* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IG_Algebra 1_Unit 5 - allianceprincipalresources
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
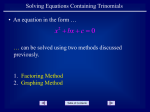
Algebra 1 Subject:____________________ Unit Title: Factoring 5 Unit:_______________________ 3 (January 17th – Quarter:_____________________ March 23rd) Unit Overview Unit 5: Factoring In the last unit algebraic expressions were multiplied to form a new expression that was the product of the factors. The focus of this unit shifts to a discussion of factoring. When the product is given and the factors are found, this process is called factoring; which is the inverse of multiplying. Algebraic skills are employed in the factoring process, such as looking for the greatest common factor, recognizing the difference in two squares, and factoring trinomials of the form ax2 + bx +c. The use of the zero product property is employed throughout the section on factoring in order to solve factorable quadratic equations. The zero product property states when the product of two or more numbers is zero, one of those numbers must be zero. An emphasis is placed on the distinction between factoring an expression and solving an equation. Math Literacy Key Vocabulary: factored form, factoring, factoring by grouping, perfect square trinomials, prime factorization, prime polynomial, quadratic expression, difference of two squares, perfect square trinomial, zero product property, double root. Supporting Vocabulary: composite number, greatest common factor, prime number 1 Common Core State Standard Alignment ASSE.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. For example, see x4 – y4 as (x2)2 – (y2)2, thus recognizing it as a difference of squares that can be factored as (x2 – y2)(x2 + y2). ASSE.3a Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression. Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines. Sample Essential Questions Explain the relationship between the multiplication (distribution) of polynomials and factoring. Explain the difference and similarities among the methods of factoring. Identify when to use each method for factoring? Anchor Standards/Central Concepts 11.0 Students apply basic factoring techniques to second- and simple third-degree polynomials. These techniques include finding a common factor for all terms in a polynomial, recognizing the difference of two squares, and recognizing perfect squares of binomials. 11.0 Students apply basic factoring techniques to second- and simple third-degree polynomials. These techniques include finding a common factor for all terms in a polynomial, recognizing the difference of two squares, and recognizing perfect squares of binomials. # CST Items Standard Learning Targets/ Key Concepts and Skills 2 College-Ready Sample Assessment Questions 11a I can find the prime factorizing of monomials. Factor 16x3 + 20x2 + 20x + 25 11b I can find the greatest common factors (GCF) of monomials. Factor 27xy - 81y 11c I can factor trinomials in the 2 # CST Items Standard Learning Targets/ Key Concepts and Skills form x2 + bx + c and ax2 + bx +c. College-Ready Sample Assessment Questions 11d I can factor a difference of two squares polynomial. Determine all values of k that make each of the following a perfect square. Explain your reasoning. 4x2 + kx + 1 11e I can factor out the GCF from polynomials with many terms. 11f I can factor a polynomial expression by grouping and identify algebraic properties that are used in the process. 11g I can use factoring to simplify expressions (reducing) involving polynomial division. 11h I can check solution(s) (e.g. substitution), and reasonableness of answer. x2 – 18x + k x2 + 20 x + k Create a polynomial that requires at least two different factoring techniques to factor completely. Describe techniques that were used. Solve the following equations. Check the solutions. (d-5)(2d -3) = 0 11i I can solve equations by factoring using the Zero Product Property and explain the process of doing so. x2 = -7x (x+3)2 = 3 3 Vertical Alignment Multiply and divide monomials 7AF2.2 Factor special polynomials 2A4.0 Additional Sample College-Ready Assessments Questions Sample College-Ready Assessment Questions 4