* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrhythmias
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
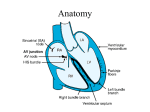
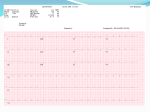
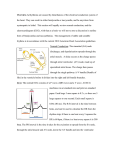
Arrhythmias ED SHO TEACHING C Brown, August 2015 Aims To be able to confidently recognise arrhythmias in patients presenting to the ED To describe the principles of management of brady and tachyarrhythmias in the ED Objectives Overview of cardiac electrophysiology Review of Resuscitation council guidelines for ECG interpretation Tachyarrhythmia management Bradyarrhythmia management Clinical Overview: Arrhythmia Arrhythmias are common in the ED population either as a cause of or a consequence of their presenting complaint The overarching principle is to decide if the patient is COMPROMISED or not as a result of their arrhythmia Having a systematic approach to describing an arrhythmia helps in the diagnosis and subsequent management A compromised position…. What “adverse features” may a patient with an arrhythmia have to indicate they are compromised? SHOCK SYNCOPE MYOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA HEART FAILURE The presence of these features indicate that a patient may be compromise and should mandate Early senior involvement Assessment of patient using ABCDE approach Full monitoring O2 + IV access Management of reversible causes Emergency management of arrhythmia instigated Resuscitation council UK Rhythm Recognition UK Resuscitation Council 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular Is the QRS complex width normal or prolonged? Is atrial activity present? How is atrial activity related to ventricular activity? Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology & the ECG Ventricular repolarization Ventricular depolarization Case 1 25 year old male, presented to ED with palpitations How’s the Patient Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width narrow or broad ? Is atrial activity (P wave) present ? Is every P wave followed by a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Does the tracing look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: Narrow Complex tachycardia or Supraventricular Tachycardia Case 2 70 year old female admitted following a mechanical fall resulting in a fractured ankle requiring admission for ORIF. How’s the Patient • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width narrow or broad ? Is atrial activity (P wave) present ? Is every P wave followed by a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Does the tracing look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: Atrial Flutter Case 3 50 year old female admitted with palpitations How’s the Patient Remember the Steps • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? (QRS) rate ? Is Is the the QRS QRS rhythm rhythm regular regular or irregular ? or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width normal narrow or prolonged broad ? ? Is atrial activity (P wave)? present present ? How is atrial activity related Is every P wave followed to ventricular activity ? by a QRS and is every QRS Then preceded by a P wave ? Does it look normal ? Then Where aretracing any changes? Does the look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: Atrial Fibrillation Case 4 A 45 year old male admitted with diarrhoea. PMH: Alcohol excess How’s the Patient • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is Is the the QRS QRS rhythm rhythm regular regular or irregular ? or irregular ? Is the QRS QRS complex complex width Is the width narrow or broad ? normal or prolonged ? Is atrial activity (P wave) Is atrial activity present ? present ? How is atrial activity related Is every P wave followed by to ventricular activity ? a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Then Does it look normal ? Does look Wherethe aretracing any changes? normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: Torsades de pointes Case 5 80 year old female admitted following a collapse How’s the Patient • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is Is the the QRS QRS rhythm rhythm regular regular or irregular ? or irregular ? Is the QRS QRS complex complex width Is the width narrow or broad ? normal or prolonged ? Is atrial activity (P wave) Is atrial activity present ? present ? How is atrial activity related Is every P wave followed by to ventricular activity ? a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Then Does it look normal ? Does look Wherethe aretracing any changes? normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: Ventricular Tachycardia Fusion & Capture beats • A fusion beat (red arrow) occurs when a supraventricular and a ventricular impulse coincide to produce a hybrid complex. • It indicates that there are two foci of pacemaker cells firing simultaneously: a supraventricular pacemaker (e.g. the sinus node) and a competing ventricular pacemaker (source of ventricular ectopics). • The fusion beats are of intermediate width and morphology to the supraventricular (blue arrows) and ventricular complexes. Management of Tachyarrhythmia's Case 6 74 year old female awaiting sedation for dislocated shoulder. PMH: Angina How’s the Patient • • • • • • > 5 little squares • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width narrow or broad ? Is atrial activity (P wave) present ? Is every P wave followed by a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Does the tracing look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: 1st Degree Heart Block Case 7 How’s the Patient • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? Is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width narrow or broad ? Is atrial activity (P wave) present ? Is every P wave followed by a QRS and is every QRS preceded by a P wave ? Then Does the tracing look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: 2nd Degree Heart Block 2:1 block Case 8 How’s the Patient Remember the Steps • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? (QRS) rate ? Is Is the the QRS QRS rhythm rhythm regular regular or irregular ? or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width normal narrow or prolonged broad ? ? Is atrial activity (P wave)? present present ? How is atrial activity related Is every P wave followed to ventricular activity ? by a QRS and is every QRS Then preceded by a P wave ? Does it look normal ? Then Where aretracing any changes? Does the look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: 2nd Degree Mobitz Type 1 AV Block Wenckebach Case 9 85 year old man. Referred by GP as ?TIA episodes. Diverted to ED en route as unresponsive in ambulance. How’s the Patient Remember the Steps • • • • • • • • Remember the Steps Is there electrical activity? Is there electrical activity? What is the ventricular What is the ventricular (QRS) rate ? (QRS) rate ? Is Is the the QRS QRS rhythm rhythm regular regular or irregular ? or irregular ? Is the QRS complex width normal narrow or prolonged broad ? ? Is atrial activity (P wave)? present present ? How is atrial activity related Is every P wave followed to ventricular activity ? by a QRS and is every QRS Then preceded by a P wave ? Does it look normal ? Then Where aretracing any changes? Does the look normal ? Where are any changes? Findings: 3rd Degree Heart Block And finally….. Make sure you can recognise this one!