* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproductive System * Outcomes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
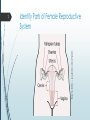
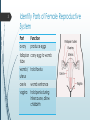
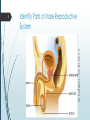
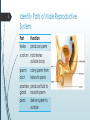
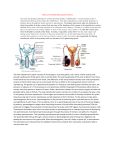
1 Reproductive System – Outcomes Identify and locate the main parts of the male and female reproductive systems. Recall the length and parts of the menstrual cycle. Discuss fertile period in the menstrual cycle, sexual intercourse, fertilisation, pregnancy, birth, growth, and puberty in relation to human reproduction. Understand various forms of contraception. Identify Parts of Female Reproductive System by CDC – public domain 2 3 Identify Parts of Female Reproductive System Part ovary Function produce eggs fallopian carry egg to womb tube womb / uterus cervix vagina hold foetus womb entrance hold penis during intercourse, allow childbirth Identify Parts of Male Reproductive System by Tsaitgaist – CC-BY-SA-3.0 4 5 Identify Parts of Male Reproductive System Part testes Function produce sperm scrotum hold testes outside body sperm duct carry sperm from testes to penis prostate produce fluid to gland nourish sperm penis deliver sperm to outside 6 Recall the Menstrual Cycle 7 Recall the Menstrual Cycle The menstrual cycle is ~28 days long on average. Menstruation (a.k.a. period), the shedding of the lining of the uterus, is day zero. Ovulation occurs around day 14, when the ovaries release an egg. Ovulation is the most fertile stage of the menstrual cycle. 8 Discuss Sexual Intercourse In the context of human reproduction, sexual intercourse is when a male’s erect penis is placed inside a female’s vagina. If sperm reach the fallopian tube during ovulation, this may result in fertilisation. Fertilisation is the fusion of male and female gametes (sex cells), resulting in a zygote. 9 Discuss Pregnancy If fertilisation occurs, the woman may become pregnant. A zygote begins as a single cell, but will divide shortly after fertilisation. A zygote divides into an embryo. Implantation occurs if the embryo reaches the uterus and attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. 10 Discuss Pregnancy At the implantation site, the placenta develops. Placenta connects the embryo to the mother’s bloodstream, allowing nutrients and waste to be exchanged. Placenta connects to the embryo via the umbilical cord. After ~8 weeks, the embryo becomes recognisably human and is called a foetus. Pregnancy typically lasts ~40 weeks. 11 Discuss Birth The process of birth begins with the muscles in the uterus contracting. The amniotic sac surrounding the foetus ruptures, allowing amniotic fluid to escape (a.k.a. “water breaking”). The cervix dilates (widens). The baby is pushed through the cervix. The umbilical cord is cut. The mother begins to lactate (produce milk). 12 Discuss Growth and Puberty In girls, puberty: 1. Increases the size of ovaries and womb. 2. Marks the start of the menstrual cycle. 3. Causes a number of other physical changes, such as pubic hair, wider hips, growth spurts, breast growth, etc. In boys, puberty: 1. Increases the size of the penis and testes. 2. Marks the start of semen production. 3. Causes a number of other physical changes, such as pubic (including facial) hair, larger muscles, growth spurts, deeper voice, etc. 13 Understand Contraception Contraception refers to the actions and devices used to prevent pregnancy. Condoms are latex covers for the penis, preventing semen from exiting. Hormone supplements oestrogen and/or progesterone (“the pill”, “the patch”, “the implant”, intrauterine devices, injections, vaginal ring) prevent ovulation and may make the female reproductive system unsuitable for sperm or egg implantation. Diaphragm / female condom physically block sperm from entering the womb.