* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download legal aspects of medication administration
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
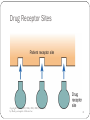
LEGAL ASPECTS OF MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION CHAPTER 3 LEVELS OF LAW FDA WATCHES OVER TESTING, APPROVAL AND MARKETING OF NEW DRUGS 1. FEDERAL LAWS CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES PRESCRIPTION DRUGS OTC MEDICATIONS 2. STATE LAWS AND REGULATIONS 3. INDIVIDUAL HOSPITALS OR AGENCY RULES Federal Legislation Harrison Narcotic Act of 1914 – limited indiscriminate use of addictive drugs Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938 – gave authority to government to determine the safety of a drug prior to marketing, labeling, specification, and advertising Durham-Humphrey Amendment of 1952 – restricted number of prescription refills Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 3 CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES ACT OF 1970 5 DRUG SCHEDULES 1. HIGH LEVEL OF DEPENDENCY 2. HIGH LEVEL OF DEPENDENCY 3. HIGH LEVEL BUT LESS THAN 1&2 4. LOW LEVEL COMPARED TO 3 5. LOW LEVEL COMPARED TO 4 Controlled Substances Nurses may possess these only if: They are administering the drugs to the patient for whom they were prescribed They themselves are the patient for whom the physician has prescribed the drug They have been delegated the responsibility for the unit supply It is a crime for the nurse to have a controlled substance UNLESS 1 OF THE 3 ABOVE CONDICTIONS ARE MET. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 5 CONTROL OF NARCOTICS MUST COUNT THE NARCOTICS BETWEEN AN ON- COMING AND OFF-GOING STAFF MEMBERS EVERY 8 HOURS CHART IN MAR AND NARCOTIC BOOK ALL NARCOTICS FOR A DISCHARGED/ DECEASED PATIENT ARE RETURNED TO PHARMACY FOR A COUNT AND DISPOSAL WASTED/ USED MEDICATION MUST BE WITNESSED ON DISPOSAL NO DRUG SHARING DEPENDENCE PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE – PHYSIOLOGICAL NEED TO RELIEVE PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS PHYSCHOLOGICAL DEPENDENCE – ANXIETY, STRESS, OR TENSION THAT IS FELT IF THE PERSON DOES NOT HAVE THE MEDICATION CAN HAVE ONE, BOTH OR NEITHER OTC MEDICATIONS DO NOT NEED PRESCRIPTION PURCHASED AT DRUG STORES LOW DOSAGE LOW RISK FOR SIDE EFFECTS WARNING LABELS AND SPECIAL INFORMATION AVAILABLE TO PURCHASERS HERBAL MEDICATIONS STATE LAW & HEALTH CARE AGENCIES CHECK THE NURSE PRACTICE ACT IN THE STATE IN WHICH YOU WORK PROFESSIONAL REPSONSIBILITY: ADMINSTER DRUGS APPROPRIATELY, ETHICALLY AND TO BEST OF ABILITY LEGAL RESPONSIBILITY: GOOD JUDGMENT PROPER ACTIONS IN CARRYING OUT PROFESSIONAL DUTY State Nurse Practice Act Determines the level of authority and responsibility of the nurse Different levels of nursing will have different levels of authority and accountability Nurses must adhere to the Nurse Practice Act of the state in which they are practicing Responsibilities may vary in state Nurse Practice Acts Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 10 Nursing Responsibilities All nurses have legal responsibility for their actions. The Nurse Practice Act determines the level of responsibility and authority of the nurse. Nurses must have the authority to delegate to a person with the authority to carry out the task. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 11 NURSE LICENSURE COMPACT HOLD A LICENSE IN ONE STATE BUT ABLE TO WORK IN A STATE WITHIN THE COMPACT WWW.NCSBN.ORG NEW JERSEY IS NOT YET IN THE COMPACT AGENCY/ INSTITUTIONAL POLICIES MAY BE MORE RESTRICTIVE OR SPECIFIC THAN STATE NURSE PRACTICE ACT WRITTEN POLICIES – EDUCATIONAL PREPARATION POLICIES ORIENTATION PARTICULAR POLICIES, PROCEDURES, AND RECORD KEEPING RULES *EXPECTED TO USE NURSING PROCESS IN MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION Question 1 Of the following, who is not permitted by law to prescribe medication? 1. 2. 3. 4. Physician assistant LPN Dentist Nurse practitioner Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 14 DELEGATION THE RESPONSIBILITY FOR PERFORMING A T ASK IS PASSED FROM ONE PERSON TO ANOTHER BUT THE ACCOUNTABILITY FOR WHAT HAPPENS (OUTCOME) REMAINS WITH THE ORIGINAL PERSON MUST HAVE THE AUTHORITY TO DELEGATE THE RECEPTOR OF DELEGATION MUST BE ABLE/ HAVE AUTHORITY TO PERFORM THE DELEGATED TASK ADMINISTRATION CHECK MAR AGAINST THE ORIGINAL ORDER BAR CODING FOR MEDICATION DELIVERY USE THREE CHECKS FOR SAFETY BEFORE TAKING FROM DRUG CART BEFORE PREPARING, MEASURING DOSE BEFORE OPENING THE MEDICATION AT THE BEDSIDE, OR PUTTING THE BOTTLE BACK DRUG DISTRIBUTION CENTERS FLOOR STOCK (FROWNED UPON) INDIVIDUAL PRESCRIPTION ORDER SYSTEM UNIT DOSE COMPUTERIZED OR AUTOMATED DISPENSING SYSTEM (PIXIS) NARCOTIC DISPENSING: Locked cabinet within locked med room Signed out in narcotics book and MAR Counted each shift REQUIREMENTS FOR ORDERS PATIENT’S FULL NAME DATE WRITTEN NAME OF DRUG ROUTE, DOSE AND FREQUENCY DURATION SIGNATURE OF PRESCRIBER ADDITIONAL NEEDED DETAILS Avoid grapefruit Empty stomach Take with food, etc TYPES OF ORDERS STANDING ORDER EX: TYLENOL 400mg PO DAILY STAT ORDER BENADRYL 50 mg PO NOW SINGLE ORDER DEMEROL 50 mg IM X1 ON CALL TO OR AS NEEDED (PRN) ORDER IBUPROFEN 200mg PO PRN EVERY 6 HOURS FOR TEMP 101 OR GREATER MEDICATION ERRORS OOPSIES DO HAPPEN CHECK THE PATIENT STATUS FIRST NOTIFY THE PHYSICIAN MONITOR THE PATIENT NOTIFY NURSING SUPERVISOR CHART EXACT CIRCUMSTANCES INCIDENT REPORTS GO TO RISK MANAGEMENT; DO NOT CHART IN PATIENT RECORD THAT AN INCIDENT REPORT HAS BEEN FILED INCIDENT REPORTS BE EXACT BE FACTUAL SEQUENTIAL HAPPENINGS AS BEST YOU CAN RECALL KEEP A PERSONAL COPY. USED TO ASSESS FOR PATTERNS OF ERRORS COULD BE A SYSTEM ERROR OR A PERSONAL DEFICIENCY MEDICATION SAFETY CHECK, CHECK AND CHECK AGAIN IF NOT SURE, LOOK IT UP DOUBLE CHECK CRITICAL MEDS ALWAYS USE 2 CHECKS FOR PATIENT ID NEVER LEAVE MEDS FOR THE PATIENT TO TAKE LATER NEVER EVER RECAP A USED NEEDLE DISPOSE OF ITEMS PROPERLY Question 2 Morphine is in the category of: 1. 2. 3. 4. Supplements. Unscheduled drugs. Scheduled drugs, or controlled substances. Over-the-counter medications. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 23 Question 3 Which of the following statements is true regarding herbal products? 1. 2. 3. 4. Very few people try herbal products. Herbal products are regulated by the federal government. Herbal products are considered supplements. There is a great amount of information known about side effects. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 24 Chapter 4 Foundations and Principles of Pharmacology Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 25 Learning Objectives Define the key words used in pharmacology and medication administration Explain differences between the chemical, generic, official, and brand names of medicines List the basic types of drug actions Describe the four basic physiologic processes that affect medications in the body Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 26 Drug Names Generic name Trade name; ® symbol Chemical name Official name Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 27 Drug Receptor Sites Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 28 Drug Attachment Agonist Antagonist Partial Agonist Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 29 Four Processes of Drug Utilization Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 30 Absorption How a drug enters the body and passes into body fluids and tissues Absorption processes: Diffusion—high concentration to lower concentration Filtration—a filter prevents passage of certain molecules Osmosis—diffusion through a semipermeable membrane from a less dense solution to a more dense solution Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 31 Distribution Blood system Lymph system Barriers: Blood-brain Placental Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 32 Metabolism Biotransformation First-pass effect Affected by genetic and developmental factors Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 33 Excretion GI tract Kidneys Lungs Skin Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 34 Question 1 A nephrotoxic drug is harmful to the: 1. 2. 3. 4. Skin. Kidneys. Lungs. Liver. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 35 Basics of Drug Action Desired action Adverse reactions Idiosyncratic reactions Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 36 Bioequivalence Define Brand name versus generic Generic equivalent Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 37 Drug Interactions Drug action may depend on ability to dissolve quickly or slowly Controlled by medication form Oil-based drugs Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 38 Food, Alcohol, and Drug Interactions Food interactions Alcohol interactions Drugs and laboratory tests Chronotherapy Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 39 Question 2 An idiosyncratic response is a drug reaction that is: 1. 2. 3. 4. Expected. Predicted. Unique. Anticipated. Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 40 Question 3 Which medicine is more likely to cause an allergic reaction? 1. 2. 3. 4. Acetaminophen Aspirin Cough suppressant Antidepressant Copyright © 2013, 2010, 2006, 2003, 2000, 1995, 1991 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 41 QUESTIONS?