* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mineralogy and Crystals
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
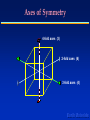
Earth Sciences: 625-102 Geology Course Presenters Dr Stephen Gallagher Prof Andrew Gleadow Dr Malcolm Wallace Prof Ian Plimer Course Coordinator Room 214 Earth Materials Earth Materials Series - Lecture Topics ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 1. Mineralogy and Crystals 2. Atomic Structures of Minerals 3. Silicate Mineralogy 4. Igneous Rocks 5. Volcanoes and volcanic rocks 6. Igneous Intrusions 7. Metamorphism 8. Contact and Regional Metamorphism 9. Conditions of Metamorphism Earth Materials 625-102 GEOLOGY Lecture 1 Mineralogy and Crystals Melbourne EarthEarth Sciences Materials Minerals and Rocks ● MINERALS - are naturally occurring inorganic chemical compounds with a specific internal structure and regular chemical composition ● ROCKS - are natural mixtures or aggregates of minerals 1-01 Earth Materials Minerals: ● are mostly crystalline with a regular atomic structure, eg Quartz, Feldspar ● are the major solid constituents of the Earth ● have physical properties which reflect their composition and atomic structure ● Silicates are the most common minerals (95% of the earth’s crust) 1-02 Earth Materials Ions and Atomic Bonding ● ● ● ● Ions are atoms with an excess positive or negative charge due to loss or gain of electrons An Ionic Bond is formed by the attraction of oppositely charged ions – eg between Na+ and Cl- in NaCl (Halite) A Covalent Bond is formed where two atoms share an electron – eg between Si4+ and O2- in the silicate unit SiO4 Most minerals share both Ionic and covalent characteristics Earth Materials Physical Properties 1 ● Crystal form 1-03 – the characteristic shape of a crystal – reflects the internal arrangement of its atoms ● Cleavage – the tendency for a mineral to split along a particular plane – cleavage occurs along layers of weak bonds ● 1-04 1-05 1-06 Fracture – appearance of broken surface when no cleavage is present – eg Quartz has a Conchoidal fracture (‘ (‘shell-like’ shell-like’) 1-07 Earth Materials Physical Properties 2 ● Hardness – – – – ● the resistance of a mineral to abrasion reflects overall strength of the atomic bonds Estimated by scratching one against another Mohs Hardness Scale Density – the mass per unit volume of a mineral – controlled both by the kinds of atoms present and especially how closely packed they are Earth Materials Physical Properties 3 ● Colour 1-08 – an obvious but variable property of a mineral – influenced by small variations in the composition ● Streak – – – ● colour of a powdered sample of a mineral seen by scratching on an unglazed porcelain plate usually more diagnostic than colour Lustre 1-09 – intensity and quality of light reflected from a mineral surface – Described as metallic, glassy, earthy, pearly etc Earth Materials Crystals ● Crystals are solid materials naturally bounded by flat faces meeting at sharp edges ● Crystalline shapes reflect the regular arrangement of their constituent atoms ● This arrangement is called the Crystal Lattice Earth Materials Crystal Symmetry ● Crystal symmetry – Crystals are usually described in terms of their Symmetry ● 1-10 Symmetry elements – Symmetry is expressed by reference to: – rotation axes – mirror planes ● Rotation axes – Axes about which a crystal can be rotated so that it occupies an exactly similar position more than once every rotation. These may be: – Two-fold (Diad ), Three-fold (Triad), Four-fold (Diad), (Tetrad) or six-fold (Hexad) Earth Materials Axes of Symmetry 4-fold axes (3) 2-fold axes (6) 3-fold axes (4) Earth Materials Mirror Planes ● Planes of Symmetry (mirror planes) – Divide a crystal into two parts which are exact mirror images of each other ● eg a Cube has 9 planes Type 2 (3) Type 1 (6) Earth Materials Crystal Systems ● There are just seven different ways in which symmetry elements can be combined ● These define seven different Crystal Systems ● All crystals belong to one of these crystal systems Earth Materials Seven Crystal Systems ● ● ● ● ● Cubic System Tetragonal Hexagonal Trigonal Orthorhombic - four Triad axes - a single Tetrad axis - a single Hexad axis - a single Triad axis or ● Monoclinic and/or ● Triclinic - three mutually perpendicular diad axes - two perpendicular mirror planes and one diad - a single diad axis - a single plane of symmetry - no planes or axes of symmetry Earth Materials REFERENCES ● Hamblin & Christiansen, Chapter 3, p.48-61 ● Skinner and Porter, Chapter 3, p. 47-53 ● Clark and Cook, Chapter 6a, 6b, 6c Earth Materials