* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 25 Section 1 The Cold War Begins
Survey
Document related concepts
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
War of ideas wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
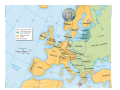
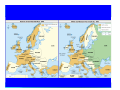
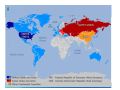
Section 1 Chapter 25 Section 1 The Cold War Begins The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Focus Question How did U.S. leaders respond to the threat of Soviet expansion in Europe? World War II convinced U.S. leaders that the policies of isolationism and appeasement had been mistakes. To counter the growing Soviet threat, they sought new ways to keep the U.S. safe and protect its interests abroad. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 A Clash of Ideologies Despite their alliance during World War II, the U.S. and the Soviet Union had little in common. The United States was a capitalist democracy. The American people valued freedom and individual rights. The Soviet Union was a dictatorship. Stalin and the Communist Party wielded total control over the lives of the Soviet people. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Postwar Goals These differences were apparent as the Allies made decisions about the future of postwar Europe. Postwar Goals U.S. and Britain U.S.S.R. Strong, united Germany Weak, divided Germany Independence for nations of Eastern Europe Maintain Soviet control of Eastern Europe The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins AS Section 1 The Big Three at Odds When the Big Three met at Yalta, Stalin agreed to allow free elections in Eastern Europe, yet free elections were not held. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Churchill Roosevelt Stalin Section 1 The Big Three at Odds When the Big Three met again at Potsdam, the U.S. and Britain pressed Stalin to confirm his commitment to free elections; Stalin refused. The Big Three alliance crumbled. The Begins Cold War Begins AttleeThe Cold War Truman Stalin Section 1 The Iron Curtain The nations of Eastern Europe and the eastern part of Germany became satellite states of the Soviet Union, separated from the free world by an “iron curtain.” Cold War Europe, 1949 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Containment After the Big Three split at Potsdam, the Cold War struggle between the world’s two superpowers began. The Soviets were determined to spread communism to other lands. The Americans were determined to stop them. Containing communist expansion became the United States’ top priority. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Truman Doctrine With the Truman Doctrine, the U.S. promised to support nations struggling against communist movements. Money was sent to Greece and Turkey to provide aid to people who needed it. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Greek Civil War Note the use of captured German equipment Approximately 1500 Americans served in Greece and more than $900 million in military ands civilian aid was given The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Marshall Plan The U.S. sent about $13 billion to Western Europe under the Marshall Plan. The money provided food, fuel, and raw materials to help rebuild war-torn cities and towns. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Marshall Plan The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Divided Germany Germany, and the city of Berlin, became flashpoints in the Cold War. After the war, Germany was divided into four zones. The zones controlled by the U.S., Britain, and France were combined to form West Germany. The Soviet zone became East Germany. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Divided Berlin Berlin was also divided. The zones controlled by the U.S., Britain, and France were combined to form West Berlin. The Soviet zone became East Berlin. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Divided Berlin The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Berlin Blockade West Berlin was controlled by the Allies. The prosperity and freedoms there stood in stark contrast to the bleak life in communist East Berlin. Determined to capture West Berlin, Stalin blockaded the city, cutting off supplies. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins In response, the U.S. and Britain sent aid to West Berlin through a massive airlift. Section 1 The Berlin Airlift The Berlin airlift saved West Berlin and underscored the U.S. commitment to contain communism. The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Berlin Airlift Cold War The Begins Cold Begins American cargo The planes at War Berlin’s Tempelhof Airport Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 •The Russian blockade lasted from 24 June 1948 to 11 May 1949, but the airlift continued for several more months •The airlift cost the United States $350 million; the UK £17 million and Western Germany 150 million Deutschmarks •Berliners received an average of 2,300 calories a day which was higher than the UK food rationing system provided at the time •At the height of the operation, on April 16 1949, an allied aircraft landed in Berlin every minute •Each aircraft was unloaded by German crews in 20-30 minutes The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 •Normal daily food requirements for Berlin was 2000 tons •Coal represented two -thirds of all tonnage; giving each family (25-30lb) per month •The airlift required 850,00 multi-layer paper sacks per month •394,509 tons of foodstuffs, coal and supplies carried by 689 military and civil aircraft - 441 US, 147 RAF and 101 British civil. •The pilots and aircrew also came from Australia, Canada, South Africa and New Zealand •83,405 tons of cargo and 68,000 people were flown OUT of Berlin •39 British, 31 American and 13 German civilians lost their lives in the Berlin Airlift. They are remembered on the Berlin Airlift monument at Tempelhof •124,420,813 miles were flown during the airlift. A total of 277,804 flights The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 Cold War Alliances As Cold War tensions mounted, both sides formed military alliances for collective security. NATO Belgium Canada Denmark France Greece Iceland Italy Luxembourg Netherlands Norway Portugal Turkey United Kingdom United States West Germany The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Warsaw Pact Albania Bulgaria Czechoslovakia East Germany Hungary Poland Romania Soviet Union Section 1 NATO vs WARSAW PACT NATO WARSAW PACT The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins Section 1 The Cold War The Begins Cold War Begins