* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
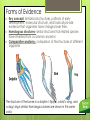
Change Over Time 7.3 Biological evolution accounts for the diversity of species developed through gradual processes over many generations. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. b. Students know the reasoning used by Charles Darwin in reaching his conclusion that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. c. Students know how independent lines of evidence from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provide the bases for the theory of evolution. d. Students know how to construct a simple branching diagram to classify living groups of organisms by shared derived characteristics and how to expand the diagram to include fossil organisms. e. Students know that extinction of a species occurs when the environment changes and the adaptive characteristics of a species are insufficient for its survival. Darwin • He discovered many fossils of extinct animals that were similar to modern species • Found many variations in plants and animals that led to the formations of his theories • Species- a group of organisms that resemble one another and are able to reproduce among themselves • Traits- genetic characteristics among similar organisms in a species that is passed from one generation to another • Offspring- child of a parent Darwin’s Voyage Charles Darwin sailed on the Beagle, from England to the Galápagos Islands. Discovered many fossils of extinct animals that were similar to modern species Found many variations in plants and animals that led to the formations of his theories Overproduction and Variation Natural selection is the process by which individuals who are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the same species. Video on Natural Selection Variations- a difference in a characteristic or trait from one organism in a species to another in the same species Competition and Selection Variations among turtles make some of them better able to survive. Turtles that survive to become adults will be able to reproduce. Survival of the fittest- theory of natural evolutionary processes that enables organisms that are best suited for their environment to survive Evolution- overall change of a population’s gene pool over time through processes such as mutation and natural selection Section 2: Evidence of Evolution Forms of Evidence Key concept: Similar body structures, patterns of early development, molecular structure, and fossils all provide evidence that organisms have changed over time. Homologous structures- similar structures that related species have inherited from a common ancestor Comparative anatomy- comparison of the structures of different organisms The structure of the bones in a dolphin’s flipper, a bird’s wing, and a dog’s leg is similar. Homologous bones are shown in the same color. Forms of Evidence Early Development- how different species develop before birth Scientists make inferences about relationships based on early development Similarities in DNA and proteins- if two species have similar DNA and proteins, probably evolved from same ancestor How Do Fossils Form? Most fossils form when organisms that die become buried in sediments. How Do Fossils Form? Mold- hollow area in sediment in the shape of an organism or part of an organism Cast- solid copy of the shape of an organism Cast is the opposite of a mold Petrified fossils- fossils in which minerals replace all or part of an organism Trace fossils- fossils that provide evidence of the activities of ancient organisms, like footprints Preserved remains- processes that preserves the remains of organisms with little or no change (tar, amber, and freezing Learning From Fossils The fossils record provides evidence about the history of life and past environments on Earth. In addition, scientists use fossils to study the rate at which evolution has occurred. Learning From Fossils Paleontologists- scientists who study fossils Fossils build a picture of Earth’s past environments Fossils show how an environment has changed Gradualism- proposes that evolution occurs slowly but steadily Punctuated equilibria- accounts for gaps in the fossil record, periods of rapid change separated by long periods of little or no change Section 3: Evolution of Species What factors have contributed to the diversity of species? How do new species form? How do scientists infer evolutionary relationships among species? What causes the extinction of species? A Variety of Species Key concept: Over time, different environments and genetic variation have produced, through natural selection, the variety of organisms that exist today. Over millions of years, natural selection has produced different species with adaptations enabling them to live in specific habitats habitats- specific environment that provides the things organisms need to live, grow, and reproduce A Variety of Species Genetic diversity- organisms within the same species are not identical Organisms have different traits, don’t all look the same Some genetic diversity is because of mutations in DNA Some genetic diversity is caused by rearrangement of genes during meiosis Species that have a lot of variety adapt to changes in the environment Most organism are genetically similar, they have a difficulty surviving environmental change With the larger variety there is a better chance that some individuals have the trait needed to survive in new conditions Kaibab and Abert’s Squirrels Key Concept: “A new species can form when a group of individuals remains isolated from the rest of its species long enough to evolve different traits.” Geographic Isolationsome members of a species become cut off from the rest of the species How Do New Species Form? These two kinds of squirrels have been isolated from one another for a long time. Eventually this isolation may result in two different species. A Branching Tree This branching tree shows how scientists now think that raccoons, lesser pandas, giant pandas, and bears are related. Inferring Species Relationship Key Concept: “Scientists have combined the evidence from DNA, protein structure, fossils, early development, and body structure to determine evolutionary relationships among species.” Extinction of Species Key Concept- “Extinction is caused by a change in a species’ environment. The members of the species may not have adaptations that allow them to survive and reproduce in the changed environment.” Extinct- no members of a species are still alive Ways an environment can change: disease strikes a species, predators kill so many prey that the prey become extinct Most species that are fossils are now extinct Environmental Changes Climate change is #1 cause of extinction Destroys habitats Example: Wooly Mammoths Had traits to live in cool climate- thick coats Climate becomes warmer Thick coats are no longer helpful Environmental change doesn’t always cause extinction Some organisms have traits that help them survive Peppered Moth and Mutation Section 5: Branching Trees How does a branching tree diagram show evolutionary relationships? A Branching Tree Branching trees show relationships between groups of organisms. It also shows the order in which specific characteristics may have evolved. Shared Derived Characteristics Shared derived characteristics- a trait that is shared by all organisms in a group A branching tree diagram shows evolutionary relationships by grouping organisms according to shared derived characteristics. Amphibians Fishes Reptiles Egg with shell Invertebrates Four limbs Backbone Ancestor of animals Constructing a Branching Tree Branching Tree Video