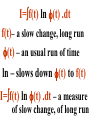* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download to the whole? - Vasil Penchev
Implicate and explicate order wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Matrix mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Scale relativity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity (alternative formulations) wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Time & Fractal Vasil Penchev, Assoc. Prof., Institute for philosophical research of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences [email protected] Forthcoming publication (where this report is posted): vasil7penchev.wordpress.com Five theses: 1. According quantum information, a physical meaning has not only Y2, but the y-function itself. 2. Two ways to describe a physical object exist: from the object to the whole (i.e. as moving object in space time, from the whole to the object (i.e. as a concrete asymmetry of a fractal structure representing the whole). And the rest three theses: 3. Y-function represents such a concrete asymmetry of a fractal structure in space-time. 4. Physical quantity representing a linear and Hermitian operator in Hilbert space (i.e. Y1Y2 transformation) means some movement of an object in space-time expressed by means of a change of its definitive asymmetry with regards to the whole. 5. Being of the physical quantity is information. The meaning of the report One of the most difficult problems of the philosophy of physics: ontological compatibilty of relativity and quantum mechanics The first one is a local theory, the second is a global one. For example, compatibility of: • Relativity: World line Time From a part to the whole Constancy Actuality • Quantum mechanics: Y-function ? Fractal structure? From the whole to a part Probability Virtuality Building Up of: World line: point by point - any point is a moment of time from a part (here and now) to the whole as development in time Y-function: level by level - any level is a level of fractal structure from the whole (here and now), the 1st level, to the part as ‘th’ level Meaning of: • Function of time Time – t E = m.c2 ds = icdt + dr • Fractal structure Frequency n = t-1 E = ħ.n dE = idE+cdp dA = ds.dE = 0, i.e ‘time “” fractal’ 2. (1) dA = ds.dE = 0, i.e. ‘time “”fractal’ What may it mean for a part not to be ‘’ to the whole? • a part an element • the whole the set a: a {a} = a a: a {a} = a: : b(0,1), b=:0,1 ‘’, ‘’ 1 About • Constancy: • Probability: So constancy converts into a special case of So probability is the relation of a relation probability, i.e between ‘part’ the relation of ‘part’ and ‘whole” and ‘whole’ Any element: • represents the whole as identity of the levels of fractal similarity • This is the basis of a vector space (for example Hilbert space) • represents it itself as difference (deflection) between the levels This is an element of a vector space So any motion as a relation between two elements may be represented by: • change of the basis of the vector space (i.e. covariant change) • change of the element of the vector space (i.e. contravariant change) Relativity: no experience might differ anyway change of the basis from change of the element From “special” to “general” relativity: Any motion “by itself” represents a change of a vector space. The simplest special case is then when the vector space is “flat”: the vector space coincides with its conjugate space (for example Riesz theorem) More about that simplest special case: Any part is independent of the whole, to which ‘belongs’. We may also say that the whole is always the same. That’s way the relation between ‘whole’ and ‘part’ is equal to some property of the part The simplest special case about subjective and objective probability • Subjective probability: waiting for the future • Objective probability: experiencing the past They are if and only if : 1) any future event is independent of any past event; 2) present is but a point Present is curvature of time! • subjective probability • waiting • objective probability • experiencing The “length” of present is the measure of time curvature! This time length is period of de Broglie’s wave, so it is inversely of mass: the macro-world is already “timely flat”! Now about: whether any future event is independent of any past one? • The future event repeats merely the preceding • The future event is absolutely independent of any past one The future event may be causally conditioned by any past one! Get started a new comprehension of causality! • Fractal repetition • Absolute independence of future from past (Markov chain) Causality represented by implication Model: Cause ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘1’ ‘1’ Effect ‘0’ ‘1’ ‘0’ ‘1’ Causality ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘0’ ‘1’ AB (AB) (A) • a fractal part: effect repeats ‘fractally’ cause • a Markov part: effect is absolutely independent of cause Probabilistic causality means: Cause causes effect with some probability ‘p’: AB If cause is available, then effect is available with probability p. If p = 1: classical causality; if p=0:A, B are absolutely independent Which would the difference between correlation and probabilistic causality be? • Correlation pre- • Probabilistic suposes that there causality excludes is a real ‘true’ such a real ‘true” cause, which is a hidden (compare cause with ‘hidden parameter’) • A correlates with B• A causes B ‘probabilistically’ It means for us to reject: BB Then ‘probabilistic causality’ means the following: • The universal set being common for both A, B doesn’t exist. We may think that they belong to two different univer-sal sets • We may also think that the universal set changes: t1t2 (AUt1 ) (BUt2 ) So some elements of A may disappear, but new elements may appear in B Returning to classic causality… • The whole is the same • Time is Newton one • Energy is conserved • Correlation requires for a hidden cause to exist • All are equal Returning back to probabilistic causality… • The whole is not the same • Time is not Newton one • Energy is not conserved • There are correlations, but there aren’t hidden parameters This is the Realm of quantum mechanics and information Probabilistic causality generalizes per se… relativity Now: no difference whether any part or the whole changes Probabilistic causality means relativity of whole and part Generalized relativity presupposes that motion of whole and motion of part are equivalent We know much about the It means change of a fracmotion of tal structure into part. What another. That is not a about the change in time. motion of Heidegger has spoken of whole? history of being We would be able to comprehend ‘history of being’ as ‘change of whole’ • On the one hand, • On the other hand, better to think for we may think ‘history of being’ to ‘history of being’ be as Braudel’s as Plato’s eons changing each other long run [la longue in millenniums durée] From our, human point of view… And now: an unexpected comparison … with the math definition of info: I=f(t) ln f(t) .dt I=f(t) ln f(t) .dt f(t)– a slow change, long run f(t) – an usual run of time ln – slows down f(t) to f(t) I=f(t) ln f(t) .dt – a measure of slow change, of long run Sat sapienti (a hint in future) • The function of • The function of ln ln transforms transforms an multiplicative axis of Hilbert (fast) groups space into an into additive inertial reference (slow) groups, so frame, so a point a field into a of it into a world (double) group line Two points of view: 1. From the whole the motion is motion of whole. So any physical quantity is a linear (Hermitian) transformation of the whole – in quantum mechanics 2. From the part: the motion is motion of part. So any physical quantity is a linear transformation of part’s world line – in relativity The concept of (quantum) information units both of them A= y(x) F [y*(x)] .dx Any physical quantity in QM F: y(x) F [y*(x)] is a transformation of the whole – the measuring instrument I= World line (t).ln y(t).dt More about: I= W (t).ln y(t).dt Granted F: ln y(t) = Force{W (-t)} Full analogy: Operator in QM, F y(x) F [y*(x)] .dx Physical quantity A Classical force acting ‘now’, F W (t). F{W(-t)}.dt Information of I motion I A general principle in two forms: • Expressed by the motion of whole: Quantum mechanics Operator Physical quantity • Expressed by the motion of part: Relativity Reality as virtuality Reality as actuality Force Motion information A basic idea of the report: A basic idea of the report: No Already Boundary – since 1989’s falling the wall! Two ways to describe a physical object exist: • TA way is: from the • AAnother way is: from the whole to object to the whole the object – as a – as a moving object concrete asymmetry in space-time of a fractal structure representing the whole Y-function represents such a concrete asymmetry of a fractal structure in space-time Physical quantity means some motion of an object in space-time expressed by means of a change of its definitive asymmetry with regards to the whole Being of the physical quantity is information