* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 50401A-ENU_Powerpnt_08
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Global serializability wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Commitment ordering wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
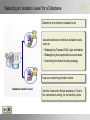
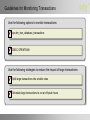
Module 8 Designing a Transaction and Concurrency Strategy Module Overview • Guidelines for Defining Transactions • Defining Isolation Levels • Guidelines for Designing a Resilient Transaction Strategy Lesson 1: Guidelines for Defining Transactions • Guidelines for Creating Transactions • Considerations for Using Nested Transactions • Demonstration: How to Create a Nested Transaction Guidelines for Creating Transactions Perform a transaction in: • Explicit Mode • Autocommit Mode • Implicit Mode Manage transactions across multiple platforms Handle the errors in a transaction by using TRY…CATCH Use transaction savepoints Considerations for Using Nested Transactions Committing inner transactions is ignored by the SQL Server Database Engine Each call to COMMIT TRANSACTION or COMMIT WORK applies to the last executed BEGIN TRANSACTION The Transaction_name should not refer to the inner transactions of a set of named nested transactions The @@TRANCOUNT function records the current transaction nesting level Demonstration: How To Create a Nested Transaction In this demonstration, you will see how to: Create a nested transaction Lesson 2: Defining Isolation Levels • Isolation Levels in the Database Engine • Comparing Read Committed Isolation with Snapshot Isolation • Selecting an Isolation Level for a Database • Considerations for Offloading Concurrent Activities Isolation Levels in the Database Engine READ UNCOMMITTED: Can read data that has been modified by other transactions but not committed READ COMMITTED: Cannot read data that has been modified but not committed by other transactions REPEATABLE READ: No other transactions can modify data that has been read by the current transaction until the current transaction completes SNAPSHOT: Data read by any statement in a transaction will be the transactionally consistent version of the data that existed at the start of the transaction SERIALIZABLE: Other transactions cannot insert new rows with key values that would fall in the range of keys read by any statements in the current transaction until it is complete Comparing Read Committed Isolation with Snapshot Isolation When to Use Read Committed Isolation When to Use Snapshot Isolation Use read committed isolation when: Use snapshot isolation when: • • Optimistic concurrency control is • Reader/writer blocking occurs to the point that concurrency benefits outweigh increased overhead of creating and managing row versions An application requires absolute accuracy for long-running aggregations or queries where data values must be consistent to the point in time that a query starts desired • Probability is low that a transaction would have to be rolled back because of an update conflict • An application needs to generate reports based on longrunning, multi-statement queries that must have point-in-time consistency Selecting an Isolation Level for a Database Determine the minimum isolation level Use alternatives to restrictive isolation levels, such as: • Redesigning Transact-SQL logic and tables • Redesigning how applications access data • Overriding the default locking strategy Use row versioning isolation levels Database Isolation Level Set the Connection Reset property to True in the connections string, for connection pools Considerations for Offloading Concurrent Activities Offloading concurrent activities helps: • Avoid contention and blocking problems • Improve system performance Methods for Offloading Concurrent Activities Scale out the system Create a data warehouse Reschedule activities Lesson 3: Guidelines for Designing a Resilient Transaction Strategy • Guidelines for Designing an Object Access Strategy • Guidelines for Transaction Rollback • Guidelines for Using Optimizer Hints • Guidelines for Using Locking Hint Functionalities • Guidelines for Monitoring Transactions • Guidelines for Troubleshooting Orphaned Transactions • Demonstration: How to Use Locking Hints • Discussion: Reducing Deadlock Errors Guidelines for Designing an Object Access Strategy 1 1 2 2 3 3 Communicate the object access order and enforce compliance Design an object access order based on usage 2 2 1 1 3 Manage conflicts when accessing objects 3 Discourage ad hoc queries Guidelines for Transaction Rollback Minimize errors Define a rollback strategy Pre-validate data Monitor for rollbacks Define an error-handling strategy Guidelines for Using Optimizer Hints The query optimizer enforces a join strategy between two tables Join Hints Query Hints Query hints enforce query optimizer to execute the select statement as a whole Overrides the default behavior of the query optimizer Table Hints Guidelines for Using Locking Hint Functionalities Locking hint functionalities of SQL Server 2008 include: • XLOCK at row level • READPAST • READCOMMITTEDLOCK Using locking hints, you can implement the following functionalities: • Provide finer locking control • Reduce deadlocking • Lower the isolation level Guidelines for Monitoring Transactions Use the following options to monitor transactions: sys.dm_tran_database_transactions DBCC OPENTRAN Use the following strategies to reduce the impact of large transactions: Split large transactions into smaller ones Schedule large transactions to run at off-peak hours Guidelines for Troubleshooting Orphaned Transactions Identify the orphaned processes using sp_who Ignore the orphaned processes or kill them Check for any improper procedures or general faults Check whether the Inter-Process Communication (IPC) session is still active Demonstration: How To Use Locking Hints In this demonstration, you will see how to: Create a locking hint Discussion: Reducing Deadlock Errors • What are good practices to prevent deadlock errors? • How would you use object access strategy to handle deadlock errors? Lab 8: Designing a Transaction and Concurrency Strategy • Exercise 1: Determining the Database Isolation Level • Exercise 2: Determining the Order of Object Access • Exercise 3: Designing Transactions Logon Information Virtual machine NYC-SQL1 User name Administrator Password Pa$$w0rd Estimated time: 60 minutes Lab Scenario You are a lead database designer at QuantamCorp. You are working on the Human Resources Vacation and Sick Leave Enhancement (HR VASE) project that is designed to enhance the current HR system of your organization. This system is based on the QuantamCorp2008 sample database in SQL Server 2008. The main goals of the HR VASE project are as follows: • Provide managers with current and historical information about employee vacation and sick leave. • Grant view rights to individual employees to view their vacation and sick leave balances. • Provide permission to selected employees in the HR department to view and update the vacation and sick leave details of employees. • Grant the HR manager with the view and update rights to all the data. The management team has a requirement to generate performance metric for the sales staff. For this purpose, you are required to add a new function to the QuantamCorp HR VASE database that will import information from the CRM database. The management then will use statistical data to generate the performance metric report. Lab Review • Describe another way to offload the services usage registration process. • If you remove the requirement for simultaneous phone number assignment, what solution would you propose? Module Review and Takeaways • Review Questions • Real-world Issues and Scenarios • Best Practices