* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scarcity
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of digitization wikipedia , lookup
Comparative advantage wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of the labour theory of value wikipedia , lookup
Microeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cambridge capital controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heckscher–Ohlin model wikipedia , lookup
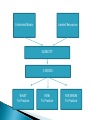
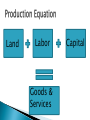
1) 2) Grab a textbook and: write down the new vocabulary words for Chapter 2 and their definitions. pick one word to explain to our classmates Chapter 2 The fundamental economic problem facing all societies is Scarcity. Scarcity is the condition that results in society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have. Even goods and services are scarce, because the resources we need to produce them are scarce A NEED is a basic requirement for survival!!! ◦ Food ◦ Water ◦ Shelter etc. A WANT is a way of expressing a need WANTS satisfy needs WANTS are broader than NEEDS Shortage Lack of something that is desired Less of a good or service available than what people are willing to pay at the current price Shortage lasts until more produced or desire ends Scarcity Simply not enough of everything to satisfy all of our wants Permanent condition Scarcity and Shortage Handout/Activity By inputs, outputs and the production equation Inputs = scarce resources that go into the process Outputs = goods and services produced by these resources Production Equation = Land + labor + Capital = Goods and Services *Entrepreneurship? Unlimited Wants Limited Resources SCARCITY CHOICES WHAT To Produce HOW To Produce FOR WHOM To Produce Land ◦ “Gifts of Nature” ◦ Natural resources not created by human effort ◦ Examples: Deserts Fertile fields Forests Animals, birds Sunshine Climate ◦ Includes both renewable and nonrenewable resources Labor ◦ The time and effort people devote to producing goods and services in exchange for wages ◦ Includes both physical and mental labor ◦ Human capital = knowledge and skill gained from education or training ◦ Strong correlation between country’s level of human capital and standard of living Capital ◦ Physical capital or capital goods = Tools, equipment, factories or buildings used in production of goods and services ◦ Financial Capital = money to invest in stocks, bonds, real estate, or businesses to produce future wealth Land Labor Goods & Services Capital Entrepreneurs ◦ Some economists consider Entrepreneurship the 4th factor of production ◦ A risk-taker in search of profits ◦ Innovative workers who are responsible for economic change Start new businesses Create new products Innovative use of resources When the four factors of production (land, capital, labor, entrepreneurship) are present, PRODUCTION, or the process of creating goods and services, can take place IMPORTANT!!! – Everything we produce requires all four factors Factors of production “I, Pencil” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IYO3tOq DISE Scarcity, Choices, and Exchange Anyone like Star Wars? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NpdZSdzymk