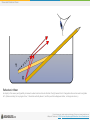
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Boundless Study Slides
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Coherence (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Boundless Lecture Slides Available on the Boundless Teaching Platform Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless Teaching Platform Boundless empowers educators to engage their students with affordable, customizable textbooks and intuitive teaching tools. The free Boundless Teaching Platform gives educators the ability to customize textbooks in more than 20 subjects that align to hundreds of popular titles. Get started by using high quality Boundless books, or make switching to our platform easier by building from Boundless content pre-organized to match the assigned textbook. This platform gives educators the tools they need to assign readings and assessments, monitor student activity, and lead their classes with pre-made teaching resources. Using Boundless Presentations The Appendix The appendix is for you to use to add depth and breadth to your lectures. You can simply drag and drop slides from the appendix into the main presentation to make for a richer lecture experience. Get started now at: http://boundless.com/teaching-platform Free to edit, share, and copy Feel free to edit, share, and make as many copies of the Boundless presentations as you like. We encourage you to take these presentations and make them your own. If you have any questions or problems please email: [email protected] Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com About Boundless Boundless is an innovative technology company making education more affordable and accessible for students everywhere. The company creates the world’s best open educational content in 20+ subjects that align to more than 1,000 popular college textbooks. Boundless integrates learning technology into all its premium books to help students study more efficiently at a fraction of the cost of traditional textbooks. The company also empowers educators to engage their students more effectively through customizable books and intuitive teaching tools as part of the Boundless Teaching Platform. More than 2 million learners access Boundless free and premium content each month across the company’s wide distribution platforms, including its website, iOS apps, Kindle books, and iBooks. To get started learning or teaching with Boundless, visit boundless.com. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Waves Other Waves Mathematics and Waves Wave Speed Energy in Waves Boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_c hapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=pow erpoint&utm_medium=direct&utm_source=boundless Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves (continued) Wave Behavior and Interaction Standing Waves on a String Waves on Strings Boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_c hapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=pow erpoint&utm_medium=direct&utm_source=boundless Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves Waves • Waves • Transverse Waves • Longitudinal Waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves Waves • A wave can be thought of as a disturbance or oscillation that travels through space-time, accompanied by a transfer of energy. • The direction a wave propagates is perpendicular to the direction it oscillates for transverse waves. • A wave does not move mass in the direction of propagation; it transfers energy. Wave motion View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-101/waves-387- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves Transverse Waves • Transverse waves oscillate in the z-y plane but travel along the x axis. • A transverse wave has a speed of propagation given by the equation v = fλ. • The direction of energy transfer is perpendicular to the motion of the wave. Sine Wave View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-101/transverse-waves-388- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves Longitudinal Waves • While longitudinal waves oscillate in the direction of propagation, they do not displace mass since the oscillations are small and involve an equilibrium position. • The longitudinal 'waves' can be conceptualized as pulses that transfer energy along the axis of propagation. • Longitudinal waves can be conceptualized as pressure waves characterized by compression and rarefaction. Longitudinal Waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-101/longitudinal-waves-389- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Other Waves Other Waves • Water Waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Other Waves Water Waves • The particles which make up a water wave move in circular paths. • If the waves move slower than the wind above them, energy is transfered from the wind to the waves. • The oscillations are greatest on the surface of the wave and become weaker deeper in the fluid. Water waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/other-waves-102/water-waves-390- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Mathematics and Waves Mathematics and Waves • Mathematical Represenation of a Traveling Wave • Energy, Intensity, Frequency, and Amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Mathematics and Waves Mathematical Represenation of a Traveling Wave • Any function u(x,t) satisfying [Equation 1] is a solution the wave equation. To solve this new equation, we introduced new variables [Equation 2]. Equation 1 View on Boundless.com Wave Equation in Two Dimensions View on Boundless.com Equation 2 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/mathematics-and-waves-103/mathematical-represenation-of-a-traveling-wave-391- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Mathematics and Waves Mathematical Represenation of a Traveling Wave • The solutions of the 1D wave equation are sums of a left traveling function and a right traveling function. • The wave function is further determined by taking additional information, usually given as boundary conditions and some others. Wave Equation in Two Dimensions View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/mathematics-and-waves-103/mathematical-represenation-of-a-traveling-wave-391- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Mathematics and Waves Energy, Intensity, Frequency, and Amplitude • The energy effects of a wave depend on the amplitude and duration (time) of the wave. Waves can also be concentrated or spread out. Considering all these factors, intensity is defined as power per unit area. • In the classical wave theory, energy of a wave doesn't depend on the frequency of the wave. However, the energy of individual photons in a beam is determined by the frequency of the beam. • Wave's energy is directly proportional to its amplitude squared. Earthquake Destruction View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/mathematics-and-waves-103/energy-intensity-frequency-and-amplitude-392- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Speed Wave Speed • Wavelength, Freqency in Relation to Speed Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Speed Wavelength, Freqency in Relation to Speed • The wavelength is the spatial period of the wave. • The frequency of a wave refers to the number of cycles per unit time and is not to be confused with angular frequency. • The phase velocity can be expressed as the product of wavelength and frequency. Frequencies of different sine waves. View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-speed-104/wavelength-freqency-in-relation-to-speed-393- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Energy in Waves Energy in Waves • Energy Transportation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Energy in Waves Energy Transportation • Waves which are more massive transfer more energy. • Waves with greater velocities transfer more energy. • Energy of a wave is transported in the direction of the waves transportation. Water Wave View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/energy-in-waves-105/energy-transportation-394- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Wave Behavior and Interaction • Superposition and Interference • Reflection and Transmission • Standing Waves and Resonance • Harmonic Wave Functions • Refraction • Diffraction Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Superposition and Interference • The disturbances of waves are superimposed when they come together—a phenomenon called superposition. • As a result of superposition of waves, inteference can be observed. Interference is an effect caused by two or more waves. Waves can interfere constructively or destructively. • The superposition of most waves produces a combination of constructive and destructive interference and can vary from place to place and time to time. Complex Pattern of Waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/superposition-and-interference-395- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Reflection and Transmission • Reflection is a wave phenomenon that changes the direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. • At the boundary, a wave must be continuous and there should be no kinks in it. • By imposing boundary conditions, we can solve wave equation and get the form of the waves. Reflection and transmission coefficients are defined as ratio of reflected/transmitted amplitudes and the incoming amplitude. Partial Transmittance and Partial Reflectance View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/reflection-and-transmission-396- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Standing Waves and Resonance • If two waves with the same amplitude and wavelength travel in opposite directions they alternate between constructive and destructive interference. The resultant looks like a wave standing in place and, thus, is called a standing wave. • Nodes are points of no motion in standing waves. An antinode is the location of maximum amplitude of a standing wave. • During an earthquake, buildings with a certain height may collapse more easily. This occurs when the building height matches the condition for setting up a standing wave for that particular height. Standing Wave View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/standing-waves-and-resonance-397- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Harmonic Wave Functions • We represent harmonic wave motion in terms of either harmonic sine or cosine function: [Equation 3]. Equation 3 View on Boundless.com Harmonic Waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/harmonic-wave-functions-398- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Harmonic Wave Functions • k and ω in the harmonic wave functinon are related to wavelength and period as follows: [Equation 4]. Equation 4 View on Boundless.com Harmonic Waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/harmonic-wave-functions-398- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Harmonic Wave Functions • The speed of a harmonic wave is given by ω/k. Harmonic Waves View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/harmonic-wave-functions-398- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Refraction • Refraction is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy and momentum. Due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed but its frequency remains constant. Refraction in Water View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/refraction-399- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction • Refraction is described by Snell's law, which states that for a given pair of media and a wave with a single frequency, [Equation 5]. Equation 5 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/refraction-399- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction • An object partially immersed in water looks bent due to refraction. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/refraction-399- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Wave Behavior and Interaction Diffraction • Diffraction is a wave phenomenon. It occurs with all waves, including sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves such as visible light, X-rays and radio waves. • Diffraction effects are generally most pronounced for waves whose wavelengths are roughly similar to the dimensions of the diffracting objects. • The effects of diffraction are often seen in everyday life. All these effects are a consequence of the fact that light propagates as a wave. Intensity Pattern View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/wave-behavior-and-interaction-106/diffraction-400- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves on a String • Standing Waves on a String Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves on a String • The reflected wave is inverted from the incident wave when a transverse wave on a string is fixed at the end point. The reflected wave is not inverted from the incident wave when a transverse wave on a string is free at the end point. • A standing wave occurs when an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string. • A standing wave contains nodes (points that remain flat due to the destructive interference) and antinodes (points with maximum oscillation due to the constructive interference). • Every point in the string oscillates up and down and the amplitude of the oscillations depends on the location of the point. Free End Reflection View on Boundless.com • A standing wave has some points that remain flat due to destructive interference. These are called antinodes. • The points on a standing wave that have reached maximum oscillation do so from constructive interference, and are called nodes. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/standing-waves-on-a-string-107/standing-waves-on-a-string-401- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings Waves on Strings • The Speed of a Wave on a String • Reflections Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics?campaign_content=book_5869_chapter_11&campaign_term=Physics&utm_campaign=powerpoint&utm_medium=di rect&utm_source=boundless Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings The Speed of a Wave on a String • The type of wave that occurs in a string is called a transverse wave. In a transverse wave, the wave direction is perpendicular the the direction that the string oscillates in. Figure 1 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-on-strings-108/the-speed-of-a-wave-on-a-string-402- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings • The period of a wave is indirectly proportional to the frequency of the wave: [Equation 6]. Equation 6 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-on-strings-108/the-speed-of-a-wave-on-a-string-402- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings • The speed of a wave is proportional to the wavelength and indirectly proportional to the period of the wave: [Equation 7]. Equation 7 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-on-strings-108/the-speed-of-a-wave-on-a-string-402- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings • This equation can be simplified by using the relationship between frequency and period: [Equation 8]. Equation 8 View on Boundless.com Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-on-strings-108/the-speed-of-a-wave-on-a-string-402- Waves and Vibrations: Waves > Waves on Strings Reflections • When a transverse wave on a string is fixed at the end point, the reflected wave is inverted from the incident wave. When a transverse wave on a string is free at the end point, the reflected wave is not inverted from the incident wave. • A standing wave occurs when an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string. • The points in a standing wave that appear to remain flat and do not move are called nodes. The points which reach the maximum oscillation height are called antinodes. • Every point in the medium containing a standing wave oscillates up and down and the amplitude of the oscillations depends on the location of the point. Transverse Wave View on Boundless.com • A standing wave has some points that remain flat due to destructive interference. These are called antinodes. • The points on a standing wave that have reached maximum oscillation do so from constructive interference, and are called nodes. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/alternative-to-college-physics-4th-giambattista-alan-0071317945-9780071317948/waves-and-vibrationswaves-11/waves-on-strings-108/reflections-403- Appendix Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Key terms • amplitude The maximum absolute value of some quantity that varies. • boundary condition A set of restraints at the boundaries, used to solve a differential equation. • boundary condition A set of restraints at the boundaries, used to solve a differential equation. • compression to increase in density; the act of compressing, or the state of being compressed; compaction • constructive interference Occurs when waves interfere with each other crest to crest and the waves are exactly in phase with each other. • constructive interference Occurs when waves interfere with each other crest to crest and the waves are exactly in phase with each other. • crest The ridge or top of a wave. • destructive interference Occurs when waves interfere with each other crest to trough (peak to valley) and are exactly out of phase with each other. • destructive interference Occurs when waves interfere with each other crest to trough (peak to valley) and are exactly out of phase with each other. • direction of propagation The axis along which the wave travels. • direction of propagation The axis along which the wave travels. • energy A quantity that denotes the ability to do work and is measured in a unit dimensioned in mass × distance²/time² (ML²/T²) or the equivalent. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • frequency The quotient of the number of times n a periodic phenomenon occurs over the time t in which it occurs: f = n / t. • group velocity The propagation velocity of the envelope of a modulated travelling wave, which is considered as the propagation velocity of information or energy contained in it. • interference An effect caused by the superposition of two systems of waves, such as a distortion on a broadcast signal due to atmospheric or other effects. • interference An effect caused by the superposition of two systems of waves, such as a distortion on a broadcast signal due to atmospheric or other effects. • Longitudinal Running in the direction of the long axis of a body. • medium The material or empty space through which signals, waves or forces pass. • oscillate To swing back and forth, especially if with a regular rhythm. • phase velocity The velocity of propagation of a pure sine wave of infinite extent and infinitesimal amplitude. • photoelectric effects In photoelectric effects, electrons are emitted from matter (metals and non-metallic solids, liquids or gases) as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation. • plane wave A constant-frequency wave whose wavefronts (surfaces of constant phase) are infinite parallel planes of constant peak-to-peak amplitude normal to the phase velocity vector. • power A measure of the rate of doing work or transferring energy. • rarefaction a reduction in the density of a material, especially that of a fluid Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • refractive index The ratio of the speed of light in air or vacuum to that in another medium. • resonance The increase in the amplitude of an oscillation of a system under the influence of a periodic force whose frequency is close to that of the system's natural frequency. • Restoring force If the system is perturbed away from the equilibrium, the restoring force will tend to bring the system back toward equilibrium. The restoring force is a function only of position of the mass or particle. It is always directed back toward the equilibrium position of the system.An example is the action of a spring. An idealized spring exerts a force that is proportional to the amount of deformation of the spring from its equilibrium length, exerted in a direction to oppose the deformation. Pulling the spring to a greater length causes it to exert a force that brings the spring back toward its equilibrium length. The amount of force can be determined by multiplying the spring constant of the spring by the amount of stretch. • simple harmonic motion (SHM) — Oscillating motion (as of a pendulum) in which the acceleration of the oscillator has an equal magnitude but opposite direction to the displacement of it from the equilibrium position. • Snell's law A formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction. • speed of propagation The speed at which a wave moves through a medium. • standing wave A wave form which occurs in a limited, fixed medium in such a way that the reflected wave coincides with the produced wave. A common example is the vibration of the strings on a musical stringed instrument. • superposition The summing of two or more field contributions occupying the same space. • superposition The summing of two or more field contributions occupying the same space. • transverse wave Any wave in which the direction of disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of travel. • transverse wave Any wave in which the direction of disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of travel. • transverse wave Any wave in which the direction of disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of travel. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • transverse wave Any wave in which the direction of disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of travel. • trough A long, narrow depression between waves or ridges. • ultrasound Sound with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing; approximately 20 kilohertz. • wave A moving disturbance in the energy level of a field. • wave equation An important second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves such as sound waves, light waves, and water waves. • wave speed The absolute value of the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. • wavelength The length of a single cycle of a wave, as measured by the distance between one peak or trough of a wave and the next; it is often designated in physics as λ, and corresponds to the velocity of the wave divided by its frequency. • wavelength The length of a single cycle of a wave, as measured by the distance between one peak or trough of a wave and the next; it is often designated in physics as λ, and corresponds to the velocity of the wave divided by its frequency. • work A measure of energy expended in moving an object; most commonly, force times displacement. No work is done if the object does not move. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Wave motion The point along the axis is analogous to the floating ball at sea. We notice that while it moves up and down it does not move in the direction of the wave's propagation. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Simple harmonic motion animation." Public domain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Simple_harmonic_motion_animation.gif View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transverse Wave With a Fixed End Point A transverse wave that is fixed at the end point. The reflected wave is inverted. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Standing Waves Standing waves in a string, the fundamental mode and the first six overtones. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Standing wave." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standing_wave View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Wavelength and Amplitude The wavelength is the distance between adjacent crests. The amplitude is the 1/2 the distance from crest to trough. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Wave." GNU FDL http://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Wave.png View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Fixed End Reflection When a transverse wave meets a fixed end, the wave is reflected, but inverted. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Frequencies of different sine waves. The red wave has a low frequency sine there is very little repetition of cycles. Conversely we say that the purple wave has a high frequency. Note that time increases along the horizontal. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Sine waves different frequencies." Public domain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sine_waves_different_frequencies.svg View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The Wave Equation A brief introduction to the wave equation, discussing wave velocity, frequency, wavelength, and period. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Water waves Surface waves in water Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Wave." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Water waves The motion water waves causes particles to follow clockwise circular motion. This is a result of the wave having both transverse and longitudinal properties. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Elliptical trajectory on ripples." GNU FDL http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Elliptical_trajectory_on_ripples.svg View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Standing Wave on a String This is what a standing wave would look like if you were to slow it down. The wave is caused by an incident wave on a string being reflected and then traveling back in the direction it came from. The two waves then meet and interfere with each other causing this phenomenon. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Standing wave." Public domain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Standing_wave.gif View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Two Strings With Different Density Two strings with different density are connected and driven by an external driving force. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Reflection and Transmission of Mechanical Waves." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m12794/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Harmonic Waves Harmonic waves are described by sinusoidal functions. The wavelength is equal to linear distance between repetitions of transverse disturbance or phase. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse harmonic waves." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m15992/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Two Types of Waves: Longitudinal vs. Transverse Even ocean waves! Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Figure 1 In transverse waves, the media the wave is traveling in moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Plane wave We see a wave propagating in the direction of the phase velocity. The wave can be thought to be made up of planes orthogonal to the direction of the phase velocity. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikimedia. "Plane Wave Oblique View." Public domain http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plane_Wave_Oblique_View.jpg View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Wave Interference A brief introduction to constructive and destructive wave interference and the principle of superposition. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Fig 2 This shows a wave with the group velocity and phase velocity going in different directions. (The group velocity is positive and the phase velocity is negative. ) Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Group velocity." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_velocity View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Earthquake Destruction The destructive effect of an earthquake is palpable evidence of the energy carried in these waves. The Richter scale rating of earthquakes is related to both their amplitude and the energy they carry. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Energy in Waves: Intensity." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42250/latest/?collection=col11406/1.7 View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Two Types of Waves: Longitudinal vs. Transverse Even ocean waves! Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Constructive Interference Pure constructive interference of two identical waves produces one with twice the amplitude, but the same wavelength. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Superposition and Interference." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42249/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Refraction in Water An object (in this case a pencil) partially immersed in water looks bent due to refraction: the light waves from X change direction and so seem to originate at Y. (More accurately, for any angle of view, Y should be vertically above X, and the pencil should appear shorter, not longer as shown. ) Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Refraction." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refraction View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Standing Wave A standing wave (black) depicted as the sum of two propagating waves traveling in opposite directions (red and blue). Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Standing wave." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standing_wave View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Electromagnetic Wave Electromagnetic waves can be imagined as a self-propagating transverse oscillating wave of electric and magnetic fields. This 3D diagram shows a plane linearly polarized wave propagating from left to right. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Electromagneticwave3Dfromside." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Electromagneticwave3Dfromside.gif View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transverse Wave With a Free End When a transverse wave meets a free end, it is reflected. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Wave Equation in Two Dimensions A solution of the wave equation in two dimensions with a zero-displacement boundary condition along the entire outer edge. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Wave equation." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_equation View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transverse Wave Diagram of a transverse wave. The wave motion moves perpendicular to the medium it is traveling in. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Complex Pattern of Waves These waves result from the superposition of several waves from different sources, producing a complex pattern. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Superposition and Interference." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42249/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Resonance A brief overview of resonance, targeted toward introductory physics students. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Longitudinal Waves A compressed Slinky is an example of a longitudinal wave. The wave propagates in the same direction of oscillation. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikispaces. "funwaves - 5.Longitudinal wave." CC BY-SA http://funwaves.wikispaces.com/5.+Longitudinal+wave View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Sine Wave The direction of propagation of this wave is along the t axis. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "ComplexSinInATimeAxe." Public domain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:ComplexSinInATimeAxe.gif View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Water Wave Waves that are more massive or have a greater velocity transport more energy. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Waves in pacifica 1." GNU FDL http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Waves_in_pacifica_1.jpg View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Partial Transmittance and Partial Reflectance A wave experiences partial transmittance and partial reflectance when the medium through which it travels suddenly changes. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Transmission (wave propagation)." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_%2528wave_propagation%2529 View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Superposition of Non-Identical Waves Superposition of non-identical waves exhibits both constructive and destructive interference. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Superposition and Interference." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42249/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Figure 2 Peaks are the top most points of the waves and troughs are the bottom, or valleys of the waves. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Free End Reflection The wave is reflected, but unlike a transverse wave with a fixed end, it is not inverted. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Intensity Pattern Intensity pattern formed on a screen by diffraction from a square aperture. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Diffraction." CC BY http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffraction View on Boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves A wave A) does not move mass in the direction of propagation; it transfers energy B) does not move energy in the direction of propagation; it transfers mass C) transfers both energy and mass in the direction of propagation D) neither move energy nor mass in the direction of propagation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves A wave A) does not move mass in the direction of propagation; it transfers energy B) does not move energy in the direction of propagation; it transfers mass C) transfers both energy and mass in the direction of propagation D) neither move energy nor mass in the direction of propagation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Depending on the direction of its oscillation, the wave can be A) transverse or longitudinal B) linear or circular C) transverse or linear D) circular or Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Depending on the direction of its oscillation, the wave can be A) transverse or longitudinal B) linear or circular C) transverse or linear D) circular or Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The following are examples of the transverse wave: A) seismic waves and sound waves B) seismic waves and the motion of the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic plane waves C) pressure waves and the motion of the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic plane waves D) pressure waves such as sound waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The following are examples of the transverse wave: A) seismic waves and sound waves B) seismic waves and the motion of the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic plane waves C) pressure waves and the motion of the electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic plane waves D) pressure waves such as sound waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transverse waves propagate through media A) in the direction of energy transfer B) against the direction of energy transfer C) propagate through media orthogonally to the direction of energy transfer D) independently of the direction of energy transfer Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transverse waves propagate through media A) in the direction of energy transfer B) against the direction of energy transfer C) propagate through media orthogonally to the direction of energy transfer D) independently of the direction of energy transfer Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Longitudinal waves A) oscillate in the direction of propagation and displace mass B) oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation and do not displace mass C) oscillate in the direction of propagation and do not displace mass D) oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation and displace mass Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Longitudinal waves A) oscillate in the direction of propagation and displace mass B) oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation and do not displace mass C) oscillate in the direction of propagation and do not displace mass D) oscillate perpendicular to the direction of propagation and displace mass Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The following are examples of the longitudinal wave: A) pressure waves with the exception of sound waves B) pressure waves such as sound waves C) seismic waves D) seismic waves and sound waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The following are examples of the longitudinal wave: A) pressure waves with the exception of sound waves B) pressure waves such as sound waves C) seismic waves D) seismic waves and sound waves Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The particles which make up a water wave move in A) linear paths B) both transverse and longitudinal paths C) both circular and linear paths D) circular paths Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The particles which make up a water wave move in A) linear paths B) both transverse and longitudinal paths C) both circular and linear paths D) circular paths Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The uniqueness of water waves is found in the observation that they comprise A) longitudinal wave motion B) transverse wave motion C) transverse and circular wave motion D) both transverse and longitudinal wave motion Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The uniqueness of water waves is found in the observation that they comprise A) longitudinal wave motion B) transverse wave motion C) transverse and circular wave motion D) both transverse and longitudinal wave motion Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The solution of the the wave equation for a traveling wave is the A) left traveling function B) right traveling function C) derivative of a left traveling function and a right traveling function D) sum of a left traveling function and a right traveling function Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The solution of the the wave equation for a traveling wave is the A) left traveling function B) right traveling function C) derivative of a left traveling function and a right traveling function D) sum of a left traveling function and a right traveling function Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The amount of energy in a wave is A) directly proportional to its amplitude B) directly proportional to its amplitude squared C) inversely proportional to its amplitude squared D) inversely proportional to its amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The amount of energy in a wave is A) directly proportional to its amplitude B) directly proportional to its amplitude squared C) inversely proportional to its amplitude squared D) inversely proportional to its amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Major characteristic properties of waves include A) frequency B) wavelength C) All of these answers D) amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Major characteristic properties of waves include A) frequency B) wavelength C) All of these answers D) amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The group velocity is the velocity with which the A) phase of the wave propagates in space B) velocity with which the envelope of the wave propagates through space C) frequency component of the wave travels D) group of waves travel Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The group velocity is the velocity with which the A) phase of the wave propagates in space B) velocity with which the envelope of the wave propagates through space C) frequency component of the wave travels D) group of waves travel Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Waves that transfer more energy are A) less massive and have greater velocities B) more massive and have greater velocities C) less massive and have smaller velocities D) more massive and have smaller velocities Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Waves that transfer more energy are A) less massive and have greater velocities B) more massive and have greater velocities C) less massive and have smaller velocities D) more massive and have smaller velocities Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Energy of a wave is transported A) opposite to the direction of the waves transportation B) independently of the direction of the waves transportation C) perpendicular to the direction of the waves transportation D) in the direction of the waves transportation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Energy of a wave is transported A) opposite to the direction of the waves transportation B) independently of the direction of the waves transportation C) perpendicular to the direction of the waves transportation D) in the direction of the waves transportation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The superposition of two identical waves that arrive at the same point exactly in phase corresponds to the A) constructive interference with a wave that has twice the amplitude of the individual waves B) destructive interference with a wave that has twice the amplitude of the individual waves C) destructive interference with a wave that has zero amplitude D) constructive interference with a wave that has zero amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The superposition of two identical waves that arrive at the same point exactly in phase corresponds to the A) constructive interference with a wave that has twice the amplitude of the individual waves B) destructive interference with a wave that has twice the amplitude of the individual waves C) destructive interference with a wave that has zero amplitude D) constructive interference with a wave that has zero amplitude Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The waves superimpose themselves on one another when they A) arrive to different points B) are identical C) have zero amplitude D) arrive at the same point Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The waves superimpose themselves on one another when they A) arrive to different points B) are identical C) have zero amplitude D) arrive at the same point Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves When the medium through which a wave travels suddenly changes, the wave often experiences A) absolute transmission through the interface B) absolute refection by the interface C) partial transmission and partial refection at the interface D) frequency doubling Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves When the medium through which a wave travels suddenly changes, the wave often experiences A) absolute transmission through the interface B) absolute refection by the interface C) partial transmission and partial refection at the interface D) frequency doubling Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transmission is a wave phenomenon that A) permits the passage of wave with some or none of the incident wave being absorbed B) changes the direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media C) blocks the passage of wave with all the incident wave being absorbed D) permits the passage of wave with its frequency being doubled Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Transmission is a wave phenomenon that A) permits the passage of wave with some or none of the incident wave being absorbed B) changes the direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media C) blocks the passage of wave with all the incident wave being absorbed D) permits the passage of wave with its frequency being doubled Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave is one in which two waves superimpose to produce a wave that A) varies in amplitude but does not propagate B) varies in amplitude and propagates C) does not vary in amplitude and does not propagate D) does not vary in amplitude and propagates Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave is one in which two waves superimpose to produce a wave that A) varies in amplitude but does not propagate B) varies in amplitude and propagates C) does not vary in amplitude and does not propagate D) does not vary in amplitude and propagates Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves An antinode is A) the location of minimum amplitude of a standing wave B) point of no motion C) the location of maximum amplitude of a standing wave D) point of minimum motion Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves An antinode is A) the location of minimum amplitude of a standing wave B) point of no motion C) the location of maximum amplitude of a standing wave D) point of minimum motion Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves During refraction, A) the phase velocity of the wave is changed, but its frequency remains constant B) both the phase velocity of the wave and frequency remain constant C) both the phase velocity of the wave and frequency are changed D) the phase velocity of the wave remains constant, but its frequency is changed Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves During refraction, A) the phase velocity of the wave is changed, but its frequency remains constant B) both the phase velocity of the wave and frequency remain constant C) both the phase velocity of the wave and frequency are changed D) the phase velocity of the wave remains constant, but its frequency is changed Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle A) another refractive index at an oblique angle B) identical refractive index at an oblique angle C) identical refractive index at a right angle D) another refractive index at a right angle Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle A) another refractive index at an oblique angle B) identical refractive index at an oblique angle C) identical refractive index at a right angle D) another refractive index at a right angle Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Diffraction effects are generally most pronounced for waves whose wavelengths are A) very small B) very large C) totally different from the dimensions of the diffracting objects D) roughly similar to the dimensions of the diffracting objects Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Diffraction effects are generally most pronounced for waves whose wavelengths are A) very small B) very large C) totally different from the dimensions of the diffracting objects D) roughly similar to the dimensions of the diffracting objects Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described as the A) bending of waves around large obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings B) bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings C) bending of waves around large obstacles and the spreading out of waves past large openings D) bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past large openings Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described as the A) bending of waves around large obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings B) bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings C) bending of waves around large obstacles and the spreading out of waves past large openings D) bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past large openings Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave occurs when A) a transverse wave meets a fixed end B) a transverse wave meets a free end C) an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string D) an incident wave is reflected Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave occurs when A) a transverse wave meets a fixed end B) a transverse wave meets a free end C) an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string D) an incident wave is reflected Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Nodes are points A) that remain flat due to the destructive interference B) that remain flat due to the constructive interference C) with maximum oscillation due to the constructive interference D) with maximum oscillation due to the destructive interference Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves Nodes are points A) that remain flat due to the destructive interference B) that remain flat due to the constructive interference C) with maximum oscillation due to the constructive interference D) with maximum oscillation due to the destructive interference Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves In a transverse wave, the wave direction is A) parallel the direction that the string oscillates in B) perpendicular the direction that the string oscillates in C) coincides the direction that the string oscillates in D) does not depend on the direction that the string oscillates in Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves In a transverse wave, the wave direction is A) parallel the direction that the string oscillates in B) perpendicular the direction that the string oscillates in C) coincides the direction that the string oscillates in D) does not depend on the direction that the string oscillates in Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The speed of a wave on a string can be found by A) multiplying the wavelength by the period B) dividing the wavelength by the frequency C) multiplying the frequency by the period D) multiplying the wavelength by the frequency Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The speed of a wave on a string can be found by A) multiplying the wavelength by the period B) dividing the wavelength by the frequency C) multiplying the frequency by the period D) multiplying the wavelength by the frequency Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave occurs when A) an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string B) a transverse wave in string meets one end C) a transverse wave is reflected D) a reflected wave meets another end Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves A standing wave occurs when A) an incident wave meets a reflected wave on a string B) a transverse wave in string meets one end C) a transverse wave is reflected D) a reflected wave meets another end Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves When transverse waves in strings meet one end, they are A) diffracted B) retracted C) reduced D) reflected Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves When transverse waves in strings meet one end, they are A) diffracted B) retracted C) reduced D) reflected Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves The points in a standing wave that appear to remain flat and do not move are called A) antinodes B) nodes C) reflected points D) incident points Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves The points in a standing wave that appear to remain flat and do not move are called A) antinodes B) nodes C) reflected points D) incident points Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless - LO. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com/ Waves and Vibrations: Waves Attribution • Wikipedia. "Phase velocity." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phase_velocity • Wikipedia. "Group velocity." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_velocity • Wikipedia. "Frequency." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequency • Wikipedia. "Frequency." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequency • Wikipedia. "Frequency." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequency • Wikipedia. "Frequency." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequency • Wiktionary. "frequency." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/frequency • Wiktionary. "wavelength." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/wavelength • Wikipedia. "wave speed." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/wave%20speed • Wikipedia. "Wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave • Wiktionary. "medium." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/medium • Wiktionary. "wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/wave • Wikipedia. "direction of propagation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/direction%20of%20propagation • Wikipedia. "Waves." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waves • Wikipedia. "Waves." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waves • Wikipedia. "Wave power." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_power • Wikipedia. "Wave power." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_power Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • Wikipedia. "Wave power." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_power • Wiktionary. "phase velocity." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/phase+velocity • Wiktionary. "group velocity." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/group+velocity • Wikipedia. "Wave power." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_power • Wikipedia. "Wind wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_wave • Wikipedia. "plane wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/plane%20wave • Connexions. "Energy in Waves: Intensity." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42250/latest/?collection=col11406/1.7 • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/ultrasound • Wikipedia. "Restoring force." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restoring%20force • Wikipedia. "photoelectric effects." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/photoelectric%20effects • Wikipedia. "Wave equation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave_equation • Wikipedia. "wave equation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/wave%20equation • Wikipedia. "boundary condition." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/boundary%20condition • Wikipedia. "Longitudinal wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longitudinal_wave • Wikipedia. "Sound waves." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sound_waves#Longitudinal_and_transverse_waves • Wiktionary. "rarefaction." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/rarefaction • Wiktionary. "compression." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/compression • Wiktionary. "Longitudinal." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Longitudinal • Wikipedia. "Refraction." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refraction Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • Wiktionary. "refractive index." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/refractive+index • Wikipedia. "Snell's law." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snell's%20law • Wikipedia. "Electromagnetic radiation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetic_radiation • Wikipedia. "Electromagnetic radiation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnetic_radiation • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//sociology/definition/power • Wiktionary. "work." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/work • Wiktionary. "energy." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/energy • Connexions. "Transverse harmonic waves." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m15992/latest/ • Wiktionary. "simple harmonic motion." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/simple+harmonic+motion • Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ • Wiktionary. "standing wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/standing+wave • Wiktionary. "amplitude." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/amplitude • Wiktionary. "transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/transverse+wave • Connexions. "Reflection and Transmission of Mechanical Waves." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m12794/latest/ • Wikipedia. "boundary condition." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/boundary%20condition • Connexions. "Superposition and Interference." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42249/latest/ • Wiktionary. "interference." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/interference • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/superposition • Connexions. "Superposition and Interference." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m42249/latest/ Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/destructive-interference • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/constructive-interference • Wiktionary. "resonance." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/resonance • Wikipedia. "Transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transverse_wave • Wikipedia. "Transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transverse_wave • Wikipedia. "Transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transverse_wave • Wikipedia. "direction of propagation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/direction%20of%20propagation • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/speed-of-propagation • Wiktionary. "transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/transverse+wave • Wiktionary. "wavelength." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/wavelength • Wiktionary. "trough." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/trough • Wiktionary. "crest." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/crest • Wikipedia. "Diffraction." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffraction • Wiktionary. "interference." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/interference • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/superposition • Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ • Wikipedia. "Wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wave#Waves_on_strings • Wikipedia. "Vibrating string." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vibrating_string • Wiktionary. "oscillate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/oscillate Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Waves and Vibrations: Waves • Wiktionary. "transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/transverse+wave • Connexions. "Transverse Waves - Grade 10." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m32635/latest/ • Wikipedia. "Vibrating string." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vibrating_string • Wikipedia. "Standing waves." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standing_waves • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/destructive-interference • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//physics/definition/constructive-interference • Wiktionary. "transverse wave." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/transverse+wave Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com