* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
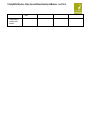
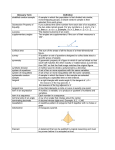
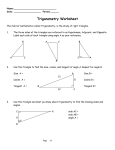
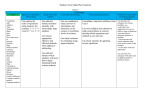
Download Tracking Shape, space and Measure/Geometry Learning Objectvies
Anti-de Sitter space wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Metric tensor wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Four-dimensional space wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup