* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organ Systems
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal self-avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
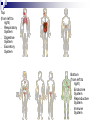
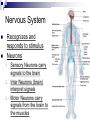
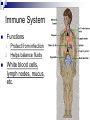
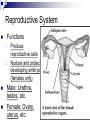
Organ Systems Objective 1 – 2 Levels of Organization Every organ system has the same basic design Cells Tissue Organ Organ System Cells are the building blocks Groups of Cells of the same type are Tissue Groups of different types of Tissue working together are an Organ Groups of Organs working together are an Organ System (Body System) 11 Organ Systems Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Top (from left to right) - Respiratory System - Digestive System - Excretory System Bottom (from left to right) - Endocrine System - Reproductive System - Immune System Homeostasis 10 body systems are required for survival They work together to maintain a stable internal environment (homeostasis) Nervous System Recognizes and responds to stimulus Neurons Sensory Neurons carry signals to the brain 2. Inter Neurons (brain) interpret signals 3. Motor Neurons carry signals from the brain to the muscles 1. Immune System Functions Protect from infection 2. Helps balance fluids 1. White blood cells, lymph nodes, mucus, etc. Reproductive System Functions Produce reproductive cells 2. Nurture and protect developing embryo (females only) 1. Male: Urethra, testes, etc. Female: Ovary, uterus, etc. Integumentary System Protective barrier Environment 2. Sunlight 1. Skin, hair, nails, etc. Skeletal System Functions: Structure 2. Support 3. Protection 4. Movement 1. Bones, cartilage, etc. Muscular System Functions Movement 2. Circulates Blood 3. Helps with Digestion 1. Muscles Circulatory System Functions Supplies cells with oxygen and nutrients 2. Removes waste 1. Heart, blood vessels Respiratory System Functions Provides oxygen 2. Removes carbon dioxide 1. Nose, trachea, lungs, etc. Digestive System Functions Converts food into nutrients the cells can use 2. Eliminates waste 1. Mouth, stomach, intestines, etc. Excretory System Eliminates waste Kidneys, bladder, urethra, etc. Endocrine System Functions Growth 2. Development 3. Metabolism 1. Pituitary gland, adrenals, pancreas, etc.