* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Potential and Kinetic Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
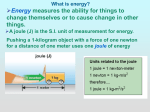
Potential and Kinetic Energy What is Energy Energy –is the ability to do WORK!!! Two types of energy –Potential Energy –Kinetic Energy Potential and Kinetic Energy Animation http://www.teachersdomain.org/resource/h ew06.sci.phys.maf.rollercoaster/ Potential Energy 1. Energy at rest 2. Stored Energy 3. Higher the object - greater the potential energy Potential Energy Which boulder has the least amount of potential energy and Why? Types of Potential Energy Elastic potential energy – Energy stored by things that stretch or compress Gravitational potential energy (GPE) – The amount of GPE an object has depends on its mass, the acceleration due to gravity, and its height above ground. Quick Write: Elastic Potential Energy Explain how this rubber band has elastic potential energy! Quick Write: Potential Energy When is the spring having potential energy? Brain Pop Movie: Potential Energy http://glencoe.mcgraw- hill.com/sites/0078802482/student_view0/ brainpop_movies.html Calculating potential energy PEg = m*g*h or PEg =Fw*h Units PEg = gravitational potential energy m = mass g = acceleration due to gravity h = height J or Nm kg m/sec2 m Fw=Force of Weight N NOTE: Units for kinetic and potential energy are J (joules). 1 joule = 1 kg × m2/sec2 = 1 Nm FLASH CARD PE g = m g h PE g =F w h PE g m g h Gravitation Potential Energy Units PE - gravitational potential energy g Fw - weight N h - height m m - mass g - acceleration due to gravity J kg m/sec2 Potential Energy Problems 1. A weight lifter lifts a 120 kg mass from the floor to a position above his head, 2.5 meters above the floor. What is the potential energy expressed by the weight? PE= m g h PE = (120)(9.8)(2.5) PE= 2940 J The potential energy of the weight is 2940 J. 2. What is the potential energy of a 90 N boat before it falls from the top of a 30 m waterfall? PE = ? Fw = 90 N h = 30 m PE = Fw*h = (90 N) (30 m) PE = 2700 N • m = 2700J If the acceleration on a new planet is 5.2 m/s2 and a meteor is sitting on a hilltop at 100 m with 650 J of PE, then what is the mass of the meteor? Kinetic Energy 1. Energy of motion 2. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on its mass and its velocity Calculating Kinetic Energy KE = ½ mv2 KE = kinetic energy m = mass v = velocity Units J or Nm kg m/sec Example: What is the kinetic energy of a 120 kg object moving at 30 m/sec? KE = ½ mv2 m = 120 kg v = 30 m/sec KE=? KE = ½ (120 kg)(30 m/sec)2 KE = (60 kg)(900 m2/sec2) = 54000 kg m2/sec2 = 54000 J Quick Writes: Kinetic Energy Which one has the highest KE? Which one has the least KE? 80 km/h 50 km/h 80 km/h FLASH CARD 2 KE = m v 2 KE m= 2 v v = 2KE m Kinetic Energy Units KE - kinetic energy J v - velocity m/sec m - mass kg Brain Pop Movie: Kinetic Energy http://glencoe.mcgraw- hill.com/sites/0078802482/student_view0/ brainpop_movies.html Potential and Kinetic Energy Practice Problems 1. A 100kg rock sets at the top of a 50 m cliff. What is the rocks potential energy? 2. A 70 kg rock is falling at 30 m/sec. What is its kinetic energy? 3. A 315 kg object sets at the top of a 50 m building. What is its potential energy? 4. A car has 3600 J of kinetic energy and is going 3 m/sec. What is its mass? Work 1. Transfer of energy through motion. 2. The force must act in the same direction as the motion. 3. Force exerted through a distance Example 1: Lifting a log is work. Log moves in the direction the force is applied Example 2: Carrying a log is not work. Log is held up, but moves forward, therefore no work is done on the log. Calculating Work W = F*d W = work F = force d = distance Units J N m Example: How much work is done when 87 kg mass is lifted 1.2 m? W=Fd d = 1.2 m FW = mg m = 87 kg g = 9.8 m/sec2 W = mgd W = (87 kg)(9.8 m/sec2)(1.2 m) = 1023 J FLASH CARD W=Fd W F d Work Units W - work J F - force N d - distance m Work Practice Problems 1.You lift 19.0 kg of books 1.3 m. How much work did you do? 2.A carpenter lifts a 80 kg beam 1.4 m and carries it 9 m. How much work is done during the lift? How much work is done on the beam during the carry? 3.If 19.6 J are used to move 16 N object, how far was the object moved? 4.If 1040 J are used to move a 76 N object, how far was it moved? 5.If 763 J are used to move an object 20 m, how much force was used? 6.If 70043 J are needed to move an object 73 m, how much force was needed?