* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CPT 299 B486 Internet Skills
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
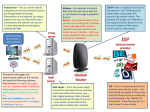
CPT 123 [299] Internet Skills Overview of the Internet Session One Class Notes DMWilliamson 1998 Objectives Describe the Internet and its history; and explain how to access the Internet Describe the WWW in context of hypertext and hypermedia Distinguish between a Web server and a Web client Objectives Distinguish between HTTP and HTML Use a browser to access the WWW Define a URL and give specific examples Describe how to enter a URL address in a browser Objectives Define a hyperlink Explain why hyperlinks within a document appear in two different colors Describe the various buttons on a browser Explain how to create a bookmark Overview of Internet The internet is a network of networks that connects computers across the country and around the world Overview of Internet Begun in 1969 to test the feasibility of a wide area computer network (WAN) over which people could share data and messages Overview of Internet Grew out of DOD experiment No central authority Each computer attached to the network (node) is equal to all others Overview of Internet Originally known as ARPAnet which consisted of four computers Today the Internet includes millions of computers worldwide Brings a worldwide library of on-line information resources concerning a myriad of topics to anyone who has connectivity to the Internet Overview of Internet Primary capabilities are information retrieval and worldwide communication Three Basic characteristics Immediacy, Two-way nature, and Global nature of medium Internet Services E-mail Most commonly used Internet service. Allows exchange of electronic messages among users. Multi-platform environment Some mail applications allow attachments with electronic messages An address of the message recipient is the major thing one needs to send electronic mail Internet Services Recipient’s address is usually the userid on the system, if system permanently attached to Internet or a user ID on an Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) system that holds mail until the user connects or requests mail. Example format userid@system [email protected] Internet Services Some mail applications allow the establishment of mailing lists or aliases for groups of Internet users Mailing lists or group aliases are similar to bulk mailings Electronic message is addressed to list and mailer routes the message to each user on the mailing list Example [email protected] Internet Services E-mail messages arrive at the mail server from a remote PC or from a node on a LAN. The message then leaves the local mail server and travels through a router (a special purpose computer) that ensures each message is sent to its correct destination. The mail message will pass through several networks to get to its destination. Internet Services Each network has its own router that determines how best to transmit the message closer to its destination. The network router considers the traffic on the network. A message passes from network to network until it arrives at the destination network. The message is then sent to the recipient, who has a mailbox on that network. Internet Services