* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth - altaastronomy
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Energetic neutral atom wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tidal acceleration wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
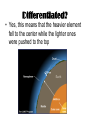
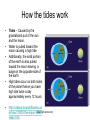
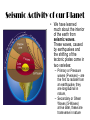
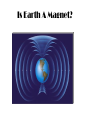
Earth Our Home Planet Where did it come from? • Gas and dust in the universe accreted and differentiated to form our solar system and Earth Differentiated? • Yes, this means that the heavier element fell to the center while the lighter ones were pushed to the top LUNA Earth’s Single moon • Composed of Basalt rock • Evidence on lava flows (Maria) • Tidally locked with earth. How the tides work • Tides – Caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon. • Water is pulled toward the moon causing a high tide. • Additionally, the solid portion of the earth is also pulled toward the moon leaving a bulge on the opposite side of the earth. • High tides occur on both sides of the planet hence you have high tide twice a day approximately every 12 hours. • http://videos.howstuffworks.co Alta High Astronomy m/hsw/10000-the-moon-tidesvideo.htm Spring and Neap Tides • When the sun and moon are aligned on the same side you get a higher than normal tide called a spring tide. • When the are on opposite sides you get a lower than normal tide called a Neap tide. Alta High Astronomy Seismic Activity Seismic Activity of our Planet • We have learned much about the interior of the earth from seismic waves. These waves, caused by earthquakes and the shifting of the tectonic plates come in two varieties: – Primary or Pressure waves (P-waves) – are the first to radiate from an earthquake, they are longitudinal in nature, – Secondary or Shear Waves (S-Waves) arrive later, these are transverse in nature Plate Tectonics • The ASTHENOSPHERE is the region of the earth that the plates slide over. • Plate boundaries sometimes collide or sub-duct resulting in seismic activity • We call these plate boundaries fault lines and we live right on top of one!! Habitability of Earth • The biosphere is the portion of earth in which all known life forms exist. It occupies a thin layer of air (atmosphere), water (hydrosphere), and land (lithosphere). Our atmospheric Gases • N • O2 • Trace gases like Argon Atmospheric Structure • Atmosphere – – Troposphere – Below 12 Km – – Stratosphere - Above 12 to about 50 Km – Mesophere – 50 – 80 Km – Ionosphere – Above 80 km – Magnetosphere – High above our atmosphere. – Troposphere – is where convection occurs due to surface heating, this gives us wind. – Ozone layer is between the stratosphere and the mesosphere – this protects us from much ultraviolet radiation. What Causes the Wind? • Wind is caused by Convection, which is defined as the mass movement of particles. • Solar heating of the air causes it to become less dense, hence warm air rises, and the denser, colder air falls to take its place. This causes what we call wind. Is Earth A Magnet? What Causes a Magnetic Field? • It is theorized that the earth’s magnetic field is caused by its “rapidly” spinning, molten, iron core. • This “dynamo” effect creates the magnetic field which surrounds the earth. • This is known as the dynamo theory of magnetism and is replicated by electrical generators which use a rapidly spinning loop of wire to generate electricity. • Magnetic fields always accompany electric fields. Earth’s Other Atmospheric Protection: The Magnetosphere • The Magnetosphere is a magnetic field which surrounds the earth. It consists of two doughnut shaped fields called the Van Allen Belts. • It protects the earth from harmful electromagnetic radiation and the buildup of electric charge which could discharge to the earth Side Effects