* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atomic emission spectrum
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Upconverting nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
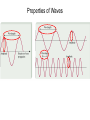
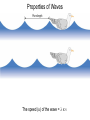
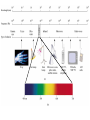
Modern Atomic Theory Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Chapter 11 Properties of Waves Properties of Waves The speed (u) of the wave = l x n electromagnetic waves Electromagnetic radiation is the emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. All electromagnetic radiation lxn=c A photon has a frequency of 6.0 x 104 Hz. Convert this frequency into wavelength (nm). Does this frequency fall in the visible region? Why all this info about light??? • atomic emission spectrum of an element. • The emission spectrum of white light is continuous. • Atomic emission spectra consist of relatively few lines and are discontinuous. • Each line corresponds to a specific amount (quantum) of energy being emitted. • The emission spectra for each element is unique. Classical physics does not explain the emission spectra of atoms. Energy (light) is emitted or absorbed in discrete units (quantum). E=hxn Planck’s constant (h) h = 6.63 x 10-34 J•s When copper is bombarded with high-energy electrons, X rays are emitted. Calculate the energy (in joules) associated with the photons if the wavelength of the X rays is 0.154 nm. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oUolVZIuv18 Photoelectric Effect • Light quanta are called photons. • Light has a “dual nature” as it exhibits wave-particle behavior. • In the photoelectric effect metals eject electrons when light shines on them. • Einstein used his particle theory of light to explain the photoelectric effect. • He recognized there is a threshold value of energy below which this effect does not occur. • Since E = h x v, if the frequency and therefore the energy of photons is too low, the photoelectric effect does not occur. http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=B2E7CD0F-A754-4BA4-8D00-B0DE326F1038&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US