* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download School`s of Economic Thought
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
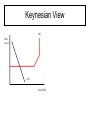
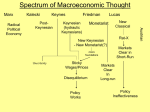
Macroeconomic Theories Classical & Keynesian versus New Classical & Supply Side CLASSICAL VIEW 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Markets are naturally self regulating No government intervention necessary Recessions are temporary Wages & prices are flexible Savings = Investment Says law: Supply will create its own demand Against: minimum wages, welfare & Gov’t assistance Great Depression challenged Classical View 9-2b Classical View FIGURE 9-1 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand in Classical Economics KEYNSIAN VIEW 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Economy is inherently unstable & not self adjusting Recessions are long & often permanent Major government intervention necessary to stimulate AD Wages & prices are sticky or fixed Support welfare & Gov’t assistance Lack of consumer demand caused great depression AS curve is very flat or horizontal Interest rates changes are not effective during recession – Money Demand not very sensitive to interest rates Keynesian View AS Price Level AD Real GDP Macroeconomic Debates • Two major schools decidedly against government intervention have developed: – Monetarism & New Classical Economics Monetarism • Main message: money matters & the economy self-regulates • Monetarism believes in the Quantity Theory of Money – MV = PQ, Inflation is purely a monetary phenomena • Generally do not advocate activist monetary policy stabilization: – expanding money supply during bad times and slowing during good • Focus on price stability • Theory not compatible with upward sloping AS curve New Classical • • • • Attempted to explain stagflation of 1970’s Business Cycles happen, but recessions are temporary AS could be broken down into Short-run & Long run curves Government intervention is unnecessary –Prices/wages are flexible in long run, sticky in short-run • People make decisions on rational expectations –This explains “shocks” to the system 9-2l New Classical Model Both models can be used as a “New Classical Model” LR FIGURE 9-5 Aggregate Supply in the New Classical Model SRAS Supply-Side Policy • Government Incentives Matter • Goal: use incentives to shift the aggregate supply curve right • The supply-side toolbox consists of: – – – – Tax cuts to stimulate work effort, saving, and investment Deregulation to reduce production cost/stimulate investment. Expenditures on education training/research expands capacity to produce Immigration policies alter the size/skill of labor force 9-4 Summary • No theory is designed to explain all the complex relationships of a macroeconomy • There is no simple relationships that can be easily manipulated to neatly solve various problems as they arise. • Assessing economic theories would be easier if we lived in closed economies.