* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download System Software - Computing Systems` Blog
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
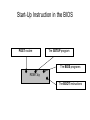
Chapter 5 System Software System Software • There is software stored in the ROM circuits contain important system routine on every motherboard. • When you switch on your PC receives instructions which are loaded into the CPU, and the CPU starts by executing the system software which is stored on the motherboard. • The startup programs are stored in ROM circuits which contain data, and can only be read. • BIOS is important system software, only after these programs have been loaded and executed, then the operating system can be loaded from the hard disk. This is called the boot process. BIOS ROM (Basic Input output System Read Only Memory) • contain software (program and instructions), which are specific for that motherboard. It will remain with the PC throughout its life. • holds the start-up instructions. In fact there are several different programs inside the start-up instructions. It can be differentiate by: – POST (Power On Self Test) – The Setup program, which connect with the *CMOS instructions – BIOS program, which connect with the various hardware peripherals – The Boot instructions, which call the operating system (DOS, OS/2, or Windows) Start-Up Instruction in the BIOS POST routine The SETUP program The BIOS programs ROM Chip The BOOT instructions POST • (POST) Power On Self Test is the first instruction executed during start-up. It checks the PC components and ensures that everything works. • It checks and executes in this order: – Information about the graphics adapter. – Information about the BIOS (name, version). – Information about the RAM (size and speed) • If POST detects errors in the system, it will write error messages on the screen. If the monitor is not ready, or if the error is in the video card, it will give a pattern of beeps. Setup program • Checks the various hardwares, configure in the CMOS, and generally “bringing the machine to life”. • Installs the other system devices: – such as floppy disk and ATA drives, – locates the “logical devices” (eg. COM, LPT, etc.). – The PCI bus is also scanned for devices. BIOS program • It initializing routine set up the BIOS functions (Basic Input/Output Systems). • It places starting values in the system’s various programmable devices. • These intelligent devices regulate the operation of different portions of the computer’s hardware e.g. data transfer control. Boot instructions • The boot instruction (bootstrap loader) is the last part of the BIOS. It will looks in the CMOS storage to find the chosen boot device. • It is a tiny program, to find the Boot Record (BR) which is located in the first sector on a hard disk or a floppy disk. • It reads the boot-strap of the Boot Record which points to the location of the startup files of the Operating System. • It hands over the control to the bootstrap routine found on the disk of the OS and continues loading the operating system from the hard disk, Operating System • Operating systems are programs designed to control the operation of a computer system. • To make the complexity of the PC as invisible as possible to the user. • Acts as an intermediary between the software applications and the hardware they run on. • It accepts commands from the computer user and carries them out to perform some desired operation. Disk Operating System (DOS) • is a collection of programs used to control overall computer operation. • work in the background. • is responsible for finding and organizing data, and applications on the disk. • It principally consists of only 4 parts: – A boot record, which activates the operating system. – IO.SYS file, which interfaced ROM BIOS with installation of device drivers. – MSDOS.SYS file, which handling the file system and program execution. – COMMAND.COM file, which provides the command line, the text based user interface. Other Operating System • A Graphical User Interface (GUI) is another form of operating environment. • The most widely used GUI is Microsoft Window OS, Apple OS and Linux. • GUIs use a graphical display to represent procedures and programs that can be executed by the computer. • It uses small pictures, called Icons, to represent different programs. • The advantage of using a GUI is that the user does not have to remember complicated commands to execute a program.