* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geographic Information Systems - Centre for Modeling and Simulation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
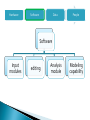
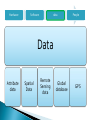
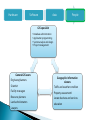
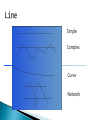
Center for Modeling & Simulation Introduction to GIS ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ General Definitions Concept of space and time History Components Objectives / why use GIS IT can be a physical entity like a solar system or a conceptual entity like a democratic political system All the systems have following characteristics 1. 2. 3. 4. Constructed to achieve certain basic objectives or functions Their continuing existence depends on the ability to satisfy the intended objectives Composed of many interrelated parts, which may be operational systems themselves They operate individually and interact with one another according to certain rules What is an Information System It is a special class of systems Collection of data and tools for working with those data which are in analog or digital format about the phenomenon in the real world Has specific objectives of collecting, storing, analyzing and presenting information in a specific manner GIS as an Information System It is a special class of Information system Word Geographic has two implications as “earth” and “Geographic space” • “Earth” implying all the data are pertinent to earth’s features and resources including human activities associated with these features • “Geographic space” relates to the system developed to solve the geography i.e location distribution, pattern and relationship within a specific geographical framework reference This makes it a unique system as it focuses on geographic data and their applications for spatial problems Information System Nonspatial Spatial accounting/ banking etc Geographic Information Systems Other spatial information systems Eg CAD/CAM Other Geographic information systems Socioeconomic information system Biophysical Information system Land Information systems Data: collection of facts or figures relating to places, people, things, events and concepts represented as numerical values, alphanumeric characters, symbols and signals Information: data transferred in a form meaningful to the user through structuring, formatting, conversion and modeling Knowledge: Using the Knowledge the user transfers the data into information to aid the decision making Intelligence: When the user deploys the knowledge to formulate principles and perceive relationships special form of spatial data characterized by Reference Geographic space i.e data registered to coordinate system Representation at geographic scale i.e data are normally recorded at relatively small scales Grid co-ordinate Place name Latitude / Longitude Post code Description Distance & bearing Kingston Centre for GIS 9 A system of hardware, software and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling and display of spatially referenced data for solving complex planning and management problems (Rhind, 1989). A computer system capable of assembling, storing, manipulating and displaying geographically referenced information (USGS, 1997) A set of computer based systems for managing geographic data and using this data to solve spatial problems. Spatial information is always related to geographic space and time Geographic space is the space of topography, landuse/landcover, climatic, cadastral and other features of the topographic world. Geographic time is the time whose effects can be observed in this geographic space Thus GIS data consists of spatio-temporal data that can be described, measured and stored in the information system • Dates back to 1960s • Initially developed by US Bureau of Census, USGS, ESRI, Canadian Geographic Information systems and notable organizations in U.K. • In early 1970’s table data structures to store and analyze map data became dominant creating topology in GIS • During 1980’s the minicomputers and workstations become dominant and the relational database became standard for the spatial data structures • 1990’s recognition of geoinformatics as a professional activity • Commercial agencies like ESRI, Intergraph, Laserscan, Autodesk etc started developing the commercial products Stage of Formative years development Maturing technology GI infrastructure Time Frame 1960-1980 1980-mid.1990s Mid.1990s-present Technical environment •Mainframe computers •Proprietary software •Proprietary data structures •Mainly raster-based •Mainframe and minicomputers •Geo-relational data structure •Graphical user interface •GPS, redefinition of datum remote sensing •Workstations and PCs •Network/Internet •Open system design •Multimedia •Data integration •Enterprise computing •Object related data model Major users •Government •Universities •Military •Government •Universities •Utilities •Business •Military •Government •Universities •Utilities •Business •Military •General public Major application areas •Land and resource management •Census •Surveying and mapping •Land and resource management •Census •Surveying and mapping •Facilities mapping •Market analysis •Land and resource management •Census •Surveying and mapping •Facilities mapping •Market analysis •Utilities •Geographic data browsing Hardware Software data People Hardware Platforms Input device Output device Personal computers Scanners Printers workstations Digitizers Plotters Minicomputers Tapes / CD’s Mainframe Keyboard / Monitors Hardware Software Data People Software Input modules editing Analysis module Modeling capability Hardware Software data People Data Attribute data Spatial Data Remote Sensing data Global database GPS Hardware Software data People GIS specialist • • • • General GIS users Engineers/planners Database administration Application programming System analysis and design Project management Geographic Information viewers Scientist Traffic and weather condition Facility managers Property assessment I Resource planners Locate business and services Land administrators education Lawyers Point data Vector data Raster data Attribute data e.g. wells, sample sites, huts, schools, clinics Simple Complex Curve Network Attached to Points Lines Polygons • Maximise the efficiency of planning and decision making • Provides efficient means for data distribution and handling • Elimination of redundant data base – minimise duplication • Capacity of integrate information from many sources • Complex analysis/query involving geographical referenced data to generate new information • What Exists at a particular location --- Location • Identifies locations where certain conditions exist --- Condition • What has changed since --- Trends • What spatial pattern exists --- Patterns • What if ……? --- Modeling