* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Maintaining a healthy body weight
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Body mass index wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Malnutrition wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
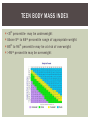
MAINTAINING A HEALTHY BODY WEIGHT Chapter 6 PHYSICAL HEALTH RISKS Excessive weight disabilities -diseases linked or resulting directly from long term overweight or obesity Breathing difficulties Sleep apnea Sleep Apnea Bone and joint problems Being over fat increases the risk of the following diseases: High blood pressure High cholesterol Heart disease Some cancers IMPAIRED GLUCOSE TOLERANCE AND DIABETES Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) -This is a disorder in which blood glucose levels become elevated. IGT is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes IGT and type 2 diabetes are increasing in teens and youth Insulin- a hormone produced by the pancreas that converts sugar to energy. UNDERWEIGHT Underweight- having a BMI that is below the fifth percentile for ones age Increase risk of colds and pathogens Undernourished, causes: Fatigue Irritability Anemia- disease associated with lack of iron Underweight teens should eat 3 -4 nutrient dense, high calorie foods meals per day TEEN BODY MASS INDEX <5 th percentile- may be underweight Above 5 th to 84 th percentile range of appropriate weight 85 th to 94 th percentile may be at risk of overweight >95 th percentile may be overweight EATING DISORDERS Eating disorders- psychological illnesses that cause people to under eat, overeat, or practice other dangerous nutrition related behaviors. Typically driven by metal or emotional factors Poor body image Social or family pressures Perfectionism Depression Substance abuse ANOREXIA NERVOSA Anorexia nervosa- an eating disorder in which a person abnormally restricts calorie intake. Can result in: serious malnutrition Stop menstruating Sterility Low bone density Heart problems death Common indicators: sudden massive weight loss, lying about eating, denying hunger, preoccupation with food or calories, exercise addiction, believing he/she is overweight Male Anorexia BULIMIA NERVOSA Bulimia Nervosa- an eating disorder in which people overeat and the force themselves to purge. Exercise Bulimia- purging calories though exercise Miss important events to exercise Do not allow for recovery Can cause: Dehydration Osteoporosis Kidney damage Irregular heart beat Tissue damage from purging Nutrition deficiencies NUTRITION MY THS AND FAD DIETS Myth: consuming large amounts of protein and lif ting weights are the best ways to increase the size of your muscles Fact: EXTRA protein in your diet is not needed to increase muscle size and strength Myth: Vegetarianism is much healthier and better for exercise performance than a diet that includes animal protein Fact: It can be a healthy lifestyle, but you have to know how to combine foods for complete proteins Myth: it is easy to lose one pound of fat by burning 3,500 calories through exercise alone Fact: best to use a combination of exercise and diet Through exercise alone to burn 1000 calories you must run 8 -10 miles in one hour FAD DIETS Fad diets- center on eating one type of food, claims eating whatever you want, requires purchase of special pills or equipment High-Protein Diets- eliminating carbohydrates from your diet. Increase risk of dehydration (stress on kidneys) Risk of calcium loss Digestive issue due to lack of fiber Diet Pills Baseball Story WEIGHT CYCLE DIET AND PHYSICAL ACTIVIT Y FOR WEIGHT CONTROL Adjust calorie intake and expenditure based on your needs Work 30-60 minutes per day or 225 minutes per week Allow plenty of time for results Reward yourself in a positive way (other than food) Continue to update short term goals along the way