* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun - Moodle
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
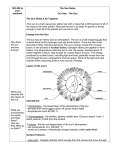
The Sun P 754 The sun is the nearest __________________. It’s name is _____________________ It takes ___________minutes for light to reach Earth How do we know what the sun is made of? ]¬ Scientists use a _____________________ Dark _______________ form when gases in the star’s outer layers absorb specific wavelengths of the light that passes through the layers THERMONUCLEAR FUSION CONVERTS H to He in the Proton – Proton Reaction (1.) 1H + 1H 2H + positron (ß+) + neutrino (v) (2.) 2H + 1H 3He + gamma ray (y) (3.) 3He + 3He 4He + 1H + 1H The energy _______________ is similar to a ____________________ bomb. Almost all of the energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The sun produces Energy through __________________ __________________ Hydrogen is turned to helium and in the process some _____________ is lost and changes into _______________ Do quick lab shown on page 757. E=mc2 Albert __________________ said that a small amount of matter yields a large amount of energy E = _________________ ________________ m = ___________________ c2= _____________ _____ ____________ ____________ The sun's energy allows ________________ to exist on earth. Almost all energy transformations can be traced back to the sun. THE SUN FORMED AROUND _____ BILLION YEARS AGO AND STILL HAS ABOUT ___ BILLION YEARS TO GO page 758 Makes up about _____________ of mass Temp about _____ million Kelvins Enormous temp and pressure cause atoms to separate to nuclei and electrons Nuclei are positive so push away, But high temp and pressure push them together Hydrogen _______________ to helium The Photosphere The sun's visible surface is called the ____________________. Photo--Greek for _______________ It is a _______________________ The Chromosphere The layer of the sun's atmosphere between the photosphere and the corona is the chromosphere (sphere of ________________) Corona—atmosphere outermost region extends out several million kilometers and merges into a hurricane of high-speed protons and electrons called the ______________ _ Solar Wind High speed electrons and electrically charged particles called ___________ that stream our into space Flows outward to the rest of the solar system Section 2 Solar Activity Page 761 Sunspots are relatively cool areas on the surface created by strong magnetic fields The sun spins on its axis but different ___________ spin at different ___________ The Sun has Storms: Sunspot Cycles Scientists have observed for hundreds of years That is how they know different ______________ rotate at different rates the numbers and position of sunspots vary in a cycle that lasts about ___________ years Look at Page 767 and answer these questions How many complete sunspot cycles are illustrated by the graph? __________ How does the range of latitudes of sunspots change over time? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ How is this change related to the sunspot cycle? _____________________________________________________ ____ According the graph, how many sunspots were located at the sun’s north pole? _____________________________ Prominences Some sunspots have prominences forming over them Magnetic _____________ ___________________ Solar Flares A sudden outward __________________ of electrically charged particles During a peak sunspot cycle ___ -____ solar flares may occur each day Coronal Mass Ejections Parts of the _________are __________________ off the sun When the particles hit the Earth’s ______________________ they generate a disturbance called a __________________________ storm Geomagnetic storms may interfere with __________communications on earth They may also lead to ______________________ when power lines become overloaded Solar Wind—our ______________ ________________ protects us Auroras Colored light produced by ______________ particles in the atmosphere that react with the _____________ and _______________in the upper atmosphere Usually seen near the _________________ We call them the __________________ ___________________________ Hydrostatic Equilibrium Why doesn’t the sun blow apart? Because of ______________________ _______________________ The ______________ ________________ from the explosions is balanced by the _________________ force of_________________