* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiration Student Copy
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
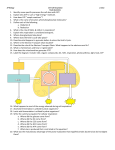
Respiration Your body does it millions of times at once! What is respiration? • Physiological definition: The act of exchanging gasses with the environment – mammals : inhale air, exhale CO2 • Biochemical definition aka cellular respiration: __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Respiration in mammals 1. Air is inhaled through the lungs (breathing) 2. _____________________ inside red blood cells capture O2 3. Blood with O2 is pumped through the body to all tissues 4. In capillaries, cells _____________________________________ _____________________________________ 5. O2 diffuses into the cell, and is _____________________________________ _____________________________________ molecules and make ATP How does O2 get into the blood? • Lungs are mostly a collection of ____________________________________, and they are surrounded by ______________________________________ • As you inhale, the alveoli fill up with air, which contains O2 • Because there is more O2 in the lungs than in the blood, ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ • Blood coming from the lungs is red because ______________________________________ How does O2 get into cells? • Cells and tissues receive all nutrients (food, O2, water) ______________________ • When blood from the lungs reaches cells, there are______________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ • At the same time, ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ where there is almost no CO2 How do animal cells use O2? • Cells break down glucose molecules to create ATP, the energy storing molecule • O2 is a crucial molecule in this process • Aerobic respiration – ______________________ – ______________________ – What our bodies do 95% of the time What happens without O2 • Anaerobic respiration – _________________________________________ – Much less efficient, takes place during emergencies when not enough O2 is available – Produces alcohol in yeasts – _______________________________________ • EX: When running away from a tiger, your muscles need lots of ATP FAST, but your heart can’t pump enough O2 for aerobic respiration to produce enough ATP. Your muscles switch to anaerobic respiration, and the next day, all that lactic acid makes that tissue sore. How does your body use ATP? • _________ is the most important energy provider for cells in all tissues • ____________________ ____________________ releases energy used in other reactions in the cell • ____________________ • ADP is recycled and the Pi group is put back on ___________________ Using ATP during active transport • ATP is ____________________ ____________________ by the Na+/K+ pump • Energy released during ATP hydrolysis is used ____________________ ____________________ concentration gradients • ADP is transported back ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ during cellular respiration Cellular Respiration • A very complicated molecular mechanism of transferring energy from glucose to ATP • Many steps that have to be memorized – Make flash cards and study them – Make up a song – Draw the mechanism over and over again – Explain it to your mom