* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Strategy Implementation
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
Public service motivation wikipedia , lookup
Management consulting wikipedia , lookup
High-commitment management wikipedia , lookup
Porter's generic strategies wikipedia , lookup
Strategic leadership wikipedia , lookup
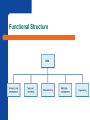
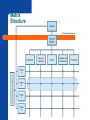
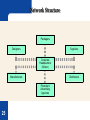
Strategy Implementation HCAD 5390 Organizational Structure Organizational – Selecting the structure and control systems that are most strategically effective for pursuing sustainable competitive advantage. The – – design role of structure and control To coordinate strategy implementation. To motivate and provide incentives for superior performance. The Role of Organizational Structure Building – Differentiation in the allocation of people and resources to create value. – blocks of organizational structure Vertical differentiation in the distribution of decision-making authority. Horizontal differentiation in dividing up people and tasks into functions and divisions. Integration The means used in coordinating people and functions to accomplish organizational tasks. Differentiation, Integration, Bureaucratic Costs Bureaucratic costs and strategy implementation: – – – – Bureaucratic costs increase with organizational complexity. More differentiation = more managers. More integration = more coordination. Better strategy implementation = better bottom-line performance and profitability. Vertical Differentiation Span – of control (division of authority) The number of subordinates that a single manager directly manages. Organizational – Flat structures – hierarchy choices Few organizational levels Wide spans of control Tall structures Many organizational levels Narrow spans of control Tall and Flat Structures Problems with Tall Structures Principle – of minimum chain of command Maintaining a hierarchy with the least number of levels of authority needed to achieve a strategy. Sources of bureaucratic costs: Centralization or Decentralization Authority – patterns in organizations: Centralized – Decision making retained in the hands of upper-level managers. Decentralized Decisions delegated to lower levels in the organization. Centralization (Structural) Choice? Advantages of decentralization – – – Reduced information overload on upper managers. Increased motivation and accountability throughout organization. Fewer managers; lower bureaucratic costs. Advantages of centralization – – – – Easier coordination of organizational activities. Decisions fitted to broad organizational objectives. Exercise of strong leadership in crisis. Faster decision making and response. Horizontal Differentiation Focus is on division and grouping of tasks to meet business objectives. Simple structure: – – – – Characteristic of small entrepreneurial companies. Entrepreneur takes on most managerial roles. No formal organization arrangements. Horizontal differentiation is low. Structure Follows Strategy: – 11 Changes in corporate strategy lead to changes in organizational structure Structure Follows Strategy: • • • • • 12 New strategy is created New administrative problems emerge Economic performance declines New appropriate structure is invented Profit returns to its previous levels Stages of corporate development Simple Structure Functional Structure Divisional Structure Beyond SBU’s 13 Simple Structure: – Stage I: Entrepreneur – Decision making tightly controlled – Little formal structure – Planning short range/reactive – Flexible and dynamic 14 Functional Structure: – Stage II: 15 Management team Functional specialization Delegation decision making Concentration/specialization in industry Divisional Structure: – Stage III: 16 Diverse product lines Decentralized decision making SBU’s Almost unlimited resources Beyond SBU’s: – Stage IV: 17 Increasing environmental uncertainty Technological advances Size & scope of worldwide businesses Multi-industry competitive strategy Better educated personnel Functional Structure Advantages – – – Task grouping facilitates specialization and productivity. Better monitoring of work processes, reduced costs. Greater control over organizational activities. Disadvantages – – – – Functional orientation creates communication problems. Performance and profitability measurement problems. Location versus function problems (coordination). Strategic problems due to structural (vertical and horizontal) mismatches. Functional Structure Mutlitdivisional Structure Advantages – – – – Enhanced corporate control by division Enhanced strategic control of each SBU in portfolio Growth is easier. New units don’t have to be integrated across organization Stronger pursuit of internal efficiencies. Performance of individual units is readily measurable. Disadvantages – – – – – – Establishing the divisionalcorporate authority relationship Distortion of information by divisions Competition for resources by divisions Transfer pricing problems between divisions Short-term research and development focus Bureaucratic costs Multidivisional Structure Matrix Structure Advantages – – – – Flexibility of the structure and membership Minimum of direct hierarchical control Maximizes use of employees’ skills Motivates employees; frees up top management Disadvantages – – – High bureaucratic costs High costs (time and money) for building relationships Two-boss employee’s role conflict Matrix Structure Two-boss employee Network Structure: – – “non structure” – elimination of in-house business functions Termed “virtual organization” 24 Useful in unstable environments Need for innovation and quick response Network Structure Packagers Designers Suppliers Corporate Headquarters (Broker) Manufacturers Distributors Promotion/ Advertising Agencies 25 Effective implementation requires: – Leadership 26 Leading people to use their abilities and skills most effectively and efficiently to achieve organizational objectives Staffing follows strategy: – Matching the manager to the strategy Executive type – 27 Executives with a particular mix of skills and experiences Executive Types: – – – – – 28 Dynamic industry expert Analytical portfolio manager Cautious profit planner Turnaround specialist Professional liquidator Matching Chief Executive “Types” with Strategy Business Strength/Competitive Position Strong Average Growth—Concentration Industry Attractiveness Dynamic Industry Expert Retrenchment— Save Company Turnaround Specialist Stability Cautious Profit Planner Growth—Diversification Analytical Portfolio Manager 29 Weak Retrenchment— Close Company Professional Liquidator Managing corporate culture: – Corporate culture 30 Affects firm’s ability to shift its strategic direction Strong tendency to resist change Corporate culture should support the strategy Strategy-Culture Compatibility: – Consider the following: 31 Is the planned strategy compatible with the firm’s current culture? Can the culture be easily modified to make it more compatible with new strategy? Is management willing to make major organizational changes? Is management committed to implementing the strategy? Managing corporate culture: – Communication 32 Key to effective management of change Rationale for strategic change should be communicated to all What Is Organizational Culture? Culture – – The collection of values and norms shared by people and groups in an organization. Shared values and a common culture increase integration and improve coordination. Values – Beliefs and ideas about common goals and proper behaviors. Norms – Act as guidelines or expectations that prescribe acceptable behavior by organizational members. Organizational Culture Ways of transmitting organizational culture: Culture and Strategic Leadership The – influence of the founder Initial cultural values and management style is imprinted on the organization by its founder. Organizational – structure Structure follows strategy. Strategic leadership affects the cultural norms and values that develop in the organization. Strategic Reward Systems Individual – – – – reward systems Piecework plans Commission systems Bonus plans Promotion Group and organizational reward systems – – – – Group-based bonus systems Profit sharing systems Employee stock option systems Organization bonus systems