* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
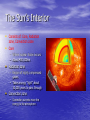
The Sun Unit 5 PESS 2 Energy from the Sun • Electromagnetic energy is a type of energy that can travel through space an example is visible light • Light travels in wavelengths – There are many things that travel in wavelengths (radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet rays, x-rays) • The electromagnetic spectrum breaks visible light down into the colors that make it up – When you shine light through a prism you can see the different colors of visible light Electromagnetic Radiation • Visible light is composed of red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet – like a rainbow Energy from the Sun • In a process called nuclear fusion the sun gives off electromagnetic energy • Nuclear fusion can only occur at extremely high temperatures (~15 million °C) – Helium and hydrogen atoms fuse together giving off an enormous amount of energy (enough to supply the solar system for billions of years!) • There is enough helium and hydrogen in the sun to last about 10 billion years – the sun is only about 5 billion years old Measuring our Solar System • Since the solar • system is so large scientists developed the unit called an astronomical unit or au The distance between the sun and Earth is 1au The Sun’s Interior • Consists of: Core, Radiation zone, Convection zone • Core – Where nuclear fusion occurs – About 400,000km • Radiation zone – Region of highly compressed gases – Takes energy “light” about 10,000 years to pass through • Convection zone – Convection currents move the energy to the atmosphere The Sun’s Atmosphere • There are 3 layers – the photosphere, the chromosphere and the corona • The Photosphere – The inner layer – Technically, the “surface” – About 5800K and 500km thick • The Chromosphere – – – – The middle layer Gives off a reddish glow About 10,000K Visible during a total solar eclipse The Sun’s Atmosphere • The Corona – The white halo around the sun – Visible on Earth only during eclipses or by special telescopes – Sends out a stream of electrically charged particles called solar wind – The Earth’s atmosphere normally blocks out solar wind, but near the north and south poles some particles enter creating auroras – About 1 million K Features of the Sun • The sun rotates on its axis, just like all the other planets in the solar system • Sunspots – Small, dark spots on the sun (small for the sun because they are about the size of Earth) – Sunspots are areas of gas that are cooler than the gases around it – since they are cooler they do no give off as much light and appear dark Features of the Sun • Scientists believe that the number of sunspots change over 10 years or so – meaning that the amount of energy produced by the sun also changes • Prominences – A group of sunspots that link together and create reddish loops – If a prominence is near the edge of the sun scientists can actually see them stick out from the sun’s surface Features of the Sun • Solar flares – When sunspots suddenly connect and release a large amount of energy into space – The gases contract an heat to even greater temperatures causing hydrogen gas to explode into space – Solar flares can cause magnetic storms in the upper atmosphere of Earth disrupting radios, telephones, television, and causing electrical problems