2 B) 4.78 kg ∙ m 2 C) 5.98 kg ∙ m 2 D) 3.59 kg ∙ m 2 6) A car of mass 1500 kg is moving north at 35.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a truck of mass 7500 kg moving due south. Immediately after the collision, both vehicles are at rest. How fast was the truck moving before the collision? A) 14.0 m/s B) 7.0 m/s C) 20.0 m/s D) 5.0 m/s E) 10.0 m/s 7) A bead on a 60 cm long string is swung in a vertical circle about a point 200 cm above the floor. The tension in the string when the bead is at the very bottom of the circle is 2.2 N. A very sharp knife is suddenly inserted, as shown in Figure 6.3 below, to cut the string directly below the point of support. How far to the right of the center of the circle does the ball hit the floor? Figure 6.3 A) 160 cm B) 190 cm C) 240 cm D) 200 cm E) answer depends on the mass of the bead 8) A moving block hits and sticks to a second, identical block that is initially at rest. The total kinetic energy of the two blocks just before they hit is K. The total kinetic energy of the two blocks just after they hit is A) K B) between K/2 and zero C) between K and K/2 D) K/2 E) answer depends on how much the blocks compress when they hit 9) An object attached to a spring is pulled across a frictionless surface. If the spring constant is 45 N/m and the spring is stretched by 0.88 m when the object is accelerating at 1.4 m/s2, what is the mass of the object? A) 36 kg B) 24 kg C) 28 kg D) 31 kg Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C 10) An astronaut is on board a spaceship on its way from Earth to Mars. The engines of the spaceship are turned off, so the spaceship follows an orbit around the Sun that will eventually take it to Mars. The astronaut feels weightless because A) the astronaut's acceleration is zero. B) the astronaut and her spaceship both have the same acceleration, which is not zero. C) the astronaut is beyond the range of the Sun's gravity. D) the astronaut is beyond the range of Earth's gravity. E) the astronaut and her spaceship both feel the same gravitational force, which is not zero. Figure 8.2 11) A block of mass m = 3.6 kg, moving on a frictionless surface with a speed v i = 9.3 m/s, makes a perfectly elastic collision with a block of mass M at rest. After the collision, the 3.6 kg block recoils with a speed of v f = 2.7 m/s. In Figure 8.2, the speed of the block of mass M after the collision is closest to: A) 12.0 m/s B) 10.7 m/s C) 8.0 m/s D) 6.6 m/s E) 9.3 m/s 12) Two crates are at rest, one touching the other, on a horizontal surface. You push horizontally on crate 1 (the one on the left) as shown by the arrow in the figure above. Which of the following is a force that acts on crate 2 (the one on the right)? A) a reaction force exerted by crate 2 B) a force exerted by crate 1 C) a force due to the acceleration of crate 2 D) a force exerted by you E) more than one of these 13) A 0.46 kg block is held in place against the spring by a 30 N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity !1 = 1.2 m/s upon separation from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity !2 = 1.5 m/s at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.38. The velocity of the block is !3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. In Figure 7.4, the distance s that the block travels between points B and D is closest to: A) 0.40 m B) 0.60 m C) 0.26 m D) 0.30 m E) 0.039 m Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 3.3 A wind farm generator uses a two-bladed propeller mounted on a pylon at a height of 20 m, as shown in Figure 3.3 above. The length of each propeller blade is 12 m. A tip of the propeller breaks off when the propeller is vertical. The fragment flies off horizontally, falls, and strikes the ground at P. Just before the fragment broke off, the propeller was turning uniformly, taking 1.2 s for each rotation. 14) In Figure 3.3, the distance from the base of the pylon to the point where the fragment strikes the ground is closest to: A) 130 m B) 150 m C) 120 m D) 140 m E) 160 m 15) A gazelle runs in a straight line (the x-axis). The graph above shows this animal’s velocity as a function of time. How far does the gazelle move during the first 10.0 s? A) 40.0 m B) 60.0 m C) 68.0 m D) 120 m E) 80.0 m 16) Rank the following four objects according to their mass, from largest to smallest. The acceleration due to gravity at the equator of Earth is 9.80 m/s2; the acceleration due to gravity at the equator of Mars is 3.69 m/s2. I. A rock on the Martian equator that weighs 10.0 N. II. A rock at Earth’s equator that weighs 10.0 N. III. A rock on the Martian equator that has a mass of 10.0 kg. IV. A rock at Earth’s equator that has a mass of 10.0 kg. A) III, IV, II, I B) II, III, IV, I C) II, I, III, IV D) I, II, III, IV E) III, IV, I, II Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 7A-6 17) Suppose you are at the center of a large freely-rotating horizontal turntable in a carnival funhouse. As you crawl toward the edge, the angular momentum of you and the turntable A) increases. B) decreases in direct proportion to the decrease in angular speed of the turntable. C) remains the same, but the angular speeed of the turntable decreases. D) decreases. E) none of these. 18) A crane lifts a 425 kg steel beam vertically upward a distance of 95 m. How much work does the crane do on the beam if the beam accelerates upward at 1.8 m/s2? Neglect frictional forces. A) 4.7 × 10 5 J B) 3.2 × 10 5 J C) 4.0 × 10 5 J D) 2.7 × 10 5J 19) You do 116 J of work while pulling your sister back on a swing, whose chain is 5.10 m long, until the swing makes an angle of 32.0° with the vertical. What is your sister's mass? A) 19.0 kg B) 17.6 kg C) 13.0 kg D) 15.3 kg 20) Which statement is true about the motion depicted in the graph below? A) At B) At C) At D) At E) At t = 5 s the object has a negative x-acceleration and is speeding up. t = 5 s the object has a negative x-acceleration and is slowing down. t = 5 s the object has a positive x-acceleration and is speeding up. t = 5 s the object has a positive x-acceleration and is slowing down. t = 5 s the object has zero acceleration. Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 10.1 21) A light triangular plate OAB is in a horizontal plane. Three forces, F 1 = 1 N, F 2 = 4 N, and F 3 = 8 N, act on the plate, which is pivoted about a vertical axis through point O. In Figure 10.1 above, the torque of force F 1 about the axis through point O is closest to: A) 0.45 N ∙ m B) 0.30 N ∙ m C) 0.60 N ∙ m D) 0.37 N ∙ m E) 0.52 N ∙ m Figure 4.7 22) A box with weight 32 N is on a rough horizontal surface. An external force F is applied horizontally to the box. A normal force and a friction force are also present, denoted by n and f. A force diagram, showing the four forces that act on the box, is shown in Figure 4.7 above. When force F equals 8.6 N, the box is in motion at constant velocity. The box decelerates when force F is removed. The magnitude of the acceleration of the box is closest to: A) 2.6 m/s2 B) 1.3 m/s2 C) 0.67 m/s2 D) 2.0 m/s2 E) zero Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 4.6 23) A 5.1-kg box is held at rest by two ropes that form 30° angles with the vertical. An external force F acts vertically downward on the box. The force exerted by each of the two ropes is denoted by T. A force diagram, showing the four forces that act on the box in equilibrium, is shown in Figure 4.6 above. The magnitude of force F is 920 N. The magnitude of force T is closest to: A) 560 N B) 486 N C) 971 N D) 388 N E) 777 N Figure 3.1 24) A projectile is fired from the origin (at y = 0 m) as shown in Figure 3.1 above. The initial velocity components are V0x = 940 m/s and V0y = 96 m/s. The projectile reaches maximum height at point P, then it falls and strikes the ground at point Q. In Figure 3.1, the y-coordinate of point P is closest to: A) 940 m B) 470 m C) 45,080 m D) 90,160 m E) 45,550 m 25) You drop a ball of mass 0.500 kg from a height of 2.00 m. The collision between the ball and the ground is inelastic, so the ball bounces back to a height of only 1.00 m. What was the magnitude of the upward impulse that the ground imparts to the ball during this collision? A) 2.21 kg-m/s B) 1.83 kg-m/s C) 0.917 kg-m/s D) 5.34 kg-m/s E) 3.13 kg-m/s Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 9.2 26) In Figure 9.2 above, two blocks, of masses 2 kg and 3 kg, are connected by a light string which passes over a pulley of moment of inertia 0.004 kg ∙ m 2 and radius 5 cm. The coefficient of friction for the table top is 0.30. The blocks are released from rest. Using energy methods, one can deduce that after the upper block has moved 0.6 m, its speed is: A) 1.40 m/s B) 3.19 m/s C) 1.95 m/s D) 1.22 m/s E) 5.44 m/s 27) The components of vector A are given as follows: Ax = +6.1 Ay = -8.6 The angle measured counterclockwise from the x-axis to vector A , in degrees, is closest to: A) 305 B) 215 C) 55 D) 125 E) 145 28) A small mass is placed on a record turntable that is rotating at 45 rev/min. The linear acceleration of the mass is A) independent (in magnitude) of the position of the mass on the turntable. B) greater the closer the mass is to the center. C) directed perpendicular to the line joining the mass and the center of rotation. D) greater the farther the mass is from the center. E) zero. 29) A train starts from rest and accelerates uniformly, until it has traveled 2.1 km and acquired a velocity of 24 m/s. The train then moves at a constant velocity of 24 m/s for 400 s. The train then slows down uniformly at 0.065 m/s2, until it is brought to a halt. The distance traveled by the train while slowing down, in km, is closest to: A) 3.6 B) 4.4 C) 4.2 D) 4.0 E) 3.8 Physics 6A Final Exam — Wednesday, March 20, 2013 — Version C Figure 6.1 30) A ball of mass 7.0 kg is suspended by two wires from a horizontal arm, which is attached to a vertical shaft, as shown in Figure 6.1 above. The shaft is in uniform rotation about its axis such that the linear speed of the ball equals 2.2 m/s. The rate of rotation is adjusted so that the tensions in the two wires are equal. The radial acceleration of the ball is closest to: A) 5 m/s2 B) 7 m/s2 C) 6 m/s2 D) 8 m/s2 E) 10 m/s2 31) An object initially at rest explodes in two fragments of masses 2.6 kg and 3.3 kg that move in diametrically opposite directions. If the speed of the first fragment is 3.6 m/s, find the energy released by the explosion. A) 30J B) 38J C) 30kJ D) 38kJ 32) A 6.0 kg box slides down an inclined plane that makes an angle of 39° with the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40, at what rate does the box accelerate down the inclined plane? A) 3.4 m/s2 B) 4.1 m/s2 C) 3.7 m/s2 D) 3.1 m/s2 E) not enough information given to decide Answer Key Testname: FINAL_EXAM_VERSION_C 1) B 2) C 3) B 4) A 5) B 6) B 7) A 8) D 9) C 10) B 11) D 12) B 13) D 14) E 15) E 16) E 17) C 18) A 19) D 20) D 21) E 22) A 23) A 24) B 25) D 26) A 27) A 28) D 29) B 30) A 31) A 32) D