* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 36
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
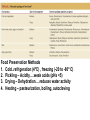
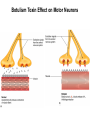
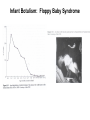
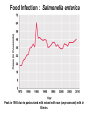
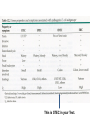
Chapter 36 Food and Foodborne Microbial Diseases Food Classification Food Preservation Methods 1. Cold..refrigeration (4oC) , freezing (-20 to -80o C) 2. Pickling – Acidity….weak acids (pHs <5) 3. Drying – Dehydration….reduces water activity 4. Heating – pasteurization, boiling, autoclaving a is Ok, something wrong b to d Food Preservation Methods 1. Cold..refrigeration (4oC) , freezing (-20 to -80o C) 2. Pickling – Acidity….weak acids (pHs <5) 3. Drying – Dehydration….reduces water activity 4. Heating – pasteurization, boiling, autoclaving 5. High Pressure Processing..up to 100,000 lb/in2 6. Chemical Preservatives. 7. Irradiation. International Symbol for Radiated Foods Clicker Question: Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Clicker Question: Staphylococcus aureus Toxins TOXIN ACTION Hemolytic toxins Animal cell lysis Hyaluronidase Breakdown of hyaluronic acid Coagulase Fibrin Formation Staphylokinase Fibrin Breakdown Leukocidin Kills WBC’s. Epidermolytic toxin Exfolation Enterotoxins–A,B,C,D,E,F. Emetic Response Enterotoxins Small: 26-30 kD Heat Stable – can resist boiling (unlike the bacterium!!) Toxic Dose: as low as 1ng, usual is 1-5 μg (cells >105/g) Emetic Response Mechanism 1. Direct on vagus nerve and sympathetic system. 2. Super Antigen (IL-2 mimics this response). 3. Both. Diarrhea Mechanism – unknown, no c-AMP involvement Incubation Period to Emesis Classic Staph Food Poisoning: Cafeteria of a College Dormitory…to the College Clinic (69 cases) Foods Involved + Symptoms Botulism : Clostridium botulinum Review of Endospore Location Clostridium botulinum Bacillus pasteuri Bacillus cereus Terminal Spore Subterminal Spore Central Spore Clostridium Fermentations – From Glucose What Can’t Clostridium spp Ferment? In what types of Foods can C. botulinum grow? Clicker Question: Botulism Toxin : Flaccid Paralysis Botulism Toxin Effect on Motor Neurons Infant Botulism: Floppy Baby Syndrome Wound Botulism Food Infection : Salmonella enterica Peak in 1985 due to pasteurized milk mixed with raw (unprocessed) milk in Illinois. Salmonella enterica : over 1,400 Serovars Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is usually abbreviated: Salmonella Typhi or S. Typhi. Typhoid Fever has a very low incidence in USA, only in people acquiring the disease outside USA. However, all the other strains (servoars) cause the data in the preceding figure: salmonellosis. Reservoirs Salmonella Taxonomy – Part 1 Gram Negative rods, facultative, catalase pos, oxidase neg Closely related to Escherichia coli Serogroups: 1941 – 100 serogropus of S. enterica 1964 – 900 serogroups now - > 2,400 serogroups. -based on H and O antigens. IMViC -+-+, Lactose neg, all H2S pos. H2S Production on TSI Triple Sugar Iron Agar 1% sucrose 1% lactose 0.1% glucose Na-thiosulfate ferrous sulfate Tryptone, Peptone Yeast Extract agar Phenol red pH 7.3 Left to Right: Control (uninoculated); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Escherichia coli; Salmonella Typhimurium; Shigella flexneri Clicker Question: H2S Production on TSI Triple Sugar Iron Agar 1% sucrose 1% lactose 0.1% glucose Na-thiosulfate ferrous sulfate Tryptone, Peptone Yeast Extract agar Phenol red pH 7.3 Left to Right: Control (uninoculated); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Escherichia coli; Salmonella Typhimurium; Shigella flexneri Clicker Question: Salmonella colonies XLT4 agar Clicker Question: Enteritis (Salmonellosis) Disease Characteristics 1. Incubation Period – mostly 6hrs to 2 days. ID50 = 10 to 106 cells 2. Symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal cramps, mild fever, nausea, vomit, chills headache --- duration 2 – 3 days. 3. Therapy – non needed, antibiotic treatment gives no benefit. Eat yoghurt! 4. Carrier state for a few months from bacteria in ileum and colon. Adherence – mannose binding pili Receptor mediated endocytosis multiply intra-cellularly and released to lamina propera involvement of inflammatory cells and release of prostaglandins increase in c-AMP and diarrhea (usually not toxin associated like cholera, but a few have enterotoxins). Salmonella World Wide Clicker Question: Infective Dose Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention Diagnosis: Symptoms, culture organisms from fecal sample .. and suspected food. Isolates sent to other labs (Food Net and Pulse Net) that use molecular methods of ID such as pulsefield gel electrophoresis of DNA fragments… pin points the source of the outbreak. Treatment: used to shorten course of disease and reduce the carrier state…but multiple drug resistant Salmonella is a significant clinical problem. Prevention: cook your food. Infected individuals are banned (in some states) from work as food handlers until their feces are negative for Salmonella on three separate cultures. E. coli can be both non-pathogenic and pathogenic. Normal human feces has 107 E. coli / gram Feces have ~ 1012 bacteria / gram Is E. coli dominant ? How have some E. coli become pathogenic? There are several major types of E. coli pathogens => This is STEC in your Text.