* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 4-8 part 2 Powerpoint - peacock
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic form wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
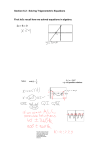
Algebra 2 Complex Numbers Lesson 4-8 Part 2 Goals Goal • To find complex number solutions of quadratic equations.. Rubric Level 1 – Know the goals. Level 2 – Fully understand the goals. Level 3 – Use the goals to solve simple problems. Level 4 – Use the goals to solve more advanced problems. Level 5 – Adapts and applies the goals to different and more complex problems. Vocabulary • None Essential Question Big Idea: Solving Equations • How are complex numbers related to the solutions of quadratic equations? Complex Solutions If a quadratic equation with real coefficients has nonreal solutions, those solutions are complex conjugates. Complex solutions always occur in pairs, complex conjugate pairs. Helpful Hint When given one complex solution, you can always find the other by finding its conjugate. Example: Solve the equation. Take square roots. Express in terms of i. Example: Solve the equation. 5x2 + 90 = 0 Add –90 to both sides. Divide both sides by 5. Take square roots. Express in terms of i. Your Turn: Solve the equation. x2 = –36 Take square roots. Express in terms of i. Your Turn: Solve the equation. x2 + 48 = 0 x2 = –48 Add –48 to both sides. Take square roots. Express in terms of i. Your turn: Solve the equation. 9x2 + 25 = 0 9x2 = –25 Add –25 to both sides. Divide both sides by 9. Take square roots. Express in terms of i. Example: Find the zeros of f(x) = 4x2 + 3x + 2 using the Quadratic Formula. f(x)= 4x2 + 3x + 2 Set f(x) = 0. Write the Quadratic Formula. Substitute 4 for a, 3 for b, and 2 for c. Simplify. Write in terms of i. Your Turn: Find the zeros of g(x) = 3x2 – x + 8 using the Quadratic Formula. Set f(x) = 0 Write the Quadratic Formula. Substitute 3 for a, –1 for b, and 8 for c. Simplify. Write in terms of i. Your Turn: Find the zeros of each function by using the Quadratic Formula. 1. f(x) = 3x2 – 6x – 5 2. g(x) = 2x2 – 6x + 5 Essential Question Big Idea: Solving Equations • • How are complex numbers related to the solutions of quadratic equations? Every quadratic equation has complex solutions. Sometimes, these complex numbers only have real parts. When a quadratic equation has no real solutions, use square roots or the quadratic formula to find the imaginary solutions. Assignments • Section 4-8 Part 2, Pg 275 – 277; #1 – 4 all, 6 – 14 even, 24, 30 – 44 even.