* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New Hampshire EMT-Intermediate Pharmacology
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
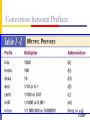
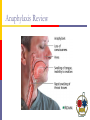
New Hampshire EMT-Intermediate Pharmacology New Hampshire Division of Fire Standards & Training and Emergency Medical Services EMT-Intermediate Medications Epinephrine – cardiac Epinephrine – anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Drug Chemical agents used in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of disease. Pharmacology The study of drugs and their interactions with the body. Drugs are NOT magical. They cannot alter the body systems qualitatively, only quantitatively Names Chemical Name Generic Name A name suggested by the manufacture and confirmed by the U.S. Adopted Name Council Official Name Most detailed, chemical description FDA’s official name Brand Name A manufacturer’s trade name or proprietary name Source Plants Animal Insulin (bovine & porcine) Mineral Purple foxglove = digitalis Deadly nightshade Atrope belladonna plant = Atropine Calcium Chloride, magnesium sulfate Laboratory (synthetic) Fentanyl Patient’s Rights Right Right Right Right Right Right medication dose time route patient documentation Pharmacodynamics Drug Receptor Interactions Agonist Antagonist Affinity Efficacy Types of receptors Beta Alpha Other definitions you need to know Agonist: drug that binds to a receptor and causes it to initiate the expected response Antagonist: drug that binds to a receptor but does not cause it to initiate the expected response Factors altering drug responses Age Body mass Sex Environmental milieu Time of administration Pathologic state Genetic factors Psychological factors Responses to Drug Administration Allergic reaction: hypersensitivity Idiosyncrasy: unique to the individual; different than seen or expected in the general population Cross tolerance: tolerance of a drug after admin of a different drug. Morphine & other opioids Tachyphylaxis: rapid tolerance. Typically w/ sympathetic agonists (decongestant & bronchodilation agents) Cumulative Effects: increased effects with several doses Drug interaction: one drug alters the response to another Synergism: 2 drugs given give greater response than their sum. 1+1=3 Predictable Responses Desired action Side effects Definitions Metric System – system of weights & measures widely used in science & medicine Based on units of 10 Apothecary System – antiquated system of measures & weights used in early medicine Weights & Measures Metric System has 3 basic units of measurements For Mass: the gram (G) For Length: the meter (M) For Volume: the liter (L) All metric units are derived from these 3 base units Conversion between Prefixes Weights & Measures – Metric Kilogram(kg)= 1,000 grams Gram (gm) = 1,000 milligrams Decigram (dl)= 100 mg or 0.1 gm Milligram (mg)= 1,000 micrograms or 0.001 gm Microgram (mcg or μg)= 1/1,000,000 or 0.000001 1 Liter (l)= 1,000 milliliters (ml) ml = cc Weights & Measures – Apothecary 1 grain = 60 milligrams ¼ grain = 15 milligrams Household 1 teaspoon = 5 ml 1 tablespoon = 15 ml 1 ounce = 30 ml 8 ounces = 240 ml 1 quart = 946 ml Weights & Measures You need to know how to Add, subtract, multiply & divide decimals Convert from liters <-> milliliters, etc. Calculate dosages If in doubt, carry a calculator, find a chart Have your partner double check you It’s better to double check than to make a mistake!!! Buy & use medication math calculation books Anaphylaxis Review Thiamine (B1) Thiamine (B1) Class Water-soluble vitamin Description Required for the synthesis of thiamine pyrophosphate, a coenzyme required in carbohydrate metabolism. Aids in energy (carbohydrate) metabolism Enables normal functioning of the nervous system Necessary for proper functioning of the heart Thiamine (B1) Indications Hypoglycemia, in the presence of chronic alcoholism, alcohol intoxication, or malnourishment, administer Contraindications do not use with substances that yield alkaline solutions, such as citrates, barbiturates, carbonates, or erythromycin lactobionate IV Thiamine (B1) How Supplied Dose 100 mg IVP Onset 100 mg vial varies Duration varies Thiamine (B1) Side Effects Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis Special Consideration Use with caution during lactation. Intranasal Administration