* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants! - AP Biology with Ms. Costigan
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
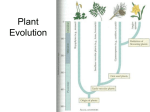
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
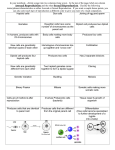
Plants! Reproduction Part 1 (lecture 15) (Bryophytes & Pteridophytes) Vegetative Reproduction Asexual Reproduction involving parts of a plant Cuttings Plant develops from stem, root, or leaf fragments Layering Formation of root off of a stem Grafting Aligning vascular cambium of 2 or more plant parts to join them into one Tissue Culture Plant tissue cultivated and grown on nutrient media Vegetative Reproduction African Violet leaf cutting Layering (raspberries) Grafted Tree V-graft (2 apple varieties) Plant tissue culture Animal vs. Plant Life Cycle Animal Plant diploid multicellular individual 2n diploid multicellular sporophyte mitosis 2n zygote 2n mitosis meiosis zygote 2n fertilization haploid unicellular gametes 1n no multicellular haploid fertilization meiosis gametes 1n spores 1n mitosis mitosis haploid multicellular gametophyte 1n alternation of generations Alternation of Generations Alternation of Generations – A life cycle that includes a multicellular diploid form (sporophyte) and a multicellular haploid form (gametophyte) Gametophyte - multicellular haploid form that mitotically produces haploid gametes that unite and grow into the sporophyte generation Sporophyte - multicellular diploid form that results from a union of gametes and that meiotically produces haploid spores that grow into the gametophyte generation Alternation of Generations WHY, OH WHY (does bio have to be so freaking confusing!) ? A “best of both worlds” idea Spore – with spores, only one parent contributes to the genes in the offspring Beneficial if the parent is in a stable environment because offspring will have all of the genes that are successful in that area Gametes – both parents contribute genes Beneficial in a changing environment where different traits may enhance survival of offspring First Land Plants haploid Bryophytes: mosses & liverworts non-vascular no water transport system no true roots swimming sperm flagellated sperm lifecycle dominated by haploid gametophyte stage fuzzy moss plant you are familiar with is haploid spores for reproduction haploid cells which sprout to form gametophyte diploid Bryophyte Reproduction Gametangia (on gametophyte) produce haploid gametes Antheridium – produces sperm Archegonium – produces egg Resulting zygote grows into a diploid structure (sporophyte) In mosses the sporophyte is a stalk Spores from sporophyte disperse & develop into haploid gametes Gametophyte Dominant! First Vascular Plants Pteridophytes: ferns vascular water transport system xylem, phloem, roots, leaves swimming sperm flagellated sperm life cycle dominated by sporophyte stage leafy fern plant you are familiar with is diploid fragile independent gametophyte (prothallus) spores for reproduction haploid cells which sprout to form gametophyte haploid diploid Pteridophyte Reproduction Produce spores that form gametophytes Sori – sporangia clusters on the underside of fern fronds Meiosis in sporangia forms spores Antheridia produce sperm and archegonia produce eggs Sperm swim to meet eggs (fertilization occurs at female reproductive structure) & diploid sporophyte results Sporophyte Dominant! Alternation of Generations Fern gametophyte (1n) small haploid plant which produces gametes homospory: male & female on same plant archegonia antheridia Fern Reproduction haploid Alternation of Generations diploid produces male & female gametes archegonia antheridia haploid Pop Quiz! 1. The evolution of plants: •a.started in aquatic environments. •b.was marked by the development of specialized tissues such as vascular tissue. •c.led to the development of specialized organs. •d.demonstrated a trend toward radiating into drier environments. •e.all of these Pop Quiz! 2. All but which of the following would be associated with vascular plants? a.root systems b.Bryophytes c.Angiosperms d.Gymnosperms e.shoot systems 3. Ferns are more advanced than mosses because mosses lack which structure found in ferns? a. spores b. cuticle c. xylem d. sporophytes e. pollen