* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Workbook 6 - Macmillan Caribbean
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
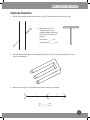
CARIBBEAN PRIMARY SCIENCE Workbook 6 David and Penny Glover David and Penny Glover This course has been written through a close This course has been written through a close collaboration collaboration between experienced teachers primary between experiencedand teachers and primary science science specialists. specialists. • Fortuna Anthony • Pamela Hunte • Nelson Longsworth • Fortuna Anthony • Pamela Hunte • Nelson Longsworth • Ryan Mongroo • Eulie Mantock • Frank•Newton Eulie Mantock • Ryan Mongroo • Frank Newton • Doltan Ramsubeik • Motielall • Dwight Steadford • DoltanSingh Ramsubeik • Moteilall Singh • Dwight Steadford CONTENTS Contents Unit 1 Sight and sound The eye Correcting eye defects Eye care and protection Optical illusions Light and materials Reflection Refraction The ear Ear problems and care Sound waves Musical instruments Sound reflection and absorption 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Unit 2 Systems in plants and animals Plants: organs and systems Plants: root systems Plants: shoot systems Leaves Flowers, fruits and seeds Body systems Skeleton Muscle power Circulation Excretion Reproductive organs Puberty 14 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Unit 3 Health Communicable disease Microbes Food preservation Vaccination Drugs Dangerous drugs Dealing with drug issues 26 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Unit 4 The environment The rainforest ecosystem Deforestation Threats to the environment Conservation The 3Rs — Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Sustainable development 33 33 34 35 36 37 38 Unit 5 Measurement and motion Measuring mass Measuring volume Types of motion Force, weight, motion and mass Energy and motion 39 39 40 41 42 43 Unit 6 Magnetism and electricity Magnetic materials Magnetic poles Making magnets Using magnets Electric circuits Circuit projects Sources of electricity Alternative energy sources Conserving electricity 44 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 Unit 7 The Earth and space What are earthquakes? Earthquakes and people How big are the planets? Observing the Universe 53 53 54 55 56 UNIT 1 SIGHT AND SOUND The eye 1. Match the words to their definitions. pupil iris cornea lens retina optic nerve The light-sensitive layer that covers the inside surface of the back of the eye.____________ The black aperture (hole) at the centre of the iris through which light passes into the eye. ____________ The nerve which carries information from the eye to the brain. ____________ The transparent disc which changes thickness to focus on objects at different distances. ____________ The coloured ring that surrounds the pupil. ____________ The outer surface of the eye. ____________ 2. Mark each of these statements as true () or false (). (a) Information from the eye travels as electrical pulses to the brain. ( ) (b) The lens focuses an image on to the cornea. ( ) (c) The image produced by the lens is upside down. ( ) (d) The point closest to the eye at which you can see clearly is called the far point. ( 3. On these diagrams of the eye draw the pupils as they would appear: (a) in bright light (b) in dim light. (a) Bright light (b) Dim light 4. Explain briefly the differences between your drawings for question 3 In bright light the pupil ______________________________________. In dim light the pupil ________________________________________. 5. Label this diagram of the interior eye. Use the words below. retina optic nerve ciliary muscles lens iris cornea 2 ) UNIT 1 SIGHT AND SOUND Correcting eye defects 1. Identify these lenses as concave or convex. 2. Draw the light rays after they have passed through the lenses. 3. Name the type of lens that concentrates light. _________________ Name the type of lens that spreads light out. _________________ 4. Match these words to their descriptions. short-sighted long-sighted Describes a person whose eyes concentrate light from distant objects too much so that the image is formed in front of the retina. Distant objects are not in focus. ______________ Describes a person whose eyes cannot concentrate light from nearby objects enough to form an image on the retina. Nearby objects are not in focus. ___________ 5. Mark each of these statements as true () or false (). (a) A short-sighted person should wear spectacles with concave lenses. ( ) (b) A long-sighted person should wear spectacles with convex lenses. ( ) (c) A concave lens works as a magnifying glass. ( ) (d) A thin convex lens concentrates light more strongly than a thicker lens. ( ) 3 UNIT 1 SIGHT AND SOUND Eye care and protection 1. Label this diagram of the exterior of the eye. eyelid eyelashes iris pupil tear duct 2. Describe briefly how the eye protects itself when: A small insect flies into it _________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Something moves towards it suddenly ____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ The Sun is very bright ___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ There is a sudden bright flash of light _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Mark each of these statements as true () or false (). You should use a matchstick to remove a piece of grit from your eye. ( ) You should never look directly at the Sun. ( ) It’s better for your eyes to turn out the room lights when you are watching TV. ( ) You should rest your eyes for a few minutes every hour when doing computer work. ( ) 4.Regular blinking spreads moisture over the surface of the eye. The moisture helps protect the eye from dust and other foreign bodies. Observe a classmate or relative as they read a book. Count the number of times they blink in 5 minutes. Calculate their blink rate in blinks per minute. Repeat the observation for different people or for one person as they do different tasks. How much do blink rates differ? What is the average blink rate? 4 UNIT 1 SIGHT AND SOUND Optical illusions 1. Which arrow passes all the way through, A or B? Check by drawing a line with a ruler. A 2. Which part of the T is longer, the top or the upright? Measure the lines with a ruler to check your answer. B Top length = _____ cm Upright length = _____ cm 3. Can you make this shape from modelling clay? Why not? (Try colouring the shape in to see why it is impossible.) 4. Which line is longer, A or B? Measure the lines to check your answer. A B A = _________ cm B = _________ cm 5 UNIT 1 SIGHT AND SOUND Light and materials 1. Match these words to their definitions. transparent translucent opaque disperse Describes a material that light does not pass through. _____________ Describes a material that allows light to pass through, but scatters the light in random direction. _____________ To separate a mixture of different light colours into a spectrum. __________ Describes a material that allows light to pass straight through it. _____________ 2. Write the names of these materials in the correct columns of the table. window glass black cloth metal milk pure water rock Transparent Translucent tissue paper air Opaque Add more materials to your table. 3. Mark each of these statements as true () or false (). (a)A mirror absorbs light. ( ) (b)Shiny metal reflects light. ( ) (c)You cannot see through a black card because it disperses light. ( ) (d)When white light is dispersed, it is separated into the colours of the rainbow. ( ) 4. Use a bright torch to compare how well different types of paper block light. Place a sheet of paper in front of the torch. Can you see the light? How many sheets of the paper are needed to block the light completely? Record your results in a table. Type of paper photocopy paper tissue paper drawing paper 6 Number of sheets to block light