* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5th Grade Chapter 3 Notes Continued
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
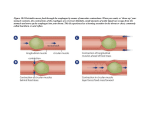
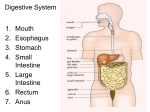
5th Grade Chapter 3 Notes Continued Respiratory, Digestive and Urinary systems Respiratory System Mucus • ____________ is a sticky, thick fluid that traps dust, germs, and other things that may be in the air. • 1. Air enters through the _______or ________. nose mouth • 2. __________warm and moisten the air. Sinuses • 3. With its hairs and layer of ________, the nose Mucus traps dust and germs. • 4. Air passes from the sinus to the back of the throat and into the _________. Larynx Vocal Cords • 5. The larynx contains the ______________. How Air Travels into and Through your Body Continued • 6. Trachea ___________ is a tube that carries air from the larynx to the lungs. • 7. The trachea leads to two branches called Bronchi Lungs ___________that go into the _______. • 8. In the lungs, these tubes branch into bronchioles smaller and smaller tubes called__________. Asthma ___________is a disease in which these tubes may become narrowed. This prevents air from easily traveling through the lungs. How Air Travels into and Through your Body Continued • 9. The bronchioles end in clusters of tiny thinwalled pouches or ________ in the lungs Air sacs oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood. Air sacs are also called alveoli _______. diaphragm • 10. The _________is a dome-shaped muscle that forms the bottom of the chest area muscle _________it moves _______ and gets muscle down flatter _______. Cilia • _______are tiny, hairlike Cilia structures on cells in the linings of many parts of the respiratory system, such as the trachea. - Cilia help clean air by waving __________ very rapidly - pushes dirty __________ out of the _________ mucuc Lungs to the _________, where it is Throat swallowed. Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working Together • Respiratory and circulatory systems work oxygen to the cells. together to get ________ • The respiratory system gets the oxygen to tiny Air sacs inside your ______. lungs ________ • The _______picks up the oxygen there and blood cells carries it to all your _____. • In the _______: Air sacs – __________ leaves the lungs and enters the blood. oxygen Carbon dioxide leaves the blood and enters the – _______________ lungs. Output / Input • Output of one system is the input of the other system. • Several systems working together to make sure your cells get oxygen - EXAMPLE Carbon dioxide When you hold your breath, ____________ brain builds up in your blood. Your _______ can sense this. Your brain sends a message to the ____________ and rib _________ telling them diaphragm muscles to _________.. breathe Digestive System changed • Food has to be ___________ before your cells can use it - broken down into very small materials. blood • Then the food can enter the __________ to get to your ________. cells organs • Digestion takes many ________ working together. Each organ has __________ that structures help it do its part of the job. Mouth and Esophagus chewing • _____________ is the first step of digestion makes food small enough to swallow, and it makes the job of the rest of the digestive system easier. esophagus • The ____________ is a tube that carries food to the stomach - pushes food to the stomach by muscles squeezing its rings of __________ in a pattern. • Food travels through the esophagus to the stomach in about two or three ___________. seconds Stomach • ___________ stomach - At the bottom of your esophagus - a tight round muscle. • When you swallow, this muscle relaxes and opens to let food into your stomach. Then the muscle closes to keep the food from moving back into your esophagus. • Stomach's walls can stretch _______ to store all the food from a meal. • The stomach produces ________ that help to digest foods. fluids squeeze • As strong muscles in the stomach's walls __________, these fluids mix with the food. • After the food becomes a soupy _________, it is ready to paste leave your stomach. Intestines • The stomach squeezes the partly digested food into a Small Intestine narrow, winding tube called the _____________ Liver pancreas • __________ and _____________are organs that send chemicals to your small intestine to help digest food. • When digestion is finished, the particles of digested food can move into ________________ that are in the Blood vessels walls of your intestine. • Tiny finger-shaped structures called _________are villi found all over the inside walls of the small intestine. Surface area • Villi give the small intestine more ______________ to absorb food. Large Intestine • At the end of the ________________, some food Small intestine that cannot be digested remains. • This food waste moves to a wider tube called the Large intestine - also known as the ______. colon ______________ Helpful bacteria live here. water • The large intestine takes _________ and _______from the wastes making the waste more salts solid. • Finally, muscles squeeze to push the ________ waste out of the body. Urinary System • ___________________ - rid the body of wastes that are in Urinary system the blood. • ______________ are a pair of organs that remove wastes kidneys from your blood. They are on either side of your ____________, just under your lowest ribs. backbone • When wastes are filtered out of the blood, many other materials also leave the blood - water, salt, calcium, nutrients, and other chemicals your body needs. • The ____________ has to put the right amount of these kidney materials back into the blood to keep the body healthy. • Kidneys help keep the amounts of these materials from regulates getting too high or too low - ____________ Urine • Mix of wastes and water is urine ___________. • A tube _________ carries urine away from the kidneys to the _______________. Urinary bladder bladder • ____________stores urine until it leaves the body. • The kidneys are not the only organs that get rid of cells’ wastes. – _______________ Carbon dioxide is a waste product removed by the lungs. – ______________Sweat Glands also release a small amount of cells’ wastes in sweat.