* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Reproduction
Reproductive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Parthenogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
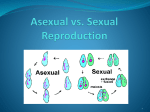
Name: Period Date Unit 3: Living Systems- Cell Reproduction Part I- Introduction Reading: skim the paragraphs and write down what you think the bold words mean. Reproduction Some organisms look and act exactly like their parent. Others share many similar traits, but they are definitely unique individuals. Some species have two parents, whereas others have just one. How an organism reproduces determines the amount of similarity the organism will have to its parent. Reproduction is the process by which organisms give rise to offspring. It is one of the defining characteristics of living things. There are two basic types of reproduction: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Each of these processes ensures that the parental generation gives genetic material, DNA, to its offspring. The process of cell division is how multicellular organisms grow and repair themselves. It is also how many organisms produce offspring. For many single-celled organisms, asexual reproduction is a similar process. The parent cell simply divides to form two daughter cells that are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent, whereas sexual reproduction produces a similar, but genetically unique offspring. In sexual reproduction, meiosis produces haploid gametes or sex cells (sperm & egg) that fuse during fertilization to produce a diploid zygote. In other words, a child inherits half of the genetic material from each parent. Take your family for example. You and your sisters or brothers may resemble your parents, but you are not identical to them. Instead, each one of you has a unique combination of characteristics inherited from both of your parents. You and your siblings result then from sexual reproduction. Vocabulary: 1. Reproduction: 2. Meiosis: 3. Asexual reproduction: 4. Sexual reproduction: 5. Zygote: 6. Gametes: Part II Guided Notes and Practice Reproduction Number of Division Process Resulting Cell Genetic makeup Parents of offspring Asexual Sexual The three important reasons for cell division are: 1) 3) , 2) and . Meiosis is the process of producing . Reproduction occurs from division of the parent cell without meiosis, gamete formation or fertilization. Mitosis is a type of reproduction that produces offspring that are parent cell. Mitosis is the type of cell division that is used for and In sexual reproduction, the offspring inherits the characteristics of parents. to the . Growth (used twice) Identical Both Gametes Repair (used twice) Asexual (used twice) Reproduction Part IV: Independent Practice- identify each example of reproduction as asexual or sexual. 1. A hen lays a fertilized egg which then hatches. 2. A starfish is cut into three pieces. After a while there are three starfishes in its place. 3. A skin cell divides to replace cells in a cut. 4. Female and male gametes are fused which results in a zygote that then divides to form an organism. Name Period Date Cell Reproduction Exit Ticket: answer the following questions. 1. What is sexual reproduction? 2. Mitosis is an example of: a. Cell Division b. asexual reproduction c. sexual reproduction d. a & b 3. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? Name Period Date Cell Reproduction Exit Ticket: answer the following questions. 4. What is sexual reproduction? 5. Mitosis is an example of: b. Cell Division b. asexual reproduction c. sexual reproduction d. a & b 6. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? Name Period Date Cell Reproduction Exit Ticket: answer the following questions. 7. What is sexual reproduction? 8. Mitosis is an example of: c. Cell Division b. asexual reproduction c. sexual reproduction 9. What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? d. a & b