* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jeff Barr - USD Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
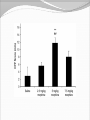
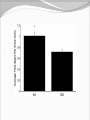
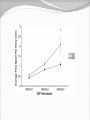
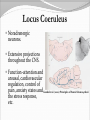
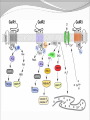
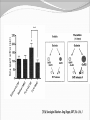
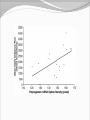
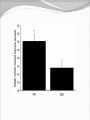
Dishman et al. (2006) Neurobiology of Exercise OBESITY Vol. 14 No. 3 Running as a Reinforcer Rodents that run have increased DA release in nucleus accumbens (natural and drug reward). Drug addiction prone rodent strains ( Lewis, C57BL/6) develop high running activity, (10km/day v. 2 km/day) This study: SD rats, 1.2-2.8 Km over three weeks (four week peak?) No absolute correlation. Rodents can be trained to lever press for access to running wheels (Self administration). Long access to wheel running- shift from low to high activity. Not seen with shorter access (as in drug selfadministration) Running rats exhibit withdrawal signs (increased aggression) when access to the running wheel is denied. DFos B – up-regulated in reward pathways after addictive drugs and voluntary wheel running. DFos B over-expression increases running activity and increases sensitivity to rewarding effects of morphine. Rodents display conditioned preference to an environment associated with running “after-effects” Attenuated by naloxone. Repeated activation of opioid systems by running could possibly change sensitivity to morphine. Cross-Tolerance Decreased response to one drug due to exposure to another pharmacologically similar drug. Opioid systems & Morphine Endogenous opioids Opioids: Naturally occurring peptides having opiate-like pharmacological effects. 3 distinct genes : preproopiomelanocortin (POMC), preproenkephalin A (PENK), preproenkephalin B/ preprodynorphin (PDYN) produce precursors of 3 major groups: 1) enkephalins 2) dynorphin 3) endorphins. They possess some affinity for any or all of the opioid receptor subtypes ( µ, d, and k ) and the effector pathways for all receptor types are G-protein-mediated. Neuropeptides Synthesized in soma and stored in dense-core vesicles in neurons which also contain a classical fast-acting transmitter (i.e. glutamate) Act as co-transmitters serving to modulate the actions of the primary transmitter. Released at high neuronal Levitan and Kaczmarek (1997) “The Neuron” 2nd ed. firing frequency or burst firing pattern Morphine Hyman et al. (2006) Annual Reviews Neuroscience 29:565-98 Exercise slows down aging . Returns levels of hippocampal neurogenesis and learning (MWM). Exercise enhances contextual learning and memory. Radial arm maze, etc. Therefore, exercise possibly will increase motivational / associative learning, i.e. CPP Notes on Neurogenesis Voluntary running increases hippocampal neurogenesis and enhances hippocampal dependant learning. Hippocampal dependant learning increases hippocampal neurogenesis. Conditioned Place Preference – Contextual / spatial learning However, Chronic opiate self-administration decreases hippocampal neurogenesis. (timing? Procedure?) Methods Adult male Sprague- Dawley rats Under reverse 12h light/dark schedule Testing during dark phase General Procedure Three week access to “activity wheels” Portion of AW rats and SED rats tested for sucrose preference. Day after – CPP to morphine. No differences in sucrose preference between activity groups. AW rats drank more sucrose & water. Exercise did not enhance appetitive properties of sucrose. Conditioned Place Preference Tested for natural preference first day. (30 min.) Next two days Morning – injected sc. saline & 5 minutes later enclosed in the non-conditioned chamber (prefered in natural preference, 45 min.) Afternoon- injected sc. Saline or morphine & 5 minutes later placed in chamber not prefered in natural preference test (45 min). Conditioned Place Preference (Cont’d) After conditioning – Test as on first day. 30 min. Time in and entries into chambers recorded CPP score = time in conditioning chamber on test day – time spent on initial day 24 hours after test decapitated for In situ Hybidization Locus Coeruleus Noradrenergic neurons. Extensive projections throughout the CNS. Function-attention and arousal, cardiovascular regulation, control of pain, anxiety states and Kandel et al. (2000) Principles of Neural Science 4th ed. the stress response, etc. Berridge & Waterhouse (2003) Brain Research Reviews 42: 33-84 Neurochemical and behavioral effects of opiate withdrawal mediated by LC hyperactivity. Opiate withdrawal syndrome Hyperactivity Rearing Teeth chattering Wet dog shakes Piloerection Ptosis Transgenic mice overexpressing Galanin – decreased morphine withdrawal signs. Galanin 29-AA peptide neurotransmitter. In CNS, expressed in regions implicated in mood and anxiety – hypothalamus, amygdala, LC, dRN, VTA. Coexists with NE ~80% LC neurons. Voluntary exercise increases preproGAL mRNA in the LC. -Chronic social stress & Chronic Fluoxetine increases GAL in LC (& GALR2). Hokfelt et al., (2000) Neuropeptides — an overview Neuropharmacology 39 1337–1356 Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Hippocampus is involved in CPP. Selective induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during contextual learning. Impaired BDNF signaling = impaired spatial learning. Conclusions Exercising and sedentary rats did not display significantly different degrees of CPP to morphine. CPP to morphine occurred in a dose-dependent manner in exercising and sedentary rats. Exercising rats displayed greater CPP when presented as time spent per entry – overcoming of crosstolerance effect? Dose dependant increase in LC preprogalanin mRNA in Exercising rats. Not related to CPP to morphine Increase of hippocampal BDNF mRNA in exercising rats that also displayed CPP to morphine.